The Romans
advertisement
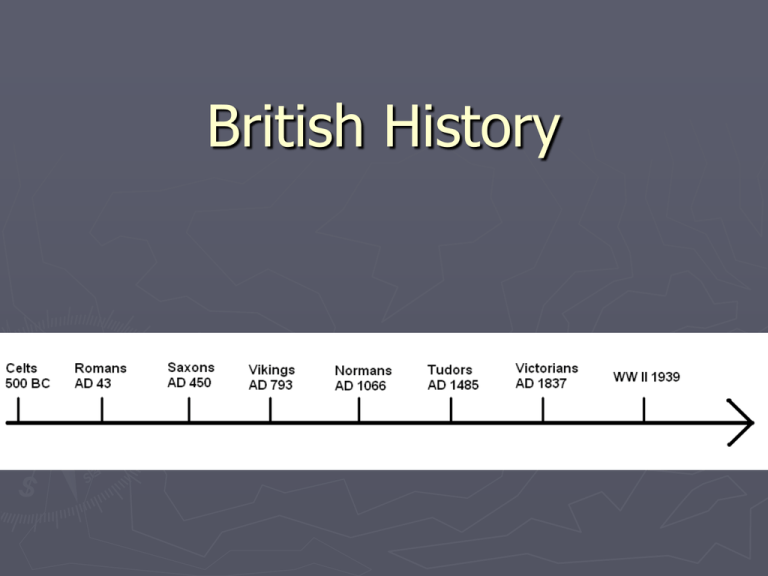
British History The Celts Who were the Celts? From around 750 BC to 12 BC, the Celts were the most powerful people in central and northern Europe. There were many groups (tribes) of Celts, speaking a vaguely common language. The word Celt comes from the Greek word, Keltoi, which means barbarians and is properly pronounced as "Kelt". ► Interesting fact No-one called the people living in Britain during the Iron Age, Celts until the eighteenth century. In fact the Romans called these people Britons, not Celts. The name Celts is a 'modern' name and is used to collectively describe all the many tribes of people living during the Iron Age. ► Why are the Celts called Iron Age Celts? The period of time in Britain immediately before the Roman period is known as the Iron Age. The name 'Iron Age' comes from the discovery of a new metal called iron. The Celts found out how to make iron tools and weapons. Before the Iron Age the only metal used in Britain to make tools was bronze. ► Where did the Celts come from? The Celts lived across most of Europe during the Iron Age. ► The Romans The Romans came to Britain nearly 2000 years ago and changed our country. Even today, evidence of the Romans being here, can be seen in the ruins of Roman buildings, forts, roads, and baths can be found all over Britain. Who were the Romans? The Romans lived in Rome, a city in the centre of the country of Italy. One day, some years before Jesus Christ was born, the Romans came to Britain. The Romans gave us… Language The language we used today was developed from the Romans. The Romans spoke and wrote in Latin and many of our words are based on Latin words. The Calendar Did you know that the calendar we use today is more than 2,000 years old? It was started by Julius Caesar, a Roman ruler. It is based on the movement of the earth around the sun, and so is called the 'solar calendar.' The solar calendar has 365 days a year, and 366 days every leap year, or every fourth year. The names of our months are taken from the names of Roman gods and rulers. The month 'July,' in fact, is named after Julius Caesar himself! Laws and a legal system The laws and ways we determine what to do with someone who is accused of breaking a law came originally from the Roman Empire. The Census The Roman Empire was huge and included millions of people living over a large area. How did they keep track of all these people? Easy! They counted them! The Roman Empire began the practice of taking a census, or a 'count,' of all the people within its boundaries every so often. Today, many countries like ours take a census every 10 years. The Romans also gave us: ►straight roads ►central heating ►concrete ►aqueducts (bridges for water) Anglo-Saxons ► Where did the Anglo-Saxons come from? The Anglo-Saxons left their homelands in northern Germany, Denmark and The Netherlands and rowed across the North Sea in wooden boats to Britain. They sailed across the North Sea in their long ships, which had one sail and many oars. They made a series of attacks on different parts of the country over a period of years and under a number of leaders. ► The Saxons settled in areas of Essex (East Saxons), Sussex (South Saxons), Middlesex (Middle Saxons), and Wessex (West Saxons). Why did Anglo-Saxons invade Britain? ► Historians are not sure why the Anglo-Saxons came to Britain. Some sources say that the Saxon warriors were invited to come, to the area now know as England, to help keep out invaders from Scotland and Ireland. Another reason for coming may have been because their land often flooded and it was difficult to grow crops, so they were looking for new places to settle down and farm. How long did the Saxons stay in England? ► They ruled in England for about 500 years ( a hundred years longer than the Romans). However, unlike the Romans, the Anglo-Saxons never 'went home'; many people living in Britain today have Anglo Saxon ancestors. The name England even comes from the Saxon word 'Angle-Land‘ ► ► One of the places they settled in was Tonbridge, in Kent. Tonbridge was an ideal place to settle as it was on the main track from Hastings to London and has a river. At the time when the AngloSaxons came to England much of the country was covered in forest. Only about a few thousand people in the whole land (today there are about 50 million people living in England). It was an easy place for newcomers to find a place to start a village and then chop down the surrounding forest to make farmland. Days of the Week Monandæg ( Moon's day - the day of the moon ), Tiwesdæg ( Tiw's-day - the day of the Scandinavian sky god Tiw,Tiu or Tig), Wodnesdæg ( Woden's day - the day of the god Woden (Othin) ), Ðunresdæg ( Thor's Day - the day of the god Ðunor or Thunor ), Frigedæg ( Freyja's day - the day of the goddess Freyja or Frigg, wife to Woden), Sæternesdæg ( Saturn's day - the day of the Roman god Saturn, whose festival "Saturnalia," with its exchange of gifts, has been incorporated into our celebration of Christmas.), Sunnandæg ( Sun's day - the day of the sun ). The Vikings About the year 800, bands of fierce raiders began to attack our coasts. They were the Vikings. They came across the North Sea, just as the Anglo-Saxons had done 400 years earlier. In time, like the Anglo-Saxons, they made their home here. They drove the Saxons out of part of the country and took it for themselves. King Alfred, Saxon king of Wessex, fought them in a great battle, but he could not drive them right away and had to let them have part of the country, called Danelaw. The Vikings lived over one thousand years ago and came from the three countries of Scandinavia: Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Who were the Vikings? ► ► Vikings were also known as the Norsemen. They were great travellers and sailed to other parts of Europe, where they traded, raided, and often settled They were also farmers, fishermen, trappers and traders. Viking craftsmen made beautiful objects out of wood, metal and bone; Viking women were skilful weavers, produced fine, warm textiles. ► ► No matter how many times the Vikings were beaten, they always came back, and in the end all their efforts paid off. It was the Vikings (Norse) of Normandy who finally conquered England in 1066 and changed British history for ever. Why did the Vikings invade Britain? Most Vikings who sailed overseas were simply searching for better land for their farms. Their land was not very good for farming. Norway was very hilly, Sweden was covered in forests, and Denmark had a lot of sandy home land. ► Alfred the Great and Danelaw Rather than face defeat, Alfred the Great, king of Wessex, paid the Vikings (Danes) to leave his kingdom alone. He bought just five years of peace. In that time the Vikings took over one third of England. Then they returned to take Wessex. Alfred fought and defeated the Vikings and their leader, King Guthrum, asked for peace. The Vikings settled peacefully in an area of Britain which became known as Danelaw The Normans ► King Edward lll of England (called "The Confessor" because he built Westminster Abbey) died on January 5, 1066, after a reign of 23 years. Leaving no heirs, Edward's passing ignited a three-way rivalry for the crown that culminated in the Battle of Hastings and the destruction of the Anglo-Saxon rule of England. Harold Godwinson was a leading Saxon Lord and the brother of Edward's wife. He had won a number of battles for Edward. Harold was chosen by the Witan (the King's council) to succeed Edward the Confessor. He also said that it was Edward's dying wish that he, Harold, should have the crown (There were no witnesses to Edward saying this) The day after Edward diedold was born and bred in England and popular with ordinary people. He was son of Earl Godwin, the most powerful noble in E, Harold became King Harold ll of England. Harold did not have a direct blood link to the king. William, Duke of Normandy, over the sea in France William was a distant cousin of Edward the Confessor and wanted to be the next king. He claimed that both Edward and Harold had promised him the throne, but English supporters of Harold challenged this. Who were the Normans? ► The Normans were people who lived in Normandy in Northern France. They were originally Vikings from Scandinavia Why did William won the Battle of Hastings? 1.William's army had time to rest before the battle. Harold Godwinson's army was tired and they did not have time to prepare properly for the battle. The English army had already fought the Battle of Stamford Bridge that day and had to march quickly down to the battlefield outside Hastings. They marched 50 miles a day! 2.William's army was stronger. He had better trained soldiers and had the use of a strong cavalry (men on horseback) and archers whereas Harold did not. 3.William's army pretended to flee. Many of Harold's men broke their sheild wall to chase after them but as they did William and his army turned back and slaughtered them. Who became the next King of England? When William won the Battle of Hastings, he earned himself the title 'Conqueror'. He marched to London and was crowned King in Westminster Abbey on Christmas Day 1066. The Tudors The Tudors were a Welsh-English family that ruled England and Wales from 1485 to 1603 - one of the most exciting periods of British history. They ruled for 118 years and during their reign encouraged new religious ideas, overseas exploration and colonisation. Tudor England had two of the strongest monarchs ever to sit on the English throne: Henry VIII and his daughter Elizabeth I. ► The ► The Tudors ruled England from 1485 to 1603. first Tudor king was Henry Vll. He became king after the battle of Bosworth field, which ended the War of the Roses. He was followed by his son, Henry Vlll, who was famous for marrying six times and beheading two of his wives! His son, Edward Vl ruled after him, followed by his daughters Mary l and Elizabeth l. ► They are famous for many things, including the Henry VIII and his six wives, the exploration of America and the plays of William Shakespeare. ► During the sixteenth century, England emerged from the medieval world. It was a time of great change, most notably it marked the end of the Catholic church in England. Great naval exploits began the great English seafaring tradition. ► Life had many problems. Towns were becoming overcrowded, roads were muddy tracks and travelling was difficult. The overcrowding caused danger from fire and disease. ► During 118 years of Tudor rule, England became richer than ever before. As the country became wealthier, towns grew, beautiful houses were built and schools and colleges were set up. Arts and crafts flourished too. England was home to great painters, writers and musicians. The Victorians ► ► ► ► The Victorians lived over one hundred and fifty years ago during the reign of Queen Victoria (1837 to 1901). Victorian times means during Victoria's rule. The time Queen Victoria was on the throne. She ruled for 64 years. There was no electricity, instead gas lamps or candles were used for light.There were no cars. People either walked, travelled by boat or train or used coach horses to move from place to place. Britain managed to build a huge empire during the Victorian period. It was also a time of tremendous change in the lives of British people. In 1837 most people lived in villages and worked on the land; by 1901, most lived in towns and worked in offices, shops and factories. During Queen Victoria's reign: ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► ► Britain became the most powerful and richest country in the world, with the largest empire that had ever existed, ruling a quarter of the world's population. Towns and cities got piped water, gas and, by the end of the century, electricity The number of people living in Britain more than doubled from 16 million to 37 million, causing a huge demand for food, clothes and housing. Factories and machines were built to meet this demand and new towns grew up, changing the landscape and the ways people lived and worked. Railways, originally built to transport goods, meant people could travel easily around the country for the first time. Railways brought new foods to towns and cities. Soldiers were at war all over the world especially in 1850 - 1880. Many households had a servant or servants – in 1891, 2 million servants were recorded in the census Seaside holidays were 'invented' (became popular). Police Force 'invented'. At the beginning of the Victorian period crossing the Atlantic took up to eight weeks. By 1901 it took about a week. New cookers and gadgets for the home were invented. It was created thanks to Woodlands Junior High School WWW. Created by: AND: Justyna Gralla Gosia Kasprzik Sabina Hulbój Beata Dobiosz Kinga Musioł Ewa Wrzeciono Bartek Gryko Magda Dobiosz











