C5 The Overthrow of Robespierre v2
advertisement
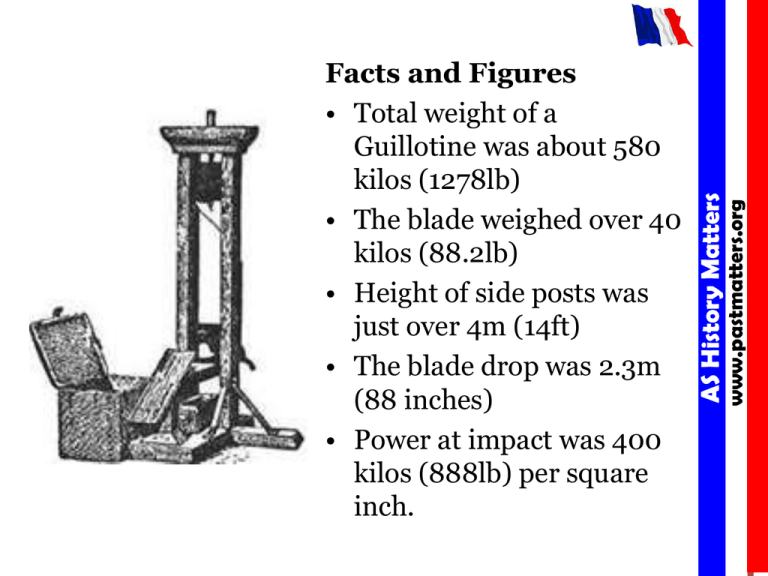
www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters Facts and Figures • Total weight of a Guillotine was about 580 kilos (1278lb) • The blade weighed over 40 kilos (88.2lb) • Height of side posts was just over 4m (14ft) • The blade drop was 2.3m (88 inches) • Power at impact was 400 kilos (888lb) per square inch. 4 revolutionary armies B fixing the prices of many goods and services. E 1793 October 21 1 Law of 14 Frimaire A Law of Revolutionary Government passed; power becomes centralised on the Committee of Public Safety. A 1793 September 9 5 Levée en masse E priests and supporters liable to death on sight. D 1793 September 29: B 1793 December 4 2 Convention passes the General Maximum 3 An anti-clerical law passed C Establishment of sans-culottes paramilitary forces D Conscription order www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters C 1793 August 23 4 revolutionary armies C Establishment of sans-culottes paramilitary forces 1 Law of 14 Frimaire A Law of Revolutionary Government passed; power becomes centralised on the Committee of Public Safety. C 1793 August 23 5 Levée en masse D Conscription order D 1793 September 29: E 1793 October 21: 2 Convention passes the General Maximum, 3 An anti-clerical law passed, B fixing the prices of many goods and services. E priests and supporters liable to death on sight. www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters A 1793 September 9 B 1793 December 4 KI3: Radical Revolution 1793-1799. www.pastmatters.org Why was Robespierre overthrown? AS History Matters Monday, 13 April 2015 Monday, 13 April 2015 • www.pastmatters.org • AS History Matters Session Aims Recall key events from Robespierre’s life. Explain why Robespierre lost support in the summer of 1794. Events of 1789. www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters WHO? WHY? WHERE? WHEN? WHAT? www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters A print portraying the execution of Robespierre, Saint-Just, Cuthon, and several other members of the Committee of Public Safety on 10 Thermidor Year II (28 July 1794), which brought to an end the Great Terror and ushered in a period of reaction known as Thermidor--a term that since has been used to describe a period of conservative reaction following a radical phase of a revolution. On the CPS & CGS Why did tensions emerge within and between the CPS and CGS? The Sans-Culottes Why was Robespierre’s losing support among the sans-culottes? www.pastmatters.org Robespierre Loses support AS History Matters Among the Catholics How did people react to Robespierre’s new religion? • You have 15 minutes!! www.pastmatters.org • Use the information from your diagram to write an answer to this question. AS History Matters Explain why Robespierre lost support in the summer of 1794. (12marks) www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters L1: Answers will contain either some descriptive material which is only loosely linked to the focus of the question or some explicit comment with little, if any, appropriate support. Answers are likely to be generalised and assertive. The response will be limited in development and skills of written communication will be weak. 1-2 L2: Answers will demonstrate some knowledge and understanding of the demands of the question. They will either be almost entirely descriptive with few explicit links to the question or they will provide some explanations backed by evidence that is limited in range and/or depth. Answers will be coherent but weakly expressed and/or poorly structured. 3-6 L3: Answers will demonstrate good understanding of the demands of the question providing relevant explanations backed by appropriately selected information, although this may not be full or comprehensive. Answers will, for the most part, be clearly expressed and show some organisation in the presentation of material. 7-9 L4: Answers will be well-focused, identifying a range of specific explanations, backed by precise evidence and demonstrating good understanding of the connections and links between events/issues. Answers will, for the most part, be well-written and organised. 10-12 www.pastmatters.org • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WGjJOz5l Dsw&feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VEhUuYF pMac AS History Matters The Terror and the Overthrow of Robespierre www.pastmatters.org Robespierre was overthrown because……. AS History Matters Complete the following www.pastmatters.org AS History Matters 18th of June Abolition of special privileges Constitution of 1791 Declaration of the Rights of Man Equality before the law (for men) Many nobles left France and became known as émigrés Reforms in local government Taxes levied based on the ability to pay www.pastmatters.org Abolishment of guilds and labor unions AS History Matters Changes under the National Assembly www.pastmatters.org What four governments ruled after the Tennis Court Oath? AS History Matters Four Phases (Periods) of the French Revolution Four Phases (Periods) of the French Revolution Convention (1792-1795) Directory (1795-1799) www.pastmatters.org Legislative Assembly (1791-1792) AS History Matters National Assembly (1789-1791) • • • • • • • • • • • • • • www.pastmatters.org • • • • • • • • • • National Convention September 20:National Convention. French Army stops advance of Coalition troops at Valmy. September 21: Abolition of royalty and proclamation of the First French Republic. September 22: First day of the French Revolutionary Calendar (N.B.: calendar introduced in 1793). December 3: Louis XVI brought to trial, appears before the National Convention (11 & 23 December). Robespierre argues that "Louis must die, so that the country may live". December 4 : A Belgian delegation is received at the National Convention to claim independence from Belgium. 1793 January 21: Citizen Louis Capet guillotined, formerly known as Louis XVI. March 7: Outbreak of rebellion against the Revolution: War in the Vendée. March 11: Revolutionary Tribunal established in Paris. April 6: Committee of Public Safety established. May 30: A revolt breaks out in Lyon. June 2: Arrest of Girondist deputies to National Convention by Jacobins. June 10: Jacobins gain control of the Committee of Public Safety. June 24: Ratification of new Constitution by National Convention, but not yet proclaimed. Slavery is abolished in France until 1802 (Rise of Napoleon Bonaparte). July 13: Assassination of Jean-Paul Marat by Charlotte Corday. July 27: Robespierre elected to Committee of Public Safety. July 28: Convention proscribes 21 Girondist deputies as enemies of France. August 23: Levée en masse (conscription) order. September 5: Start of Reign of Terror. September 9: Establishment of sans-culottes paramilitary forces - revolutionary armies. September 17: Law of Suspects passed. September 22: A new calendar is introduced, denoting September 22, 1792 as being the start of year I. September 29: Convention passes the General Maximum, fixing the prices of many goods and services. October 10: 1793 Constitution put on hold; decree that the government must be "revolutionary until the peace". October 16: Marie Antoinette guillotined. October 21: An anti-clerical law passed, priests and supporters liable to death on sight. October 24: Trial of the 21 Girondist deputies by the Revolutionary Tribunal. October 31: The 21 Girondist deputies guillotined. AS History Matters • • • • •