NSC-68
advertisement

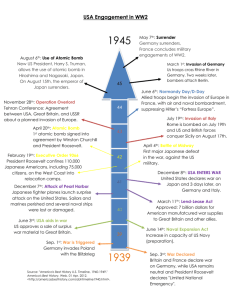
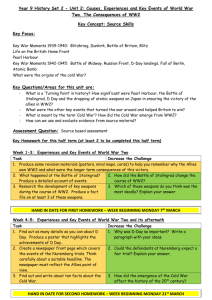
Essential Question: – What are the key themes of writing a DBQ? – How can students improve their most recent DBQ? Reading Quiz Ch 27B (984-993) Unit 12 Review Game Prepare for team vs. team review of the 1940s & 1950s Nuclear War Death Match! Name 6 specific examples of American foreign policy from 1920 to 1939 Failure to join the League of Nations or sign Treaty of Versailles Washington Naval Conference (4, 5, & 9 Power Treaties) Kellogg-Briand Pact Dawes Plan (and Young Plan) Hawley-Smoot Tariff Neutrality Acts of 1935-1937 Cash-Carry Policy Name 10 specific acts of totalitarian aggression prior to the outbreak of World War 2 Japan: Invasions of Manchuria & China Italy: Invasions of Libya & Ethiopia Germany: – Annexations of Austria, Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia – Defying Treaty of Versailles via militarization, troops to the Rhineland – Treaties such as Munich Pact and Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact Name 5 ways the USA evolved towards greater intervention in WW2 prior to December 1941 FDR’s “Quarantine Speech” Destroyers-for-bases deal in 1940 Peacetime draft $10 billion for “preparedness” Lend-Lease aid in 1941 Arming U.S. naval ships & permission to fire on German subs Atlantic Charter with FDR & Churchill oil embargo to Japan Name 2 effects each of World War 2 on: African-Americans, Mexican-Americans, Japanese-Americans, women African-Ams: migration north & west, segregated military units, banned discriminatory hiring practices, “Double V” campaign Mexican-Americans: agrarian work in SW, zoot-suit riots, eased immigration restrictions Japanese-Americans: internment, fought in European theater Women: joined WAC & WAVES, “Rosie the Riveter,” massive entrance into the workforce Define each of the following homefront initiatives: Office of War Mobilization War Production Board Office of Price Administration Office of War Information Fair Employment Practices Commission Office of Strategic Services Executive Order 9066 OWM—oversaw military priorities & the draft WPB—oversaw industrial production OWI—propaganda OPA—controlled inflation by rationing essential goods FEPC—banned racial discrimination in war-related industries OSS—conducted espionage 9066—Japanese internment camps WW1: Name 3 Central & 5 Allies Powers WW2: Name 3 Axis & 5 Allied Powers World War 1 World War 2 Allies before Pearl Harbor; Allies after Pearl Harbor Name 4 military operations or strategies used by the Allies or Axis in WW2 America’s “Europe First” strategy Operation Barbarossa; Hitler's invasion of USSR Operation Husky in North Africa Operation Overlord (D-Day) Doolittle Raid on Tokyo Island Hopping in the Pacific Blitzkrieg attacks by Germany Kamikaze attacks by Japan Firebombing by USA Atomic bomb vs. Operation Olympic Name 4 battles in the European Theater Name 4 battles in the Pacific Theater Europe Invasion of Poland Battle of Britain Stalingrad D-Day Battle of the Bulge Italian Campaign Bombing of Dresden Soviet occupation of Berlin Pacific Midway Coral Sea Guadalcanal Leyte Gulf Okinawa Saipan Iwo Jima Bombing of Tokyo Hiroshima & Nagasaki Explain significance of each conference: Atlantic Charter Tehran Yalta Potsdam Atlantic Charter: FDR & Churchill discussed strategy IF the USA enters; discussed a future United Nations Tehran: USA & Britain agreed to open a western front; Stalin agreed to United Nations Yalta: Stalin agreed to selfdetermination & invasion of Japan Potsdam: ultimatum to Japan, division of Germany, Stalin broke promise of self-determination in Europe Name 2 effects of WW1 Name 2 effects of WW2 WW1: Formation of the League of Nations U.S. retreat into isolationism Dawes Plan, but world depression Spread of fascism & totalitarianism 30 million deaths Led to WW2 Disarmament talks WW2: Formation of the United Nations U.S. accepts role as superpower Marshall Plan & economic recovery Spread of communism 70 million deaths Led to Cold War Atomic weapons Identify each of the following: “America First” Manhattan Project Truman’s Executive Order 9981 NSC-68 ICBM America First: Group dedicated to keeping USA out of WW2 (Lindbergh) Manhattan Project: initiative to build an atomic bomb 9981: Truman’s order to desegregate the military & civil service NSC-68: communism is a threat, must be contained, liberate communist nations ICBM—intercontinental ballistic missile What “caused” each event? Berlin Airlift U.S. hydrogen bomb Formation of NATO Creation of NSC-68 National Defense Education Act “Military Industrial Complex” speech Berlin Blockade → Berlin Airlift Soviet development of atomic bomb → U.S. hydrogen bomb Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia → Formation of NATO Communism in China → NSC-68 Sputnik → NDEA (& NASA) Eisenhower’s fear of having to out-spend the USSR in the Cold War → Military Indust Complex Name 8 new programs, policies, or agencies developed by the USA as part of the Cold War Containment: Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, NATO Dept of Defense (and the Air Force) Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) National Security Council (NSC) NSC-68 House Un-American Activities Committee & Loyalty Review Board Massive Retaliation, Brinksmanship Atomic arsenal, ICBMs NASA Eisenhower Doctrine Name these people? Robert Oppenheimer Joseph McCarthy Alger Hiss A. Philip Randolph Jack Kerouac Mohammed Mossadegh Oppenheimer: Manhattan Project McCarty: Led the “Red Scare” Hiss: Spy in the Dept of State; “Pumpkin Papers” Randolph—led the “Double V” campaign during WW2 Kerouac: Beatnik; anti-conformist Mossadegh: Iranian prime minister; Overthrown in 1st ever CIA led coup Name 7 examples that America was an “Affluent Society” in the 1950s Culture of consumerism Boom in # of televisions (50 million) Baby boom Cars, highways, drive-ins Growth of the suburbs Teen market Gov’t spending on military Expectation of college for middle- class kids