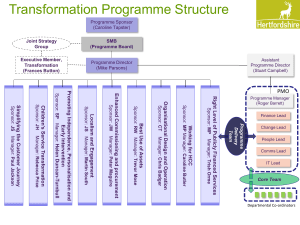
TDRp_Implementation - Center For Talent Reporting
advertisement

TDRp: Implementation Critical Success Factors David Vance, Executive Director Peggy Parskey, Assistant Director Center for Talent Reporting December 2, 2014 Logistics for Today’s Webinar • PowerPoint and Recording will be available to you afterwards • If calling from a phone, enter you PIN # if you want to be able to ask a question (necessary for us to unmute you) • Also, if at your computer and using a phone, select Telephone on the control panel • May also type a question in • We will take questions at the end Our Sponsors We want to thank the following sponsors for their support of the Center for Talent Reporting. FOUNDING ORGANIZATION SILVER SPONSORS Cigna and Skillsoft are Founding Silver Sponsors FOUNDING GOLD SPONSOR Our Sponsors We want to thank the following sponsors for their support of the Center for Talent Reporting. BRONZE SPONSORS ADP, Aventus Partners, Bellevue University Human Capital Lab, Development Dimensions International, McBassi & Company, Motorola Solutions, ROI Institute, Skyline Group, and Tata Interactive Systems are Founding Bronze Sponsors Today’s Discussion Three critical success factors » Engaged sponsors and stakeholders » Planning the impact on organizational goals » Communicating results throughout the year Q&A Sponsor and Stakeholder Engagement Definitions: Sponsors and Stakeholders • Sponsors: officers directly accountable for achieving the business goal » Usually direct reports to the CEO at most one level further down » Examples: SVP of Sales, President of Manufacturing • Stakeholders: those with a direct interest in the outcome » Head of the HR function (e.g. the CLO) » Managers/staff in the HR function responsible for the initiative » Managers/staff in the client function (like Sales) responsible for the initiative » May include the SVP of HR Engage Sponsors and Stakeholders Early and Often • Sponsor » Up front to agree on role of HR initiative » If role exists, then agree on broad outline (scope), cost and impact » Identify stakeholders in sponsor organization » Agree on roles and responsibilities » Plan to update regularly • Client Stakeholder » Up front to discuss role of HR initiative » If role exists, then discuss broad outlines (scope), cost and impact » Plan to work closely with stakeholder managers and staff » Agree on deadlines • A good practice: document these agreements and share Planning the Impact on Organization Goals Impact on Organization Goals • One of the most difficult aspects of TDRp » One of the most important if HR is to be a true business partner delivering bottom line value to the organization » Without it, how does anyone know… - If the initiative is worth doing? - What the target or plan should be for the initiative? - If the initiative was or was not successful? • Ideally, the impact will be the planned impact of the HR initiative on the company goal » May be quantitative or qualitative » Sometimes is a proxy or other measure of success • Think of this as a business planning exercise isolated L&D Summary Report 11 Learning and Development Sample Summary Report for the Private Sector with Mixed Impacts Results through June 2014 Actual Impact of Learning and Development Initiatives Revenue: Increase Sales by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: 25% contribution to goal For 2015 Plan Jun YTD % of Plan Forecast % % 10% 1% 20% 5% Engagement: Increase Engagement Score by 3 Points to 69.4% (1) Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Low Impact on goal Points H/M/L 1 pt Low 3 pts Low Safety: Reduce Injuries by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: High Impact on goal % H/M/L 10% Medium 20% High 15% High Costs: Reduce Operating Expenses by 15% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Medium Impact on goal % H/M/L 5% Low 15% Medium Points None planned -3 pts 1.6 pts 84% Retention: Improve Retention of Top Performers by 5 Points to 90% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives Call Center Satisfaction: Improve Satisfaction Score by 4 Points to 80% Corporate Goal or Actual Application of Key Behaviors Talent Development Reporting principles • CTR Points % 17% 4% Forecast as % of Plan 85% 80% 20% 5% 100% 100% 1.9 pts 63% Low Below plan 3 pts Low On plan 75% On plan 20% High On plan 2% Low 13% On plan 10% Low On plan 5 pts 2 pts 67% 5 pts 100% 4 pts 95% 2.9 pts 70% 73% 74% 4 pts 80% 100% 84% 100% 100% 67% November 12, 2014 Note on Stating the Goal: Must be in Terms of the Delta • Delta as a % » Say the sales goal is to increase sales from $50M to $55M - Delta is $5M or 10% - State the goal as 10% increase in sales Not as achieving sales of $55M • Delta as change in points » Say the goal is to improve employee engagement score from 71 to 75 - Delta is 4 points (4/71 =5.6%) - State the goal as a 4 point increase in engagement Not as a 4% increase in engagement Plan the Meeting • Needs to be with the sponsor » Only the sponsor has the authority to make the forecast » May start with client stakeholder, but needs to be approved by sponsor » Start with “Friendlies” who are supportive and who are likely to get it • Set up appointment with sponsor to discuss expected results from HR initiative » 30-60 minutes » Staff may be present » Do not let sponsor delegate the meeting to manager • Plan should be realistic and achievable How to Open the Discussion: Possible Opening “Thank you for your time today. We wanted to take a few minutes to discuss this important initiative we are planning to help you achieve your goal of 10% higher sales. We want to ensure we meet your expectations. We also want to ensure we make the best possible use of company resources. Let’s talk about the impact we can reasonably expect from this initiative and see if we can agree on some measures of success that we can hold ourselves accountable to. The plan is to provide training to …… to be completed by ….with the expectation that after the training your people will be able to…….. Now, let’s discuss the impact this training could have on the goal to increase sales by 10% if we work together. Methods to Assign Impact • Isolated Impact » Qualitative - What: Non-numeric (e.g. High, Medium, Low) assessment of the impact of HR programs on a business goal - Why: Good for first-time impact discussion. » Quantitative - What: Numerical impact of HR programs on the business goal - Why: Sets measureable expectation of HR’s contribution to the business • Proxy measures » What: A substitute measure for impact that is considered a leading indicator or at least is highly correlated to the impact » Why: Used when a direct impact cannot be agreed upon. What We Mean by Isolated Impact » The business goal is a 10% increase in sales for next year » L&D and the sponsor agree training could help achieve the 10% increase » Specific programs, target audiences, completion dates are agreed » What portion of the 10% increase might reasonably come from this agreed-upon program? - Most, some, a little => qualitative impact (high, medium, low) If High, then the expected isolated impact of sales training on the goal will be High - A percentage like 20% => quantitative impact If 20%, then the expected isolated impact of sales training on the goal is 20% x 10% = 2% increase in sales due to training Agreeing on Qualitative Impact • A good starting point for those new to isolated impact discussions with sponsors. Try for agreement on a qualitative impact like High, Medium, Low, or Essential • “Essential” should be used sparingly. » Only where the mission could not be accomplished without the HR initiative » If the mission could be accomplished without the initiative, even though it may take longer and/or be more expensive, the initiative is not “Essential” • High • Medium • Low • Essential Process to Help Sponsor Determine Qualitative Impact (continued) » If the initiative is not deemed essential then 1. Ask sponsor to list all factors or drivers contributing to goal. 2. Ask sponsor to prioritize factors 3. Use ranking to discuss relative importance » If one factor is dominant (more important than all others and by itself responsible for most of the goal), label it “High Impact” » If no factor is dominant, but one or two are very important and considerably more important than the others, label them “Medium Impact” » Label all the other factors “Low Impact” » Should not have more than one High and two Mediums Process to Help Sponsor Determine Qualitative Impact (continued) » By end of discussion, you should have a good idea of the relative importance of your initiatives compared to the other factors - Tells how much is expected from you: a little, a lot? No right or wrong answer But it is important for you and the sponsor to agree on your mutual expectations Also for other things like application rate and reinforcement And on your respective roles and responsibilities - Remember, this is a planning discussion. The goal is to be roughly right » This is meant to be a “business” discussion - You will learn a lot - Great way to become more of a business partner Reaching Agreement: An Example Start with list of drivers • Potential drivers to increase sales by 10% • • • • • • Hiring five new salespeople Growth in economy New salesperson incentive system New advertising campaign Growth in market share due to new products Consultative sales and product features training Reaching Agreement: An Example Prioritize and assign relative contribution Prioritized Drivers 1. Growth in economy Relative contribution High 2. Consultative sales and product features training Medium 3. Growth in market share due to new products Medium 4. New salesperson incentive system Low 5. Hiring 5 new salespeople Low 6. New advertising campaign Low Agreeing on Quantitative Impact: The Percentage Contribution Method (This will a number or %) • Good for second or third-year discussions. • Starts like qualitative approach 1. 2. Ask sponsor to list all factors contributing to achieving the goal Now ask sponsor to prioritize the factors • Then ask sponsor to list the expected % contribution of each. Work the percentages until they add up to 100% • The percentage next to the HR initiative in question is what we are looking for. This is the expected isolated impact of the initiative on achieving the business goal. • Note that the expected impact came from the sponsor, not HR Reaching Agreement: An Example Prioritize and assign contribution % Prioritized Drivers % contribution HR Initiative? 1. Growth in economy 50% 2. Consultative sales and product features training 20% Prioritized Yeslist of drivers to 15% increase sales by 10% 3. Growth in market share due to new products 4. New salesperson incentive system 5% Yes 5. Hiring 5 new salespeople 5% Yes 6. New advertising campaign 5% Prioritized list HR initiatives in of drivers with total are expected percentage to contribute 30% contribution to toward the goal of increase sales increasing sales by 10% (These by 10% add to 100%) Proxy Measures • Definition: An alternative choice of measure, used when a better measure is not available • When should we use a proxy? • How we use proxies every day • How do we determine the right proxy measure? » Example: Years of education » Cost-effective measure of competence. » Compared to other measures - Relatively easy to measure and verify - A decent proxy measure for a potentially wide range of basic competencies important at work » L&D Example: - Desired measure: Demonstrated application of training on the job - Proxy measure: Self report of % of training applied on the job • Proxy: related to the Latin word procuratia or procuratio, meaning substitute agent or authorized stand in. • A neighbor to the Latin word approximatus meaning, to draw near to or to be close to. Use of Proxies • Use a proxy when agreement cannot be reached on an isolated expected impact - Should be correlated with impact and ideally a leading indicator - Examples: Application rate for an L&D or Leadership Development initiative Number of performance coaching sessions for a performance management initiative - Start with higher level proxies For L&D, choose L3 before choosing L2 Pros and Cons of Each Method to Assign Impact Method Pro Con Quantitative • Fosters joint accountability between the business & HR to achieve the impact • May be difficult to assign a numerical goal particularly when several factors contribute to the outcome Qualitative • Makes it easier to reach • More subjective. May be hard to agreement on impact reach agreement on what ‘high, medium or low’ looks like. Proxy • Makes it easier to reach • May not demonstrate as tight a agreement on the link as desired between HR and impact the business. • Simplifies data • Requires agreement on leading collecting and reporting indicators of impact If Sponsor Will Not Help Plan Impact • Then do it yourself » Follow same steps » Assign percentages » Or make a direct plan of initiative’s impact • Share with Sponsor for feedback » His or her opportunity to disagree and correct the plan • If sponsor will not provide feedback, then share your planned impact and assumptions with governing board, CEO and ask for their feedback. Planning for Impact Summary • Remember, this is a planning exercise • Senior leaders want the best thinking from you and the sponsor • What can the two of you, and your organizations, make happen if you work together? • This is just like any other planning number. Should » Be directionally correct » Be reasonable and achievable » Lead to specific action plans to realize the impact Communicating Results Through the Year and Updating the Forecast Use Summary and Program Reports to Share YTD Results and Forecast • Check in regularly with sponsor and stakeholders • Ask: are they still comfortable with planned impact? » If yes, continue to use planned % contribution to calculate YTD results - Example: Training will contribute 20% towards achieving goal of increasing sales 10% - For June YTD results, if sales are up 4%, then training’s contribution is 20% x 4% = .8% higher sales due to training - Show planned impact as forecast (2% higher sales due to training) » If no, then adjust up or down. - Example: Sponsor believes training is now likely to have smaller impact than planned. Say only 10% contribution instead of 20% - So, for June YTD results, if sales are up 4%, then training would be responsible for 10% x 4% = .4% higher sales due to training - And lower forecast accordingly to 1% » Use actual results if available (like an ROI study on the pilot) L&D Summary Report Quantitative Version Impact of Learning and Development Initiatives Revenue: Increase Sales by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: 25% contribution to goal 2011 Actual Plan For 2012 Jun YTD % of Plan Forecast % % 10% 1% 20% 5% 17% 4% 85% 80% 20% 5% Points Points 1 pt 0 pts 3 pts .5 pt 1.9 pts .3 pt 63% 60% 2.5 pts .5 pt Safety: Reduce Injuries by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: 70% contribution to goal % % 10% 3% 20% 14% 15% 10% 75% 71% 20% 14% Costs: Reduce Operating Expenses by 15% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: 30% contribution to goal % % 5% 0% 15% 5% 10% 3% 67% 60% 18% 6% Points Points 1.6 pts NA 4 pts 1 pt 2.9 pts .7 pt 73% 73% 4 pts 1 pt Engagement: Increase Engagement Score by 3 Points to 69.4% (1) Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives Call Center Satisfaction: Improve Satisfaction Score by 4 Points to 80% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives L&D Summary Report Qualitative Report 2013 2011 Actual Plan 2014 For 2012 Jun YTD % of Plan Forecast Impact of Learning and Development Initiatives Revenue: Increase Sales by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Medium % H/M/L 10% Low 20% Medium 17% Medium 85% 20% Medium Engagement: Increase Engagement Score by 3 Points to 69.4% (1) Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Low Points H/M/L 1 pt Low 3 pts Low 1.9 pts Low 63% 2.5 pts Low Safety: Reduce Injuries by 20% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: High % H/M/L 10% Medium 20% High 15% High 75% 20% High Costs: Reduce Operating Expenses by 15% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Medium % H/M/L 5% Low 15% Medium 10% Medium 67% 18% Medium Call Center Satisfaction: Improve Satisfaction Score by 4 Points to 80% Corporate Goal or Actual Impact of L&D Initiatives: Low Points H/M/L 1.6 pts NA 4 pts Low 2.9 pts Low 73% 4 pts Low Sample Program Report for L&D Programs in Support of the Goal to Reduce Injuries Results through June Sponsor: Swilthe, VP of Manufacturing Enterprise Goal: Reduce Injuries Expected Impact of Learning: Metric % H/M/L 2014 Actual 12% Medium 2015 Plan 30% High YTD as YTD % of Plan 20% 67% High Below Plan Forecast 30% High Programs to Reduce Injuries 1 Deliver Phase 1 Courses for Factory A Effectiveness measures Level 1: Participants Sponsor Level 2: Test score Level 3: Application rate Efficiency measures Unique Participants Total Participants Metric 2011 Actual 2012 Plan YTD YTD as % of Plan Forecast % % % % 70% 75% 86% 53% 80% 90% 90% 65% 85% 88% 95% 62% 106% 98% 106% 95% 82% 88% 92% 63% 103% 98% 102% 97% Number Number 452 858 3,000 6,000 2,800 5,542 93% 92% 3,200 6,300 107% 105% 2 Develop Phase 2 Courses for Factory B Efficiency measure: Complete by 5/30 Effectiveness measure: Sponsor Satisfaction Number % NA NA 3 90% 3 90% 100% 100% 3 90% 100% 100% % % % % NA NA NA NA 80% 90% 90% 70% 80% 90% 92% 61% 100% 100% 102% 87% 82% 88% 90% 65% 103% 98% 100% 93% Number NA 1,000 100 10% 1,100 110% 3 Deliver Phase 2 Courses for Factory A Effectiveness measures Level 1: Participants Sponsor Level 2: Test score Level 3: Application rate Efficiency measures Unique Participants Forecast as % of Plan 100% On Plan Forecast as % of Plan Learn More Become a Member of the Center for Talent Reporting • Benefits » Access to Enhanced Content on the website - Members-only webinars What’s New, Business Acumen, Implementation webinars - Formulas and references for measures - Excel versions of sample statements and reports - Detailed implementation guidance - Members only page - Business acumen resources » $200 discount on workshops and conference » Priority for TDRp certification • Investment: Only $299 Accelerate Your Mastery • Two-day workshops offered » April 8-9 Atlanta » October TBD • Custom Workshop » At your location » Using your own goals • Coaching » We can help you succeed • 3rd Annual CTR conference planned for February 2016 • Website Overview Webinar » Next one in January • Business Acumen Webinars » Financial Acumen: Tomorrow! » More coming • Have your Department Head attend our Senior Leaders Webinar Visit us at: CenterforTalentReporting.org • White papers » Introduction to TDRp for L&D: Executive Brief (six pages) » Introduction to TDRp for L&D: Overview (20 pages) » Full White Paper for L&D (55 pages) » Introduction to TDRp (all processes) (20 pages) • Over 600 measures in total with definitions » Definitions of Terms and Measures for L&D (37 pagesmembers only) » Definitions, formulas, and references for members • Over 70 sample statements and reports (In excel for members) • Detailed written guidance • Sign up for email Contact Information • Dave Vance: Executive Director » Email: DVance@CenterForTalentReporting.org » Phone: 970.460.0837 • Peggy Parskey: Assistant Director » Email: PParskey@CenterForTalentReporting.org » Phone: 323.931.6589 • Andy Vance: Operations Director » Email: Avance@CenterforTalentReporting.org » Phone: 970.646.1843 • Kevin Jones: Research Director » Email: KJones@CenterforTalentReporting.org » Phone: 718.230.0363 @Center4TR Center for Talent Reporting or TDRp