PowerPoint - Izzit.org
advertisement

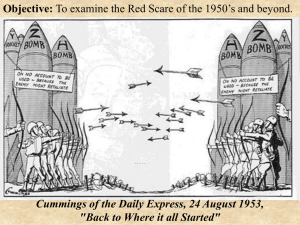
Understanding the Cold War through the Singing Revolution AIM How does the experience of Estonia reflect the political evolution of the Cold War? Bell Ringer Read the following quote by President Truman at the start of the Cold War. 1) What does he foresee as the Soviets’ strategy for winning the ideological battle between them? 2) What did this mean for countries with less political and military strength than the Soviets? "I Suppose that history will remember my term in office as the years when the Cold War began to overshadow our lives. I have hardly a day in office that has not been dominated by this allembracing struggle. And always in the background there has been the atomic bomb. But when history says that my term of office saw the beginning of the Cold War, it will also say that in those eight years we have set the course that can win it. The Soviet Union does not have to attack the United States to secure domination of the world. It can achieve its ends by isolating us and swallowing up all our allies." Cold War Definition • The Cold War was an ideological conflict between the two main victors of World War II: The United States and the Soviet Union. • The end of this war meant: A realignment of the international order that had broken down with the beginning of the first World War. It was replaced by a new order dominated by the United States and the Soviet Union. • The ideological battle was between ideas of how to govern society and manage its economy: These ideas are known as “Communism” and “Capitalism.” Understanding the Conflict We will investigate the Cold War using two approaches: 1) You will learn of the conflict using a “global” approach in which we examine a four-stage issue cycle. 2) You will observe the “local” impact of the Cold War by viewing its effect on the Baltic country of Estonia. The Issue Cycle To better comprehend the Cold War, we will use the following issue cycle: • Genesis • Crisis • Ritualization • Resolution This format matches your graphic organizer. You will fill in the appropriate definitions and local examples next to each term. Genesis “An issue’s genesis places it on the global agenda by bringing it to the attention of leaders. The global agenda consists of matters which attract attention and to which participants are prepared to devote resources.” (Mansbach, 99) We will now watch the opening to The Singing Revolution and a 1945 newsreel of Yalta. As you watch the film clips, identify the: a. Issue(s) b. Leaders c. Participants d. Resources (think of tools the leaders and participants are capable and willing to use.) Crisis “During the crisis stage, an issue assumes urgency -- the belief grows that, unless something is done quickly, matters will deteriorate.” (Mansbach, 100) It is at this point that a clear division and area of contention was established between the two powers. In this stage, you will learn how the United States and Soviet Union took firm positions against each other. Research Time! • Using the internet or school-provided online databases, identify the following terms that demonstrate the crisis stage of the Cold War. Note: If a library or computer lab is not available, textbooks can be used. If there is no other way to conduct research, the information is provided in the PowerPoint on slide #10. • Next to each term on your graphic organizer, write a description and an explanation of how it “escalated” the conflict. For example: NSC-68 is a report written by the U.S. National Security Council in 1950, outlining the U.S. position on the Soviet Union and the spread of International Communism. This document essentially outlined the Soviet threat to the United States and its allies. - Truman Doctrine - Marshall Plan - Berlin Air Lift - Korean War Crisis Summation Compare your responses to those below. Did you reach the same conclusions? If not, add them to your notes. If you found more info, or a more significant event, please write that on your exit ticket. – Truman Doctrine: As the Soviets attempted to expand their control, President Truman established the U.S. position of aiding people across the world (Greece, Turkey) in danger of losing their free institutions. This directly placed the U.S. in conflict with Soviet ideology of Communism. – Marshall Plan: A plan created by the U.S. to provide economic assistance and rebuild Western Europe. This was meant to hold back Soviet expansion and unite Western Europe against the Soviets. – Berlin Air Lift: The German city of Berlin, that had been divided between the allies after World War II, was blockaded by the Soviets in a pressure move against the other allies. The Western allies initiated a massive program to bring food, fuel, and other supplies to the besieged city. This established the manner in which the war would be fought: through proxy nations, thus preventing the major powers from directly going to war. – Korean War: This war spread the Cold War from Europe to Asia, as Korea split between Communist and Democratic factions. The Soviets backed the Chinese who assisted the Northern Koreans, while the U.S. intervened in the South through the United Nations. This demonstrated to the world that the Cold War was not a European, but a global conflict. Exit Ticket On a small slip of paper, write down which event you found to be the most ESCALATING. (In other words, which event brought the world closest to another World War?) Explain your reasoning. Stage 3: Ritualization a. “Having groped in the dark to find mutually acceptable and stable norms of behavior, actors may acquire patterned and stable mutual expectations about how they should interact in the future.” (Mansbach, 101) b. “By the 1960’s the superpowers concluded that their relations had to be governed by rules and procedures that would reduce the likelihood of mutual annihilation and allow them to coexist.” (Mansbach, 115) c. The basic rule was that each superpower would not intervene in the “spheres” of another. In essence, “I’ll stay out of your backyard” (e.g., Czechoslovakia and Hungary). d. The Cold War would be a series of hot/cold moments defined by massive military escalation on both sides and indirect confrontation through proxies (other nations engaged in the conflict). • As you watch the film, identify the “normalizing” features of life under the Soviets. How have the Soviets established their control in Estonia, beyond the use of military force? What aspect of Soviet Ritualization created an opening for the Estonians to reclaim their independence? Extension activity: • Describe the events that took place in Hungary in 1956. How does this reflect the larger theme of ritualization of the Cold War? Stage 4: Resolution • The resolution stage is the removal of an issue from the agenda by formal or informal agreements among competitors. • The Cold War would come to an end by the early 1990s. Following 50 years of competition against more prosperous nations, economic decay in the Soviet Union and an aggressive military build-up by the United States, the Soviet leadership responded with a new program that would result in its destruction from within. • We will observe how this took place in the country of Estonia. As you watch the film, add key events to your timeline and define the vocabulary. Writing Prompt • Over sixty years ago, President Truman recognized the danger of the internationalization of the Soviet Union and engaged the United States in a process that led to a “Cold War.” • Your task is to use the information you’ve gathered to: – Define and describe the conflict including the major and minor players you’ve learned about. – Explain the development of this conflict using the four-stage issue process identified in your graphic organizer. – Explain how the experience of Estonia reflects the political evolution of the Cold War. Works Cited Books: Mansbach, Richard. The Global Puzzle. Houghton Mifflin. New York. 1997 pgs. 98-127 Images: • http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c3/Flag_of_the_Soviet_Union. png&imgrefurl=http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Flag_of_the_Soviet_Union.png&usg=__gN3vnpVvyr999__sLKM DjQXOqMQ=&h=800&w=1600&sz=7&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=HE3VHzY_cDWOWM:&tbnh=106&tbnw=170&ei =8YdgTdTzL4bWgQfQsZi2AQ&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsoviet%2Bunion%2Bflag%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff%26biw %3D1345%26bih%3D583%26as_st%3Dy%26tbs%3Disch:1,iur:fc&itbs=1&iact=rc&dur=101&oei=8YdgTdTzL4bWgQfQ sZi2AQ&page=1&ndsp=26&ved=1t:429,r:1,s:0&tx=69&ty=40 • http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.freeclipartnow.com/d/25744-1/large-vertical-USflag.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.freeclipartnow.com/holidays/veterans-day/large-vertical-USflag.jpg.html&usg=__CjFdHgwOv6yk_cDsZJTN4PUpfRw=&h=350&w=270&sz=23&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=LFE fyFRb9YeTRM:&tbnh=105&tbnw=79&ei=PIhgTcSTJIHfgQfJgOmpAQ&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dus%2Bflag%26hl%3De n%26safe%3Doff%26biw%3D1345%26bih%3D583%26as_st%3Dy%26tbs%3Disch:1,iur:fc&itbs=1&iact=rc&dur=404& oei=PIhgTcSTJIHfgQfJgOmpAQ&page=1&ndsp=26&ved=1t:429,r:7,s:0&tx=44&ty=37 • http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/bigs/amer0023.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.photolib. noaa.gov/htmls/amer0023.htm&usg=__gLLzt6FPDQK9kYqqyp6WUjQLAY=&h=2391&w=1890&sz=455&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=DWLpy19O4U5bqM:&tbnh=118 &tbnw=93&ei=M4tgTfPB4vUgQfjusGtAQ&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dliberty%2Bbell%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff%26biw%3D1345%26bih%3 D583%26as_st%3Dy%26tbs%3Disch:1,iur:fc&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=736&vpy=235&dur=3639&hovh=253&hovw=200&t x=129&ty=150&oei=M4tgTf-PB4vUgQfjusGtAQ&page=1&ndsp=25&ved=1t:429,r:13,s:0