A Second Global Conflict and the End of the European World Order
advertisement

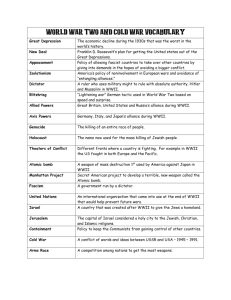
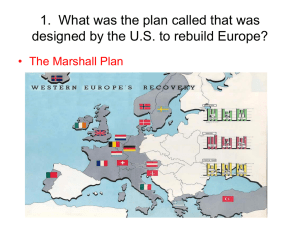
A Second Global Conflict and the End of the European World Order Ryan Harris, Isabella Martinez-Lugo, Cole Hoffer Key Concepts - 6.2 Global Conflicts and Their Consequences III. Political changes accompanied by demographic/social consequences C. ethnic violence and displacement of peoples IV. Military conflicts occurred on an unprecedented global scale A.ideologies used for purpose of waging war B.sources of global conflict Causes of WWII • Social, economic, & political unrest o • social tensions => brought on by 1930s Great Depression Japan o o gradual militarization up until 1930s moderate political parties Causes of WWII • China o o o 1920s => nationalistic forces Guomindang party General Chiang Kai-Shek unified China Japanese concern worried Chinese would resist Jap. control in Manchuria Causes of WWII • Japan o o • seized Manchuria => Manchukuo civ. politicians reluctance of resistance Germany o o change of regimes => more abrupt Weimar Era => experienced civil war, hyperinflation => social discontent, political turmoil Causes of WWII • Nationalist Social Party (Nazi) o o gained votes and parliamentary seats promised: work, political stability o Hitler => throwback communist power o remilitarization program need to destroy Soviet Empire systematic dismantling of political system Causes of WWII • Italy o Mussolini inspiration o Hitler Ethiopia bombing fascists => cruel use of weaponry Germany+Italy=intervened in Spanish civil war • Western Powers o refused to fight Unchecked Aggression • Totalitarian states => unchecked aggression o • • • WWII - Sept. 1st, 1939 lack of outside intervention Winston Churchill => inevitability of war Japanese - first move o o invasion of Manchuria draconian reprisals Unchecked Aggression • • Tripartite pact - not signed until 1940 Hitler o nonaggression pact with Stalin - 1939 invasion of Poland days after Britain & France joined war World War II: 1939-1941 Europe • • • Nazi Blitzkrieg France taken in 1940 Britain holds out o Battle of Britain • • Mid 1941: Germany controls most of Europe and Mediterranean After Britain → Nazi’s turn south and east Japan • • Engaged in major war with China Attacks Pearl Harbor (1941) o Allows for further expansion into Southeast Asia o US enters war WWII: 1941-1945 Europe • • Germany invades Soviet Russia Russians able to stop German advance o Stalingrad • o Late 1944: Red Armies capture Eastern Europe US and allies invade from West o Normandy • o Battle of the Bulge Early 1945: Allied armies enter Western Germany WWII: 1941-1945 Japan • • • • • Army was highly vulnerable → too spread out Tried to colonize Asia o Met with resistance Naval Battles o Battle of Coral Sea & Midway Island 1944: US within striking distance Atomic Bomb o Hiroshima and Nagasaki o Japan Surrenders Nazi War Against the Jews • Wannsee Conference (1942) o “Final Solution” o Destruction of Jews becomes policy of the Reich • Genocide increased as Nazi’s started losing war o Vital resources used for concentration camps o Those fit were forced to work o Those unfit were killed • 12 million killed → Holocaust o 6 million Jews o Most severe of the 20th C genocides After the War • • • • Allies met to create framework for lasting peace o United Nations (UN) o International diplomacy/assistance expand beyond Western Powers The beginning of the Cold War o Started by debates on post war settlement o How much territory should Soviets gain? Tehran Conference o Allies invade France instead of Mediterranean o Soviets could take Eastern Europe (Balkan Region) Yalta Conference o Split Germany into 4 zones After the War • • Conference of Potsdam o Soviets gained Poland o Treaties with Axis powers Results o • • Japan was occupied by US Stripped of wartime gains Korea split o Problems with regaining colonial regimes o Boundaries of Soviet Union moved West Stage set for two great movements Decolonization & Confrontation between US and Soviet Union Decolonization ● Defeat of EU colonies ● Harsh regimes and strong demands of Japanese conquerors => desire for self-rule in SE Asia ● “Total war” in EU => less desire for colonies ● American and Soviet govt's = anti-colonization ○ Atlantic Charter of 1941 (US-GB) ● Result: peaceful gain of independency of many colonies Independence in India ● Ruled by Britain ● 1942: Sir Stafford Cripps fails ○ Quit India Movement ● British respond harshly ● Communist party and Muslim League supported GB ○ Muhammad Ali Jinnah => Pakistan ● 1943-4: inflation + famine = social unrest ● 1945: Labour party Independence in SE Asia ● 1947: Partition of Indian subcontinent ● British give up power an leave ● Religious warring still occurs ● Burma and Ceylon ● Ruled by British ● After India, gained independence peacefully Independence in the Philippines ● Ruled by US ● Transfer of power to Filipinos before WWII ● Loyalty to US during war and resistance to Japanese occupation => easy independence with end of war Last to Gain Independence in Asia ● French unwilling to give up Indochina ○ Pushed out by communist revolution ● Dutch unwilling to give up Indonesia ○ ○ Tried to break up newly formed nation 1949: gave up and left Liberation of Non-Settler Africa ● African vets of WWII => new nationalists ● Wartime needs => factories => urban workforce ○ Those unable to find work => disgruntled => become revolutionary ● Kwame Nkrumah - British Gold Coast => Ghana ○ Convention People’s Party (CCP) ○ 1957: recognized as Prime Minister ○ Brits Leave Independence in Settler Colonies ● High EU population => don’t want to leave ● No peaceful agreements ● Violent revolutions (guerrilla warfare) ○ ○ Jomo Kenyatta in Kenya National Liberation Front in Algeria White Supremacy in South Africa ● Afrikaners couldn’t go to EU ● Afrikaner National Party (30s and 40s) gained total white control ● Apartheid - racial segregation system (1948) Conflicting Nationalisms in Mid-East ● Arabs vs. Israelis vs. Palestinians ● Holocaust => Israel (Jewish homeland) ● Piece of Palestine => Israel ○ Palestinians not happy ● Rise of Israel => <100,000 Arab and Palestinian refugees Work Cited • "EUROPE AFTER THE FIRST WORLD WAR: Territorial CHANGE AND POLITICAL DEVELOPMENT (1919 - 1923 Gg.)." Ukr Map. Ukrainian Map, 2013. Web. 14 Apr. 2014. • "Sykes, Charles Henry (1882-1942)." Political Cartoon - Comic Memorabilia. Political Cartoon Society, 2014. Web. 14 Apr. 2014. • http://www.alternatehistory.com/foralltime/FaTL-postWWII.html • "General Chiang Kai-Shek - Stimulated Boredom." Stimulated Boredom. Stimulated Boredom, n.d. Web. 17 Apr. 2014. • "Britain’s WW2 Cabinet in 1939." WW2 Memories & History. WordPress, 23 July 2011. Web. 17 Apr. 2014. • http://www.pearlharboroahu.com/images/Attack-pearl-harbor.jpg • http://gausschildren.org/genwiki/images/1/1d/WWII_Europe_1941-1942_Map_EN.png • http://www.conjay.com/Japan%20Naval.gif • http://static.guim.co.uk/sys-images/Guardian/Pix/pictures/2012/4/19/1334794231944/Holocaust-survivors-Israe-008.jpg • http://www.jewishomaha.org/jewish-press/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/logo.jpg • http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/af/Potsdam_conference_1945-8.jpg