The Presidency
12
Video: The Big Picture
12
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch12_The_Presidency_S
eg1_v2.html
Edwards Learning Objectives
12.1
12.2
12
Characterize the expectations for
and the backgrounds of presidents
and identify paths to the White
House and how presidents may be
removed
Evaluate the president’s
constitutional powers and the
expansion of presidential power
Edwards Learning Objectives
12.1
12.4
12
Describe the roles of the vice
president, cabinet, Executive Office
of the President, White House staff,
and First Lady
Assess the impact of various sources
of presidential influence on the
president’s ability to win
congressional support
Edwards Learning Objectives
12.3
12.6
12
Analyze the president’s powers in
making national security policy and
the relationship between the
president and Congress in this arena
Identify the factors that affect the
president’s ability to obtain public
support
Edwards Learning Objectives
12.7
12.8
12
Characterize the president’s
relations with the press and news
coverage of the presidency
Assess the role of presidential power
in the American democracy and the
president’s impact on the scope of
government
Video: The Basics
12
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg2_The_Presidency_v2.html
The Presidents
Great Expectations
Who They Are
How They Got There
12.1
Great Expectations
12.1
Are expectations realistic?
Ensure peace, prosperity and security
Power does not match responsibilities
Cognitive dissonance:
Americans want strong leader but fear concentration of
power
We want government to be small and limited, yet solve all
societal and economic problems
“Bring in the new guy”
12.1
Who They Are
Basic requirements:
Natural-born citizen
35 years of age or older
Resident of the U.S. for previous 14 years
White, male, Protestant
First female president?
12.1
TABLE 12.1: Recent Presidents
12.1
How They Got There
Elections: The Typical Road to the White
House
Twenty-Second Amendment (1951)
Succession
Twenty-Fifth Amendment (1967)
Impeachment
Watergate
Clinton’s sex scandal
12.1
TABLE 12.2: Incomplete Presidential Terms
12.1
Nixon Resigns
12.1
12.1 Which amendment creates a
means for selecting a vice
president when the office becomes
vacant?
a. Twenty-second Amendment
b. Twenty-fifth Amendment
c. Twelfth Amendment
d. Tenth Amendment
12.1
12.1 Which amendment creates a
means for selecting a vice
president when the office becomes
vacant?
a. Twenty-second Amendment
b. Twenty-fifth Amendment
c. Twelfth Amendment
d. Tenth Amendment
12.1
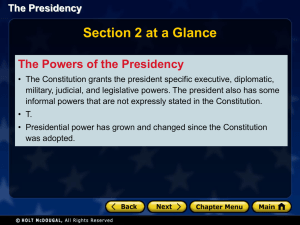
Presidential Powers
Constitutional Powers
Expansion of Power
Perspectives on Presidential Power
12.2
Video: In Context
12.2
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg3_Presidency_v2.html
Constitutional Powers
12.2
Constitution says little
“The executive power shall be vested in a president of the
United States of America.”
Fear of abuse of power
Madisonian system
Shared powers
Checks and balances
Short term of office
TABLE 12.3: Constitutional Powers of the
President
12.2
Expansion of Power
Changes leading to expansion of
presidential power
Military
Technological
Economic
Presidents take initiative to expand role
Lincoln
FDR
12.2
Perspectives on Presidential
Power
1950s-1960s
Strong = good; weak = bad
1970s
Vietnam War
Watergate
1980s and beyond
Mixed feeling about presidential power
12.2
12.2 Which of the following is NOT
an enumerated power of the
president?
a. Make treaties with other nations
b. Veto legislation
c. Nominate ambassadors
d. Declare war
12.2
12.2 Which of the following is NOT
an enumerated power of the
president?
a. Make treaties with other nations
b. Veto legislation
c. Nominate ambassadors
d. Declare war
12.2
Explore the Simulation: You
Are a First-Term President
12.2
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/long/long_longman_media
_1/2013_mpsl_sim/simulation.html?simulaURL=8
Running the Government:
Chief Executive
Vice President
Cabinet
Executive Office
White House Staff
First Lady
12.3
Vice President
Mainly ceremonial in previous years
Increasing role in modern presidency
Cheney
Biden
12.3
Cabinet
Traditional, not mandated
Heads of federal agencies and executive
departments
12.3
TABLE 12.4: Cabinet Departments
12.3
Executive Office
12.3
National Security Council (NSC)
Council of Economic Advisers (CEA)
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
FIGURE 12.1: Executive Office of the
President
12.3
White House Staff
President’s personal support team
Chief of staff
Press secretary
Anonymous and loyal
President sets style and tone
12.3
FIGURE 12.2: Principal Offices in the White
House
12.3
First Lady
12.3
No longer just a well-dressed homemaker
Abigail Adams
Edith Wilson
Eleanor Roosevelt
Hillary Rodham Clinton
Michelle Obama
Michele Obama with military families
12.3
12.3 What is the main duty of the
12.3
Council of Economic Advisors?
a. Advise the president on banking regulations
b. Advise the president and Congress on trade
c. Advise the president on economic policy
d. Advise the president on intelligence
12.3 What is the main duty of the
12.3
Council of Economic Advisors?
a. Advise the president on banking regulations
b. Advise the president and Congress on trade
c. Advise the president on economic policy
d. Advise the president on intelligence
Presidential Leadership of
Congress: Politics of Shared
Powers
Chief Legislator
Party Leadership
Public Support
Legislative Skills
12.4
Chief Legislator
State of the Union
Veto
Pocket Veto
Line-item veto
12.4
TABLE 12.5: Presidential Vetoes
12.4
Party Leadership
Bonds of Party
Slippage in Party Support
12.4
Obama with Reid and Pelosi
12.4
Party Leadership
Leading the Party
Presidential Coattails
12.4
TABLE 12.6: Congressional Gains or Losses
for the President’s Party in Presidential
Election Years
12.4
TABLE 12.7: Congressional Gains or Losses
for the President’s Party in Midterm
Election Years
12.4
Public Support
12.4
Influence in Congress depends on popularity
Public Approval
Electoral Mandates
Legislative Skills
Bargaining
Moving Fast
Exploiting the honeymoon period
Setting Priorities
Limited success
12.4
Clinton signing welfare bill
12.4
12.4 A president will usually have
12.4
the most legislative success when
a. he has persuasive powers with Congress
and the public
b. he presides over good foreign relations
c. his party controls both houses of Congress
d. he has strong staff support
Video: Thinking Like a
Political Scientist
12.4
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg4_Presidency_v2.html
12.4 A president will usually have
12.4
the most legislative success when
a. he has persuasive powers with Congress
and the public
b. he presides over good foreign relations
c. his party controls both houses of Congress
d. he has strong staff support
President and National
Security Policy
Chief Diplomat
Commander in Chief
War Powers
Crisis Manager
Working with Congress
12.5
Chief Diplomat
Extending diplomatic recognition
Treaties
Executive agreements
12.5
Carter with Begin and Sadat
12.5
Commander in Chief
President can deploy troops
Congress must declare war, appropriate funds
Framers did not envision standing army
Or nuclear arsenal
12.5
Capture of Obsama bin Laden
12.5
War Powers
War Powers Resolution (1973)
Presidents must seek Congressional approval before
deploying armed forces
Legislative veto
What do you think?
12.5
Crisis Manager
What constitutes a crisis?
Cuban Missile Crisis
9/11
Modern communications technology
12.5
Responding to 9/11
12.5
Working with Congress
Two presidencies
Domestic policy
Foreign policy
12.5
12.5 The president has the most
influence in
a. national security policy
b. domestic policies
c. public welfare
d. public opinion
12.5
12.5 The president has the most
influence in
a. national security policy
b. domestic policies
c. public welfare
d. public opinion
12.5
Power from the People: Public
Presidency
Going Public
Presidential Approval
Policy Support
Mobilizing the Public
12.6
Going Public
“Public sentiment is everything. With
public sentiment nothing can fail;
without it nothing can succeed.”
Ceremonial duties build public support
12.6
President Bush announces end
of Iraq war
12.6
Presidential Approval
Product of many factors
Party affiliation
Honeymoon period
Policy success
Integrity and leadership skills
Rally events
12.6
FIGURE 12.3: Presidential Approval
12.6
Explore the Presidency: What
Influences a President's Public
Approval?
12.6
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/long/long_edwards_mpslgi
a_16/pex/pex12.html
Policy Support
Using the bully pulpit effectively
Media skills
Public not receptive
Not interested in politics and government
Biased reasoners and partisans
Weak on facts
12.6
Reagan
12.6
Mobilizing the Public
12.6
When the people speak, Congress listens
This is a rare event
Inattentive public
Apathetic public
Congress responds to this, too
12.6 As a president’s time in office
increases, his approval ratings
a. also increase
b. generally go down
c. remain stable
d. decrease but rise as his term ends
12.6
12.6 As a president’s time in office
increases, his approval ratings
a. also increase
b. generally go down
c. remain stable
d. decrease but rise as his term ends
12.6
President and the Press
Nature of News Coverage
12.7
Obama press conference
12.7
Nature of News Coverage
Media serves as intermediary
Does not always verify facts
Are news outlets biased?
Press secretary
12.7
12.7 With which statement would
12.7
most press secretaries agree?
a. The media have a liberal bias.
b. Coverage of the presidency is generally
positive.
c. Media bias has little impact on the way the
American people are informed.
d. Media coverage is based solely on facts.
12.7 With which statement would
12.7
most press secretaries agree?
a. The media have a liberal bias.
b. Coverage of the presidency is generally
positive.
c. Media bias has little impact on the way the
American people are informed.
d. Media coverage is based solely on facts.
Understanding the American
Presidency
12.8
Presidency and Democracy
Presidency and the Scope of Government
Presidency and Democracy
Wanting and fearing a strong president
Safety in checks and balances
What happens when government is
divided?
12.8
Presidency and the Scope of
Government
What made Theodore Roosevelt,
Woodrow Wilson, and Franklin Roosevelt
noteworthy presidents?
Government growth not inherent in
presidency
Ideologically conservative and
operationally liberal
12.8
Video: In the Real World
12.8
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Seg5_The_Presidency_v2.html
12.8 According to the text, which of
12.8
the following is true?
a. Divided government cannot pass legislation.
b. Change occurs in unified as well as divided
government.
c. All presidents work toward increasing
presidential power.
d. Presidents since LBJ have championed
growth of government.
12.8 According to the text, which of
12.8
the following is true?
a. Divided government cannot pass legislation.
b. Change occurs in unified as well as divided
government.
c. All presidents work toward increasing
presidential power.
d. Presidents since LBJ have championed
growth of government.
Discussion Question
12
How do presidents use the “power to
persuade” to implement their agenda? In
what way is this power considered to be
their most important?
Video: So What?
12
http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/SSA_SHARED_MED
IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch12_The_Presidency_S
eg6_v2.html
Further Review:
On MyPoliSciLab
Listen to the Chapter
Study and Review the Flashcards
Study and Review the Practice Tests
12