The Path To Empire
advertisement

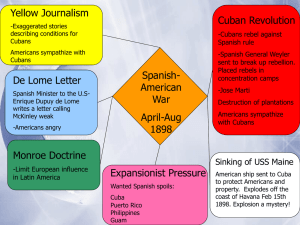
The Path To Empire Chapter 27 1890-1899 Isolation • After the Civil War, the US remained indifferent to the outside world • The last decades of the 19th century marked a shift in US foreign policy • America would become an imperial power Imperialist Stirrings • Farmers and factory owners looked to foreign markets as production increased • The US had to expand or explode • A new sense of power, population, wealth, and productive capacity engulfed the US • Imperialism – the economic and political domination of a strong nation over weaker nations. Missionaries • Pious missionaries looked to harvest new souls • Superior Americans looked to spread values and religion to “backwards” people Great White Fleet • The US built a new and modern navy • 15 major battleships made of steel • US Naval Cpt. Alfred Thayer Mahan stirred a world naval race Captain Alfred T. Mahan • Captain in US Navy • Published series of lectures in a book called The Influence of Seapower Upon History, 1660-1783 • Suggested that a nation needed a large navy to protect merchant ships and defend right to trade • Americans also wanted an isthmus canal Secretary of State James G. Blaine • Proposed idea that the United States and Latin America work together…idea became known as Pan-Americanism • “Big Sister” policy • 1899 – presided over 1st PanAmerican Conference • Set the stage for many American assemblies America & Germany • 1899 – nearly came to blows with Germany over Samoan Islands • Located in South Pacific Ocean near Australia • Germany was looking to expand empire International Conflicts • 1891 – the lynching of 11 Italians in New Orleans brought the US and Italy to the brink of war (US paid compensation) • 1892 – 2 US sailors died in the Chilean port of Valparaiso (Chile paid compensation) • 1893 – US and Canada battled over seal hunting rights near Pribilof Islands near Alaska (arbitration) Venezuela-British Guiana Boundary Dispute • President Cleveland claimed Britain was trying to dominate Venezuela • In violation of Monroe Doctrine • Gold was discovered in disputed area Venezuela-British Guiana Boundary Dispute • • • • • England denied relevance of M.D. War seemed inevitable Brits 32 warships v. U.S. 5 warships Brits had no real urge to fight Canada was vulnerable, and British shipping would be hurt Germans Anger Brits • Kaiser Wilhelm II congratulated Dutch Boers of South Africa for capturing British ship • Brits turn aggression toward Germany • The Great Rapprochement is reached with the US (reconciliation) The Monroe Doctrine • Monroe Doctrine is strengthened • Most of Latin America was pleased that US would protect them from Europe Hawaii • Halfway station for US ships going to Asia • 1st missionaries arrive in 1820 • Honolulu looked like a New England town • US regarded Hawaii as their own Hawaii • 1840s – US State Department warned other nations to stay away • 1875 – commercial reciprocity treaty, meaning sugar could be traded without subject to tariff • 1887 – treaty with native Hawaiian government for rights to Pearl Harbor Queen Liliuokalani • Strong-willed native Queen of Hawaii • Insisted natives should control the islands • 1893 – small group of Americans org. a successful revolt against the royal government • Openly assisted by federal troops Hawaii • Grover Cleveland denied annexation b/c he felt Liliuokalani was wronged • 1893 – G.C. sent investigators to Hawaii and found that a majority of Hawaiians did not favor annexation • 1st imperialist debate in US History Jose Marti • Cuban exile to New York • • • • City Led Cuba’s revolt from Spain 1868 – Cuban rebels declared independence from Spain Attack failed and they fled to US 10% of Cubans were enslaved Cuban Revolution • 1894 – US imposed new tariff on sugar, and this devastated the Cuban economy • 1895 – Rebels seized control of eastern Cuba • Americans were neutral at first, but newspaper writers wrote exaggerated stories that got Americans on Cubans side • Yellow journalism – exaggerated stories of Spanish attacks on Cubans Cuban Revolution • Cubans used a scorched-earth policy of destruction • If they damaged enough, maybe the Spaniards would leave • Insurrectos – torched cane fields, sugar mills, and dynamited trains • US had $50 million invested in Cuba with yearly trade at $100 million Gen. Valeriano Weyler • 1896 – Spain sent Gen. Weyler to Cuba • Weyler a.k.a. “The Butcher” • Crushed Cuban Rebellion with barbed wire concentration camps • Poor sanitation, deadly holes US Reaction • 1896 – US Congress called on President Cleveland to recognize the revolting Cubans • Cleveland said he would not mobilize army even if Congress declared war • Cleveland felt the US should stay out of Cuba at all cost USS Maine • February 1898 – The USS Maine sent to Havana harbor to protect Americans in Cuba • Exploded, killing 266 American officers and sailors • Cause unknown but Americans blamed Spanish USS Maine • Feb. 9, 1898 – private letter written by Dupuy de Lome, a Spanish ambassador to the US, describing President McKinley as an ear-to-theground politician who lacked good faith • Hearst published letter • Feb. 15, 1898 – USS Maine explodes • 1976 – Adm. H. G. Rickover proves the USS Maine was subject to an internal explosion US Clamors For War • US wanted to go to war with Spain over the USS Maine explosion • Madrid had already agreed to end the concentration camps, and an armistice with the Cuban rebels • BUT, the American public wanted a war • April 11, 1898 – McKinley asked Congress to declare war on Spain • Claimed the Teller Amendment US would give Cuba self-rule after it defeated Spain • Imperial Europe not sure what to think over this declaration The Spanish-American War • 1898 • Regular US Army – run by ex-Civil War officers • Unready, untrained for a tropical war • Only 2,100 officers and 28,000 men • 200,000 Spanish troops in Cuba The Spanish-American War • The Spanish Navy was in wretched condition • 1000s of miles away from home • US Navy was new, steel (15 years old) • 5th largest navy in the world John D. Long • Secretary of Navy – John D. Long • Asst Sec. Of Navy – Theodore Roosevelt • Long rarely left T.R. in charge b/c he was unpredictable Theodore Roosevelt • 2/25/1898 • Long was away for the weekend • T.R. instructed Commodore George Dewey to attack Spanish fleet at Manila, Phillipines • McKinley confirmed orders Philippines • May 1, 1898 • 6 warships under Dewey sailed into Manila Bay & defeated Spain’s 10 ship fleet • 400 Spanish dead • 0 Americans dead George Dewey • Became national hero, but could not attack land b/c he needed reinforcements • Awarded the rank of Admiral • Other foreign ships besieged Manila to offer protection for their citizens • Germany, England Philippines • August 13, 1898 • US troops finally arrive in the Philippines and capture Manila • Assisted by Filipino insurgent Emilio Aguinaldo • Brought in from Asian exile Hawaii • July 7, 1898 • Annexation of Hawaii rushed through Congress • Residents granted full citizenship • Full territorial status in 1900 Invasion Of Cuba • Spain sent fleet of ships under Admiral Cervera to Cuba when the US declared war • Eastern US in panic, so Navy sent useless Civil War boats to ‘protect’ the east coast Gen. William R. Shafter • Sick and gout stricken • Put in command of unprepared US forces in Cuba • Army was in wool designed for sub zero temperatures • Shafter nor the Army was prepared for a tropical war • Summer clothing didn’t arrive until the war was over Rough Riders • Colorful regiment of volunteers • Short on discipline • Western cowboys and Eastern polo players • Ex-convicts Col. Leonard Wood • Commander of the Rough Riders • Organized by gloryhungry Theodore Roosevelt after he resigned from the Navy Department Invasion of Cuba • June 1898 – 17,000 US troops left Tampa, Florida for • • • • • • Cuba ½ of Rough Riders horses didn’t arrive “Woods Weary Walkers” Gen. Shafter lands uncontested at Santiago, Cuba July 1 – fighting at El Caney and San Juan Hill lead to US victory RR charge San Juan Hill with 2 black regiments Heavy casualties Invasion of Cuba • US Army gained control of Santiago • Admiral Cervera wanted to retreat, but was told to fight for the honor of the flag • July 3, 1898 – Spanish fleet was destroyed as wooded decks caught on fire • 500 Spanish killed • 1 American killed Gen. Miles in Puerto Rico • Gen. Nelson Miles met little resistance taking over Puerto Rico • Aug. 12, 1898 – Spain signed armistice ending the war Tropical Troops • Troops were falling to tropical malaria, typhoid, dysentery, and yellow fever • 80% of troops were transferred to chilly Long Island, NY where their light summer uniforms were delivered • 400 Americans died in battle • 5,000 died from disease Treaty of Paris - 1898 • Spanish and US negotiators met in Paris in 1898 • Cuba – freed from Spanish control; US would make free • Guam – US secured as a territory • Puerto Rico – becomes US territory Philippines • Philippines had 7 million Asians living in its borders • US did not want to give back to Spain, and did not want to leave them alone for fear of Germany taking over the islands • US purchases Philippines for $20 million b/c Manila was captured one day after the armistice • McKinley prayed for guidance America’s Empire • All previous land acquisitions had been thinly populated and on the continent • Philippines, Guam, Cuba, Puerto Rico – distant, tropical, foreign populations; alien race, culture, tongue, religion, and government • The Anti-Imperialist League • Organized to fight McKinley’s expansionist policies • Some of most prominent people in US • University presidents, philosophers, novelists, Samuel Gompers, Andrew Carnegie Puerto Rico • Nearly 1 million inhabitants, • • • • most poverty stricken Foraker Act of 1900 – Congress gave P.R. limited popular govt. 1917 – full citizenship US helped work wonders in edu, transportation, sanitation, Many Puerto Ricans moved to NYC Insular Cases - 1901 • Did the Constitution follow the flag? • 1901 – The Supreme Court ruled that the Constitution did not extend to people in territories acquired by the US • Puerto Ricans and Filipinos subject to US rule, but did not enjoy all American rights Cuba • Gen. Leonard Wood set up a military govt. • Advances in govt, finance, edu, agr, and public health Yellow Fever • Dr. Walter Reed found that mosquitoes were the carrier of yellow fever • US forces cleaned up breeding grounds in Cuba, and wiped out yellow fever in Havana Cuba • The US withdrew from Cuba in 1902, • • • • honoring the Teller Act Cubans were forced to write the Platt Amendment into their constitution 1901 – Platt Amendment Could not incur debt past resources US could intervene for mutual protection Guantanamo Bay • Platt Amendment also secured Guantanamo Bay as a military base for the US • The lease was to last until both parties agreed to end it • Still in use by US forces today Spanish-American War • Coming out party of US power • It did not cause the US to become a power, it just proved it already was • 113 day war, low in casualties • American prestige rose sharply, Europe gave US more respect, A new American spirit emerged John Philip Sousa • The new American spirit was ushered in with music by famous director John Philip Sousa • American cockiness indcreased “Bloody Chasm” Ends • The strain between North and South was eased after the SpanAmerican War • 1000s of Southerners served the military • Gen. Joseph Wheeler – ex-Confederate was given command in Cuba