RUSSIA From Tsarism to Communism
advertisement

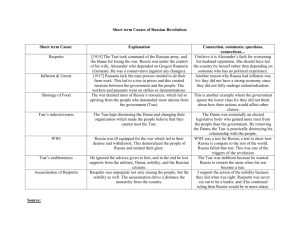
The Rise and Impact of Authoritarianism Emphasis on “authority of the state” • Non-elected leaders • Unregulated exercise of political power • Limited civil liberties • Lack of opposition Communism Nazism Fascism Ideology emphasising classlessness Inspired by Marx and Engels’ The Communist Manifesto • One party only – the Communist party • Collective and planned economy • No private ownership • Everyone is equal in wealth and rank in Russia • On hindsight, Communism is seen as an authoritarian system • Russian leaders were not democratically elected, especially in Joseph Stalin’s time • Opposition was forcefully silenced Tsar Nicholas II – 1868-1918 What can you infer from this cartoon about Russian society? • Many levels of hierarchy • The poor (the ‘proletariat’) had to support many people •Middle-class do not have much say • Autocratic, insufficient political representation MATI Makan no enough Army no good • Not enough • Lousy to eat, leaders, insufficient training, shelter, food weapons and and morale necessities – led to lost not well men, distributed resources and pride Trouble at work Inflation at home • Workers diverted to the army factories empty, production declines • Basic necessities rise in price, Russians cannot afford goods Political discontent • Alienated middleclass who wanted to participate in government • Socialist revolutionaries not pleased with autocratic system; wanted to create a socialist state Social discontent • Long hours, low pay, terrible working and living conditions • Periodic famines, insufficient to eat • High cost of living Inefficient and corrupt Tsarist regime • Weak, indecisive Tsar obsessed with personal affairs (his son’s medical condition) • Did not grant any political concessions to the people • Unable to meet people’s needs • Persisted with an unpopular war Poor economic conditions • Poor harvests • Economic adviser implemented high taxes, low wages Outbreak of War • 1915: Tsar personally took over the war • Worsened socioeconomic effects • Insufficient people to fill factories • Caused loss of Russian pride • Caused shortages of fuel and food Took over in March 1917 Known as the ‘February Revolution’ Forced the Tsar to abdicate Did not carry out land or economic reforms Put in most of Russia’s resources into the unpopular war Disunited and weak – could not reach out to the masses • Postponed decisionmaking: did not implement reforms • Peasants still as poor as before Did not carry out land or economic reforms Put in most of Russia’s resources into the war • Pledged to continue the war until victory was won • Did not call for reparations anymore • Continued socioeconomic strife • Initial head Lvov a puppet leader • Kerensky government did nothing to save the economy • Government was not backed by the army • Democratic ideals not understood by the people • Had to struggle with the increasingly popular soviets Disunited and weak The Bolsheviks, led by Lenin, established the new Communist government in November 1917. NAME: ______________________ [ ] CLASS: ________ Promised to help Russia regain military status and end the war Promised to meet the domestic needs of the people Promised to reorganise and revitalise the economy “Peace, Land, Bread” “All power to the soviets” Bolsheviks managed to capitalise upon the unrest in the capital Overwhelmed Kornikov (army general) completely Seized power at a critical moment Social factors Political factors Failure of previous government to carry out their functions Military factors Economic factors Think about short term and long term factors • What set the conditions for Communism? • What events made everything come to light? • Who/what made the revolutions happen?

![Leader_Analysis_Sheet_Peter_the_Great[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009220992_1-b864ff548a7d360a25262ba94c316f4a-300x300.png)