- Toolbox Pro

Unit 15
Imperialism
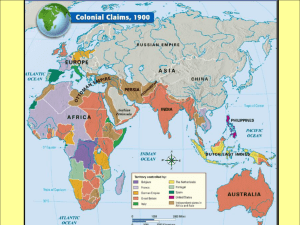
Map
Unit 15 – Imperialism
Timeline
Imperialism
European
Imperialis m
Japanese
Imperialis m
European nations divided Africa up into colonies
Britain rules
India
Many foreign nations tried to trade with
China
Japan expanded looking for raw materials
1830 1840
1854
Matthew
Perry in
Japan
1868
Meigi Emperor was restored to power in
Japan
1894
Sino-
Japanese
War
1850 1860 1870 1880 1890 1900
1904
Russo-
Japanese
War
1910
1839
Opium
War
1850
Taiping
Rebellion
1857
Sepoy
Mutiny in
India
Imperialism: When Powerful nations take over weaker nations for some benefit: economically militarily nationally
1899
Boer War 1900
Boxer
Rebellion
Scramble for Africa: 1880 –
1914
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Define imperialism
Partner B: Identify the 3 reasons countries imperialize.
Reasons why Europeans imperialized other areas
Nationalistic:
– To make their nation more powerful by taking over other lands
– “Social Darwinism” – it was natural for stronger nations to dominate weaker ones
Stop and Think!
Partner A: How is nationalism a cause of imperialism?
Partner B: How does Social
Darwinism justify imperialism?
Reasons why Europeans imperialized other areas
Political
– New colonies were important locations for military bases
– Colonies helped provide a nation with power and security
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Give one reason why new colonies were important.
Partner B: Give the other
Reasons why Europeans imperialized other areas
Economic
– To get raw materials for industry
– To establish new markets for industrial products
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Give one reason why countries imperialized for economic reasons.
Partner B: Give the other
Reasons why Europeans imperialized other areas
White Man’s Burden: poem by
Rudyard Kipling
– “Justified” European imperialism to
Europeans
– Implied that Europeans (white people) had a “moral duty” to bring civilization to less developed people
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Explain the White Man’s
Burden
Partner B: Explain whether you think this is accurate or not
Take up the White Man's burden--
Send forth the best ye breed--
Go bind your sons to exile
To serve your captives' need;
To wait, in heavy harness,
On fluttered folk and wild--
Your new-caught, sullen peoples,
Half-devil and half-child.
-- Rudyard Kipling
"The White Man's
Burden"
The phrase "White Man's burden" in this excerpt refers to the
1) negative attitude of
Europeans toward peoples of the non-
Western world
2) advantages Europeans would gain by colonizing Africa, Asia, and Latin America
3) positive role of the
Roman Catholic Church in Africa and Asia
4) challenges non-
Europeans faced when trading with Europeans
With your partner…
Create a poster that visualizes what imperialism means and the 4 main reasons why countries imperialized others.
Nationalistic Political
Imperialism
Economic White Man’s Burden
Nationalistic
Imperialism
Political
Economic White Man’s Burden
III. European Imperialism
Where : Africa
What happened : Scramble for Africa –
European nations divided Africa up into small colonies at the Berlin Conference of 1884.
Main Events: Boer War –British defeated
Dutch farmers called “Boers” for control of
South Africa
Important Information: Europeans created new borders on their own – without consideration of “tribal” concerns.
Stop and Think!
Partner A: What was the Scramble for Africa?
Partner B: What was the Berlin
Conference?
Partner A: What was the Boer War?
Partner B: How did Europeans divide up Africa?
Which is an accurate statement about the partitioning (dividing) of Africa by
European imperialist nations during the
1800s?
1. New nations were based on old tribal boundaries.
2. The cultural and ethnic diversity of the African people was disregarded.
3. The continent was divided equally among the colonial powers.
4. African unity was encouraged.
The major factor that enabled Western
Europe to dominate large parts of Asia and
Africa in the 19th and early 20th centuries was the
1) technological and military superiority of European nations
2) acceptance of Christianity by many
Asians and Africans
3) desire of Asians for European raw materials
4) refusal of Asians and Africans to fight against European imperialism
Between 1880 and 1914, which nations were most involved in colonizing Africa?
1) industrialized western European nations
2) eastern European nations controlled by Russia
3) East Asian nations seeking to establish new markets
4) oil-rich Middle Eastern nations
Why were European nations able to conquer large sections of Africa in the
19th and early 20th centuries?
1. Europeans easily adapted to
African climate and topography.
2. Europeans possessed more advanced military technology.
3. Europeans wanted to learn about
African culture.
4. Africans wanted to trade with
European nations.
Which region was most affected by the decisions made at the Berlin
Conference of 1884?
1)
2)
3)
4)
Latin America
South Asia
East Asia
Africa
Which would be the best title for this time line?
1) African Independence Movements
2) Mineral Discoveries in Africa
3) European Imperialism in Africa
4) Ethnic Conflict in Africa
Wednesday, March 25 th
Warm – Up:
Explain what is meant by this cartoon.
Objective:
How did imperialism effect India and China?
T/F
Strong countries have the right to take over weaker ones?
III. European Imperialism
Where: India
Imperialism in India
What happened : The British East
India Company controlled India until Britain took control after the Sepoy Mutiny
Imperialism in India
Main events : Sepoy Mutiny –
Indian soldiers (Sepoys) in
British Army rebelled against
British rule in India because they disrespected their religions
(Greased rifle cartridges with beef and pork fat – Muslims can’t eat pork; Hindus can’t eat beef) –
Sepoys lost
Imperialism in India
Important information: The colony was run by the British
East India Company – later by the British government
1.
2.
3.
4.
The Sepoy Rebellion is considered an important event in Indian history because it was one cause of the
Independence movement in India
Secession of Bangladesh from
Pakistan
Establishment of French colonies in
India
Creation of the Mughal Empire by
Muslims
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Which country imperialized India?
Partner B: Who were the Sepoys?
Partner A: Why did the Sepoys revolt?
Partner B: Was the revolution successful? Why not?
III. European Imperialism
Where: China
Imperialism in China
What happened:
– Foreign powers tried to open up
China to trade in 1800s
– China resisted foreigners: ethnocentrism
– Because of superior military weapons, foreigners were able to force China to open up to trade
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Why were foreign countries interested in China?
Partner B: Why were foreign countries able to defeat the Chinese?
III. European Imperialism
Main Events:
– Opium War : British defeated China in battle over sale of opium and forced them to trade.
The unequal Treaty of Nanking ends war giving
Hong Kong to Britain.
– Taiping Rebellion: Peasants in China rebelled against new foreign influences in China; millions killed
– Boxer Rebellion : Chinese citizens fought foreign armies and lost – after that, Chinese government called for more western style government
Stop and Think!
Partner B – explain one event that took place in China
Partner A – explain a different event that took place in China
Partner B – explain the third event that took place in China
What was a direct result of the Opium War in 19th-century China?
1. Japan gained control of Hong Kong.
2. Kublai Khan rose to power in China.
3. Chinese ports were opened for trade with
European powers.
4. Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-shek) fled to
Taiwan.
1)
2)
3)
4)
The Opium Wars of the mid-19 th century marked the beginning of the
Rivalry between China and Taiwan
Domination of China by foreign powers
Decline of European influence in
East Asia
Global effort to combat drug use
A major result of the Opium War in China was
1. an increase in the power of the
Emperor
2. the establishment of spheres of influence in China by Europeans
3. the expansion of chinese influence to
India and the Middle East
4. the expulsion of Europeans from China
During the 1840s, China signed
"unequal treaties" with Western nations mainly because
1) China had won the Opium War
2) Western nations had superior military technology
3) leaders in China favored expansion
4) China had requested economic assistance from the West
Which event is the best example of imperialism?
1. the Opium Wars in China
2. the Spanish Inquisition
3. the Yalta Conference
4. the Hundred Years' War
What effect did the Opium War and the treaty of Nanjing have on
China?
1) Chinese Nationalists increased their influence on rural areas.
2) The Manchu government expelled the Western Powers.
3) China was divided into spheres of influence.
4) China adopted a democratic system of government.
The outcome of the Opium War showed that in the 19th century,
1) the Chinese Army was the most highly disciplined army in the world
2) China was no longer strong enough to resist Western demands for trading rights
3) the Chinese people were successful in eliminating foreign influence
4) the Chinese Government preferred to continue the opium trade
1)
2)
3)
4)
One way in which the Sepoy
Mutiny in India and the Boxer
Rebellion in China are similar is that both attempted to
Remove foreign influences
Restore democracy
Modernize their economy
End religious conflict
The Sepoy Mutiny in India and the
Boxer Rebellion in China were responses to
1) Mongol invasions
2) European imperialism
3) Japanese aggression
4) African slave trading
III. European Imperialism
Important
Information :
China was forced to allow foreign nations to control small areas of
China for trade –
“Spheres of influence”
Stop and Think!
Partner A: What is a “sphere of influence?”
Partner B: How were foreign countries able to create these spheres of influence?
How does the picture demonstrate the idea of “Spheres of Influence?”
The political cartoon depicts the
1.ethnocentrism of the Chinese during the Manchu Ch'ing dynasty of the 17th century
2.separation of China into spheres of influence by 19th century imperialist nations
3.military aid given to the Chinese revolutionaries by the Soviet Union during the 1940s
4.favored trading-partner status awarded to China by many Western
European countries in the 1980s
During the 19th century, Europeans were able to divide China into spheres of influence mainly because the
1) Chinese were eager to adopt
Western culture
2) Europeans had technologically superior military forces
3) Europeans were willing to adopt
Chinese customs
4) Chinese lacked raw materials and resources
One result of the Opium War was that China
1) adopted democratic reforms
2) gained control of Hong Kong
3) regained control of Manchuria
4) was divided into spheres of influence
During the 19th century, Western nations were able to gain control over parts of China mainly because
1) the Chinese had a strong tradition of non-violence
2) China lacked the military technology needed to stop these ventures
3) China was promised aid for its industries
4) the Chinese lacked a strong cultural identity
Negative Effects on the Native
Peoples (Not in notes but needs to
be)
Their land and materials were taken from them
They were forced to adapt to European cultural ways (language, money, laws, customs, etc.)
Local customs were not considered
(relationships between tribes, religions, etc.)
Local economies were changed to support
European needs (from sustenance farming to cash crop farming and mercantilism)
Positive Effects on the Native
Peoples
New technologies were introduced, especially transportation and communication
Medical care improved
Western education was spread
Negative effects for imperializing nations
Seen as oppressors and creates tension between those who rule and those being ruled
Positive effects for imperializing nations
Resources
New markets
Gained power throughout the region and/or world
With your partner
Create a poster that visually describes the negative and positive effects of imperialism on both natives and imperialists.
Negatives Positives
IV. Japanese Imperialism
1600s: Japan’s shoguns chose a policy of isolationism – no one in no one out.
Shogun –
“Commander of the
Armies”
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Japan chose to follow a policy of isolationism. Explain what that means.
Partner B: China also chose to follow a policy of isolationism. Why did
China follow this policy?
Which situation best illustrates the concept of isolationism?
1) The Spanish government required that gold found in its colonies be brought directly to Spain.
2) Japan closed its ports to trade with other nations.
3) France, Germany, Belgium, and Great
Britain negotiated to divide various areas of Africa into colonies.
4) The British ruled much of India through the control of local rulers.
Mid 1800s – Treaty of Kanagawa
American, Matthew Perry forced
Japan to open up to trade with
United States
Treaty ended Japanese isolationism
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Who is Matthew Perry and what did he do?
Partner B: How is what Matthew
Perry did and the Opium War similar?
Commodore Matthew Perry’s visits to Japan in 1853 and 1854 resulted in the
1) colonization of Japan by the United
States
2) transfer of spheres of influence to
China
3) introduction of Christianity to
Japanese society
4) opening of trade and diplomatic relations with Japan
The primary reason that the
Japanese policy of near-isolation ended in 1853-54 was that Japan
1) needed additional territory as an outlet for its surplus population
2) needed European markets for its manufactured goods
3) became involved in a war with
China
4) was pressured by United States naval power to open its ports
The Opium Wars in China and the expedition of Commodore Matthew
Perry to Japan resulted in
1) the economic isolation of China and
Japan
2) an increase in Chinese influence in
Asia
3) the beginning of democratic governments in China and Japan
4) an increase in Western trade and influence in Asia
Meiji Restoration
:
Shoguns were now seen as being weaker (still supported isolationism and lost)
More Japanese wanted to become westernized
Shoguns overthrown
Emperor “restored” to power
(Meiji family of emperors)
Which action in Japanese history occurred during the Meiji
Restoration?
1) Japan modernized its economy.
2) Mongols invaded the islands of
Japan.
3) The Japanese government adopted an isolationist policy.
4) Buddhism became the official religion of Japan
In Japanese history, what was the impact of the Meiji Restoration?
1)
2)
3)
4)
Japan adopted a policy of isolationism
Contact with Western nations encouraged Japan to industrialize
Chinese influence on Japanese literature and the arts was limited
Japan adopted a feudal society
In Japan, the Meiji Restoration resulted in the
1) division of the nation between the
European powers
2) modernization of the nation's industry
3) abolition of the position of Emperor
4) government being controlled by the samurai
Westernization:
Japan copied western style culture to become more powerful
– Get more industry
– Build up a western style military
(militarism)
Japanese Imperialism
Sino (China) – Japanese War:
– After taking over Korea, Japan defeated China and took over areas of China
Russo – Japanese War:
– Japan defeated Russia’s navy
– First time an Asian nation defeated a western nation in war
Industrial Needs:
– Japan continued to take lands (imperialism) in
Asia – looking for more raw materials
Stop and Think!
Partner A: Who fought in the Sino-
Japanese War? Who won?
Partner B: Who fought in the Russo-
Japanese War? Who won and why was this significant?
Partner A: Why was Japan imperializing others?
Partner B: How is this reason similar to that of Great Britain?
What was one effect of the Russo-
Japanese War (1904-1905)?
1) Japan emerged as a major world power.
2) Korea gained its independence.
3) Czar Nicholas II gained power in
Russia.
4) Russia formed a military alliance with Japan.
1)
2)
3)
4)
The primary reason France and
Japan were interested in controlling parts of Indochina in the 20 th century was to
Dominate the Indian Ocean
Obtain valuable natural resources
Stop the spread of communism
Prevent Spanish colonization