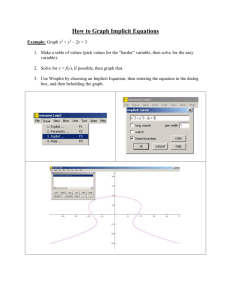
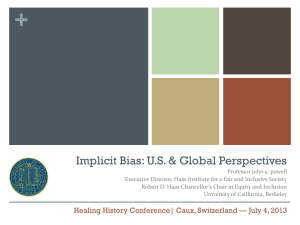
Implicit and Explicit Memory
advertisement

Implicit Memory in Physiotherapy w Derby 2014 w andrew.clyne@nhs.net w Avon and Wiltshire Mental Health Partnership NHS Trust User Warning A Person Centred Approach will help you decide which approaches to use. Please keep this in mind: This is not MSK Physiotherapy. 3 Approaches 1. Traditional Approach (Fitts & Posner) 2. Rosemary Oddy http://www.alzheimers.org.uk/mobilitystrategies 3. Implicit Memory Approaches . Andrew Clyne - Agility Journal Summer 2013 Fitts and Posner Model 1967 Objectives • • • • • • Implicit vs. Explicit Memory Priming Errorless learning Repeated Constant Practice Required Repetitions Avoiding Multi-tasking Implicit and Explicit Memory . Changing Lanes Macuga et al 2007 Implicit Memory and Mood • . Sabat 2006 Implicit Memory and Communication Priming . Henry Gustav Molaison - HM Errorless Learning Errorless Learning Maxwell et al 2001 80 x 50 = 400 Reps Error full Learning Errorless Learning Develop hypothesis Correct Errors Explicit Learning Passive Learning Little hypothesis Implicit Learning • More vulnerable to breakdown under dual task • Lower level of retention of skill • • Less likely to breakdown under dual task Higher level of retention of skill Constant Practice (Dick et al 1996) 3 2.5 2 HC AD 1.5 1 0.5 0 PreTest PT1 PT2 PT3 Variable Practice (Dick et al 1996) 3 2.5 2 HC AD 1.5 1 0.5 0 PreTest PT1 PT2 PT3 How Many Reps? How Many Passes? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ahg6qcgoay4 Avoiding Multi-Tasking Boyd and Winstein 2006 Case Study (Aug 2013) Objectives • • • • • • Implicit vs. Explicit Memory Priming Errorless learning Repeated Constant Practice Required Repetitions Avoiding Multi-Tasking Rehab Potential? Motor learning may represent an island of saved functioning in the midst of the devastating cognitive losses associated with (Alzheimer’s) dementia. (Dick et al 1996) We should be fitting our approaches to the patient not judging people’s ability to fit our traditional approach. “The session you did for us has stuck in my mind” andrew.clyne@nhs.net