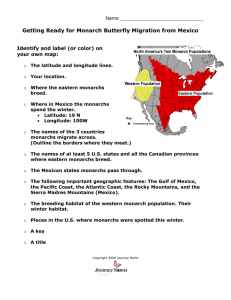
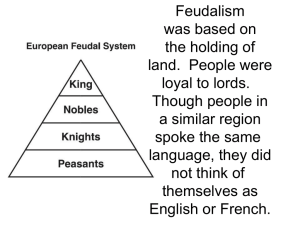
The Renaissance
advertisement

Renaissance Princes aka New Monarchs st 1 Among Equals • No strong monarchs in the late Middle Ages – Hundred Years War caused kings of England and France to struggle to raise money… further weakened the crown New Monarchs Tried to Rise Above ‘First Among Equals’ • So who do you turn to in order to do this? • Union between townspeople and the king. – Townspeople want stability to make money and want protection from greedy feudal nobility – King needs to have some allies against nobility who won’t be strong enough to challenge his authority – ‘middle class’ New Monarchs’ Techniques • Raise taxes – Taxes on the towns and peasants – Most nobles were immune • Build up standing armies – First one was in… ? • Wrestle power from Rome – Key example France • Pragmatic Sanction – New Monarchs versus Rome – Council over Pope – French king has basic control of church in France • Concordat of Bologna- Compromise between French monarchs and Pope – Ok- Pope is boss – Pope gets some money and has some say in France’s church New Monarchs’ Techniques (cont.) • Semi-secret and sometimes violent courts to do the bidding of the monarch – Court of the Star Chamber in England • Encouraged economic growth – Brings more tax revenue • Expelling ‘troublesome’ minorities – Reconquista – Conversos • Root of racial identification of Jews • Marriage – Rulers of Spain – Helps to explain the interlocking web of royal families The War of the Roses • Hundred Years War weakened English monarchs • War of the Roses was a clash between ‘first of equal’ king and powerful noble family • Yorkist line won, and (along with the Tudor line who took over after the Yorks died out) began to build royal power Social Impacts of the Renaissance • Women– Upper class women • Lost status (didn’t run households anymore) • Had to mold themselves to get a man, rather than vice versa in medieval times • Did get educations, but only to… ??? • Laura Cereta example… successful, but only because... ??? • Men believed that publicly active women were a threat • Not really ‘sexual beings’ – Lower class women • Didn’t get educational advantages • Hard to say, but fact that rape was punished more harshly if _____________ than if _____________ gives some evidence that even lower class women lost status – What was the punishment in the Middle Ages for Rape? Things You Should Know That I Didn’t Have Time For • Savonarola • Social Change (I covered women, but not the other parts) – Perception of Black Africans – Homosexuality • Thomas More – Utopia Hansen AP Euro Name _____________________ Period _________ The Renaissance- The Rise of New Monarchs (and Miscellaneous) (Lecture #3) Note-Taking Guide ►First Among Equals- ____________________________________ ________________________________________________________ •No __________________ monarchs in the late Middle Ages •Hundred Years War caused kings of England and France to struggle to raise money … ______________________________ ► New Monarchs Tried to Rise Above ‘First Among Equals’ •So who do you turn to in order to do this? •Union between ____________ ___________ •Townspeople want ___________________________ __________________________and want protection from _______________________________________ •King needs to have ___________________________ ___________who won’t be strong enough to challenge _______________________ •‘_______________________’ ►New Monarchs’ Techniques •Raise taxes •Taxes on the ________________________________ •Most nobles were _______________ •Build up standing armies - __________________________________ •First one was in… _________________ •Wrestle power from ______________ •Key example _________________ •Pragmatic Sanction – New Monarchs versus Rome •_____________________________ •French king has basic ___________________ _____________________________________ •Concordat of Bologna- ________________between French monarchs and Pope •Ok- __________________________ •Pope gets ____________ money and has some say in France’s _____________ •Semi-secret and sometimes violent courts to do the bidding of the monarch •Court of the __________________________in England •Encouraged economic growth •___________________________________________________ •Expelling ‘troublesome’ minorities •Reconquista - _______________________________________ ____________________________________________________ •Conversos - __________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ •Root of racial identification _______________ •Marriage •_______________________ •Helps to explain the interlocking web of __________________ ►War of the Roses •Hundred Years War weakened ___________________________ •War of the Roses was a clash between ‘_______________’ king and _________________________________________________________ •Yorkist line won, and (along with ____________________________ who took over after the Yorks died out) began to __________________ ►Social Impacts of the Renaissance •Women •Upper class women •Lost ____________ (didn’t run households anymore) •Had to mold _____________________to get a ________, rather than vice versa in medieval times •Did get educations, but only to… _______________ ___________________________________________ •Laura Cereta example… successful, but only because... _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ •Men believed that publicly active women ____________ •Not really ‘___________________________’ •Lower class women •Didn’t get ______________________________ •Hard to say, but fact that rape was punished more harshly if _____________ than if _____________ gives some evidence that even lower class women lost status