WWII- section 2
advertisement

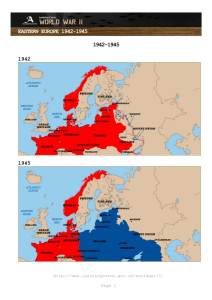
World War II The Road to Victory in Europe Before our entry into WWII, the Allies were losing on all fronts! The Atlantic Charter FDR and Churchill meet. The two pledge “A peace that will afford all nations the means of dwelling in safety inside their own boundaries.” This is known as the Atlantic Charter, and lays the basis of today’s United Nations. President Roosevelt talks of “Four Freedoms” “In the future days which we seek to make secure, we look forward to a world founded upon four essential human freedoms.” Freedom of Speech • The first is freedom of speech and expression --everywhere in the world. Freedom of Worship • The second is freedom of every person to worship God in his own way-- everywhere in the world. Freedom from Want • The third is freedom from want, which, translated into world terms, means economic understandings which will secure to every nation a healthy peacetime life for its inhabitants --everywhere in the world. Freedom from Fear • The fourth is freedom from fear, which, translated into world terms, means a worldwide reduction of armaments to such a point and in such a thorough fashion that no nation will be in a position to commit an act of physical aggression against any neighbor -anywhere in the world. Propaganda The 4 Freedoms were illustrated by Norman Rockwell, and became great propaganda posters in the U.S.. What does GI stand for? • Government issue. • Everything worn and issued to you to use while in service. All ethnic and racial backgrounds fought during WWII. • The Navajo served as radio operators, they developed a code based on their language. • The Japanese could not break this code! Although in internment camps. . • Many Japanese volunteered to fight. • They were allowed to in early 1943. • Their unit was the most decorated unit in American History. Women in WWII • They were used in all areas except combat. • Is this good or bad? • What were their jobs? So now we have soldiers, what is our plan? The Battle of the Atlantic • German subs were trying to isolate Great Britain. • It was very difficult to get food and supplies in. North Africa campaign • Generals Montgomery (Great Britain) and Eisenhower (U.S.) fight their way through Africa. They meet in Tunisia • And trap Rommel’s forces. • 240,000 Italians and Germans surrender. • The U.S. force is making a difference!!! The Casablanca Conference • Roosevelt and Churchill decide to concentrate on Europe before trying to win the war in the Pacific. • They want unconditional surrender. July 1943 • General George Patton (U.S.) attacks Sicily, Italy. • It falls in 38 days. • Mussolini is overthrown. • (It takes until April 1945 for the Germans in N. Italy to surrender.) War in the Soviet Union • Hitler needs living space to the east. • He breaks his pact with Stalin and launches an attack against the Soviet Union. PACT What can the Soviet Union do? • Russia’s Red Army soldiers were poorly equipped and not well trained. • German ground troops moved into Soviet territory. They begin rounding up and executing civilians. The Soviets begin a scorchedearth policy. • They destroy everything useful to the enemy as they retreated. • (It does hurt the enemy, but it also hurts your own homeland.) • What do you think these would be? Useful items to the enemy. Stalin wants help • But the Allies decide to invade Italy instead. • (This will make for ill feelings, and the rise of the Cold War) September 1942 • Germany bombs Stalingrad. This lasts for more than 2 months • The Soviets take positions in the rubble and engage in houseto-house fighting. Troops in the streets of Stalingrad The road of death Fighting for each floor of every building. Stalingrad’s front line Fighting in the streets Fighting in the rubble January 1943 • The Soviet’s counter-attack and surround Germany’s army. • 90,000 Germans surrender • The Battle of Stalingrad was the turning point of the war in the east. With Stalingrad in Russian hands The allies will begin a massive assault on Germany. D-Day • George Marshall was the army chief-ofstaff, • He was later credited for the allied victory • Named Time’s person of the year in 1943 and 1947. D-Day • The invasion was led by Dwight Eisenhower. • (A future U.S. President) The D-Day plan • The RAF (Great Britain) began a technique called carpet bombing, where bombs were scattered over a wide area. • Allied bombing also intensified. • They hoped to soften Germany for the planned allied invasion. Where was this happening? • Many countries were building up troops in southern England. • Germany strengthened their defenses along the French coastline. In preparing for the invasion. . Germany adds machine gun emplacements barbed wire fences on beaches land and water mines June 6, 1944 • The largest landing by sea in history begins. • The ships crossed the English Channel • Bombers were pounding Germany at Normandy, France. 23,000 British and American soldiers were dropped behind enemy lines. D-Day, the code name for the invasion had begun. 150,000 allied troops and equipment begins coming ashore. August 1944 • American troops liberate Paris • Later we cross the western border of Germany. • 2 months after our invasion, we are sending Germany back. The Battle of the Bulge • Germany will not give in • they reinforce their army, some draftees as young as 15. • They counter-attack in Belgium and Luxembourg. • This becomes known as the Battle of the Bulge. The German attack overwhelms the American forces. But General Patton moves his army in to stop the German advance The end is near for Germany March 1945 • American troops cross the Rhine River and advance towards Berlin. • At the same time the Soviets move in from the east. One month later • April 1945 • Soviets are in Berlin • The city was 80% destroyed by the bombing. • April 25, 1945 Russian and American troops meet at the Elbe River Hitler refuses to flee Berlin • May 1, 1945- German government announces that Hitler has committed suicide. • His wife Eva Braun is also dead. (cyanide tablets) May 8- Germany surrenders • American soldiers celebrate V-E day or Victory in Europe • The war in Europe was over, but Japan still had to be defeated. Before the fall of Germany • February 1945leaders meet at the Yalta conference. • Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin • They plan for the postwar world. • As a result of this meeting, Germany would become divided into zones The agreements at the Yalta conference were not fulfilled and would lead to problems between the Soviet Union and the western allies. Take a breath, study. You have learned a lot. 12 question fill-in-the-blanks quiz is coming up.