The West Between the Wars
advertisement

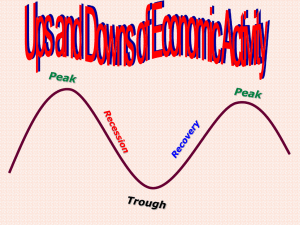
The West Between the Wars Chapter 17 Uneasy Peace, Uncertain Security The Treaty of Versailles created new boundaries, states & occupied territories; however many were unhappy. The League of Nations was weak. France demanded reparations from Germany; when unable to pay, France occupied the Ruhr Valley. The Dawes Plan: Reduced reparations Coordinated Germany’s payments with ability to pay Granted a $200 million loan (Am. Investment) Treaty of Locarno Guaranteed Germany’s borders with France and Belgium Germany joins League of Nations (1926) Kellogg-Briand Pact 63 Nations “renounce war” No reinforcement Causes of the Great Depression # 3 in the Section Review Great Depression The Great Depression Causes: 1. 2. 3. Slump in the economies of many nations International financial crisis U.S. Stock Market Crash Responses: Unemployed and homeless filled the streets. Govt. interference in the economy Renewed interest in Marxist doctrines Worksheet questions Answer for each country (include vocab) How did the Great Depression affect the country? What did the government do in order to help boost the economy? What effect did these have on the country? Were the changes a success? How so? Germany Germany experienced major inflation which caused serious social problems. A German democratic state was created known as the Weimar Republic. The country was not able to pull themselves out of the Great Depression for a long time. The Germans were severely affected by unemployment during the depression and caused the rise of extremist parties. Great Britain Declines in the production industries led to a rise of unemployment. The Labour Party failed to solve the economic problems. Fell from power in 1931 A new Conservative led Gov. brought Britain out of the worst stages of the Depression by using traditional policies of balanced budgets and protective tariffs. Keynes- advocated deficit spending (going into debt). France France had a balanced economy Leftist parties formed the Popular Front government. Created the French New Deal which gave workers the right to collective bargaining – the right of unions to negotiate with employers over wages and hours France pulled out of the depression rather quickly due to a more balanced economy and the French New Deal United States The U.S. production industry fell by half Roosevelt wanted a policy of active government intervention in the economy, that was called The New Deal. The New Deal created the U.S. welfare and social security system, including pensions and unemployment insurance. Although the New Deal didn’t solve the unemployment problem, eventually WW II would because of the need for weapons and supplies. Section 2 RISE OF DICTATORS The Political Spectrum The Political Spectrum Rise of Dictators Totalitarian state – a government that aims to control political, social, intellectual, and cultural lives of citizens. Wanted to conquer the minds and hearts of their subjects Propaganda Modern communication Fascist Beliefs & Policies Fascism - a political movement that stresses extreme loyalty to the state and its leader. Support for Fascists comes from aristocrats, industrialists, veterans, and the lower middle class. Fascism similarities to Communism 1. 2. 3. Ruled by dictator & one party system Both denied individual rights State is supreme Difference is that Fascists didn’t want a classless society. Strict laws against those criticizing the regime Made a deal with the Catholic Church to gain support Secret police, OVRA, had unrestricted authority Methods used by Mussolini Promoted the main ideals of Fascism through organizations Outlawed all other political parties Controlled mass media Mussolini in Power The perfect Italian – fit, disciplined, war loving, held traditional values. Family is the pillar of the state Catholic Church state religion Still unable to truly control every aspect Large gap between ideals and practices A New Era in the Soviet Union Lenin abandoned war communism in favor of his New Economic Policy (NEP). allowed private ownership of small businesses Sell produce openly Heavy industry and banking gov. run the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) Lenin dies 1924 – no successor named Politburo – the Communist Party’s main policy making body. Leon Trotsky Commissar of War Called for rapid industrialization Spread communism abroad ( world-wide revolution Joseph Stalin Party general secretary Appointed officials (received their support) Remove Bolsheviks from power end NEP Economic Costs Stalin shifts from the NEP with his Five-Year Plans. Transform the USSR into an industrial country Maximum production of military equipment and capital goods Social Costs not much money spent on housing creation of slums Private farms were eliminated under collectivization – a system in which private farms were eliminated and the government owned all of the land peasants worked on. Strict laws limited movements Political Costs Strengthened hold over party. Those who resisted were sent to labor camps in Siberia. Old Bolsheviks removed or put to death Promoted women’s rights Divorce easier Women work Stalin Mussolini Eastern Europe fall to Dictators In Hungary & Poland, the new democratic governments formed after WWI fall to dictators. By 1935, Czechoslovakia is the only democracy in eastern Europe. they see authoritarian rule as the only way to prevent instability. Spain Civil war in Spain leads to a Fascist dictatorship. Francisco Franco — a young general who rose quickly as dictator of Spain. Supported by Italy & Germany The Soviet Union supported the Republican government Authoritarian more than totalitarian The ancient Basque village of Guernica was destroyed on April 26, 1937 by a German air force more interested in practicing than in any military aims. Wave after wave of planes dropped heavy bombs as well as incendiary devices on the defenseless town. Fighter pilots strafed civilians attempting to escape. Hundreds of Guernica citizens lost their lives during the raid. Up to one-third of the town's 5,000 residents were killed. T H E N This image shows the center of Guernica shortly after the raid. Some three-quarters of all buildings in the town were damaged with the center almost completely destroyed. N O W Guernica by Pablo Picasso Section 3 RISE OF HITLER AND NAZI PARTY Hitler’s Germany Hitler wanted to create another Roman Empire Create an Aryan race that would dominate Europe Third Reich Holy Roman Empire Germany empire after unification Hitler’s Germany Use variety to maintain a totalitarian state Schutzstaffeln (SS) – police force used to maintain order Directed by Heinrich Himmler 2 principles – terror and ideology Chief goal was to further the Aryan race. Economic policies Put people back to work to reduce unemployment propaganda press, radio, literature, painting and film Rallies (Nuremberg) Youth programs Women’s roles Traditional role of wife and mother of the Aryan race Jobs reflected Nazi ideals for women Anti-Semitic Policies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Kristallnacht “night of broken glass”, November 9, 1938 Destruction against Jewish synagogues, businesses, and people clean up everything from Kristallnacht Many encouraged to leave the country Kristallnacht