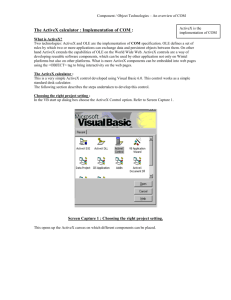
ni.com What is COM?
advertisement
Understanding COM/ActiveX
Jeff Paulter
Staff Software Engineer
Thurs Aug 17
10:15-11:30 a.m., 1:45-3:00 p.m.
Ash (10A)
ni.com
Outline
What is ActiveX?
Why use COM/ActiveX
What is COM?
What are ActiveX/COM
•
•
•
•
ni.com
Servers
Objects
Interfaces
More
What is ActiveX all about?
Demonstrations
•
•
•
•
ni.com
Document objects
Automation
Controls
Containers
What is ActiveX?
The name for technologies built on top of
COM
Examples include:
•
•
•
•
Document objects
ActiveX controls
Automation
OLE for process control (OPC)
Grew out of OLE
ni.com
Motivation for COM/ActiveX
Component software development
• Reuse of binary software components
• Create and use components from various
languages
• Update components without recompiling or
breaking existing clients
Object-based model
Distributed software
Location transparency
ni.com
What About DLLs?
Calling conventions can vary
DLLs are not object based (Flat API)
Versioning can be difficult
Memory management concerns
Linkage issues
ni.com
What is COM?
Component object model
Binary and network standard
Run-time system
• Calls across network
• Location transparency
• Security
ni.com
COM Servers
Can be DLLs or EXEs
Provide objects for clients
• A single server can provide implementations for
more than one object
• The set of objects that a server provides and the
relationships between them is referred to as an
object hierarchy
Are activated by the COM run-time services
ni.com
Object Hierarchy
Top Level
Objects
(Creatable)
Lower Level
Objects
(Non-Creatable)
ni.com
COM Objects
Clients view objects as black boxes
Clients communicate with objects only
through interfaces
Objects can handle more than one interface
Interface1
Interface2
Interface3
ni.com
Object
COM Interfaces
Sets of related methods
Immutable contracts
Implementations not described
• NO member data (functions only)
COM defines a standard for in-memory layout
of interfaces
ni.com
Interface Benefits
Compiler neutral
Language neutral
Object implementations can change without
affecting clients
• Clients never need to be recompiled
Versioning
ni.com
Sample Interfaces
IAnimal
• Eat
• Sleep
• Walk
IDog : IAnimal
• Bark
• Fetch
• ChaseCat
ni.com
IGuard
• SoundAlarm
• AttackBadGuy
Sample Object
IAnimal
IDog
IGuard
ni.com
Guard Dog Object
IUnknown Interface
Every COM interface inherits from IUnknown
IUnknown includes functionality needed by
every object
• Provides a mechanism for clients to obtain one
interface from another interface
• Provides object lifetime manangement
ni.com
IUnknown Interface
Mechanism to get from one interface on an object to
another interface on the object
HRESULT QueryInterface (REFIID riid, void **ppvObject);
Mechanism to manage object lifetimes
• Clients do not delete COM objects directly
• COM objects are responsible for deleting themselves
• COM objects are reference counted
ULONG AddRef ( );
ULONG Release ( );
ni.com
Registration of Servers
Servers are registered with the system
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
CLSID
{E312522E-A7B7-11D1-A52E-0000F8751BA7}
Default = “Guard Dog Object”
InprocServer32 = "D:\Examples\AnimalLib\AnimalLib.dll"
AnimalLib.GuardDog
CLSID
Default = “{E312522E-A7B7-11D1-A52E0000F8751BA7}”
ni.com
Event Interfaces
Interface provides communication from the
server back to the client
Server defines an interface that it calls to
notify the client that an event occurred
Client supplies server with a pointer to the
interface
Client’s code is executed when the server
calls methods in the event interface
ni.com
Example Event Interface
IDogEvents
• AmHungry
• WantAttention
• NeedToGoOutside
ni.com
IDispatch Interface
Automation servers must handle IDispatch
ActiveX controls must handle IDispatch
IDispatch gives scripting clients access to
COM objects
• Microsoft Office
• Internet Explorer
• Old versions of Visual Basic
ni.com
IDispatch Interface
IDispatch::Invoke provides access to an entire
interface through a single function
Clients use the Invoke function to call all methods
• Specify method by method ID
• Pass parameters in a single large structure
Invoke understands only Automation types
• Yes: int, double, enum, boolean, structures
• Yes: BSTR, SafeArray, Variant
• No: unions, C style arrays, C style strings
ni.com
COM/ActiveX Programming
Many environments provide some tools to
make writing COM servers and clients easier
•
•
•
•
Wrappers for accessing COM servers
Wizards to create skeleton servers or controls
Tools to add interfaces, methods, properties
Free implementations of some standard interfaces
Measurement Studio
• Visual Basic, Visual C++, LabWindows/CVI
LabVIEW™
ni.com
ActiveX and NI Products
ActiveX controls
• Measurement Studio
Containers
• LabVIEW, BridgeVIEW™
Automation servers
• LabVIEW, Measurement Studio, HiQ™, DataSocket™
Clients
• LabVIEW, BridgeVIEW, Measurement Studio, TestStand™
ni.com
COM/ActiveX Resources
Essential COM
• Don Box (Addison-Wesley, 1998)
Inside COM
• Dale Rogerson (Microsoft Press, 1997)
Various MSDN Articles
NI Product Examples
ni.com