Chapter11
advertisement

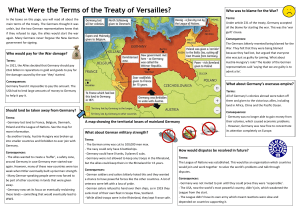
Chapter 11 Section 4 Making the Peace The Costs of War • Loss of human life and materials – 1918 “pandemic” of influenza killed 20 million • Financial Toll – Rebuilding period, resentment among citizens – Allies demanded “reparations” • Political Turmoil – Governments collapsed, “radicals” emerged – Radicals pushed bolshevism (later Communism) – Colonial troops saw weakness and hoped for independence The Paris Peace Conference • Allies met to discuss the future of Europe • Conflicting Goals “The Big Three” – Wilson urged “peace without victory” – British prime minister David Lloyd George wanted money to build a post-war Britain “fit for heroes” – French leader Georges Clemenceau wanted a weak Germany that wouldn’t threaten France • Problems with Peace – Other leaders had other demands and interests – Many demanded land promised to them and their own national states (Italy, people governed by Russia, Austri-Hungary, or the Ottoman Empire) – Wilson wanted a League of Nations based on “collective security” The Treaty of Versailles • June 1919: Allies demanded that Germany sign the treaty – Germany was to take all the blame for the war – Germany had to pay huge reparations ($30 billion then, $2.7 trillion today) – Limited Germany military, returned Alsace and Lorraine to France, removed hundreds of miles of German territory in the east and west, stripped Germany of its colonies – Compelled many Germans to leave Russia, Poland, AlsaceLorraine, and German colonies – Germans had no choice but to sign – led to resentment that would last for 20 years and eventually help cause another world war Outcome of the Peace Settlements • Other treaties were signed with the other Central Powers, leaving similar dissatisfaction • Self-Determination in Eastern Europe – New nations emerged where German, Austrian, and Russian Empires once ruled – Poland, Baltic states of Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia all gained independence – New Republics of Czechoslovakia, Austria, and Hungary in the Hapsbrg heartland – In the Balkans, Yugoslavia was created and dominated by Serbia Outcome of the Peace Settlements • The Mandate System – European colonies in Africa and Asia hoped for similar independence and an end to imperial rule – Instead, through “mandates” they were divided among the Allies (Britain, France, Japan, Australia) – Overlapping claims threatened peace settlements – It was supposed to be temporary, but the colonies felt betrayed • The League of Nations offers Hope – More than 40 nations joined, hoping for negotiations instead of future wars – Not the US. Senate wanted to prevent the US from being forced into war. This weakened the power of the League – The League only had influence over its members and could not prevent war – Still, a step in the right direction