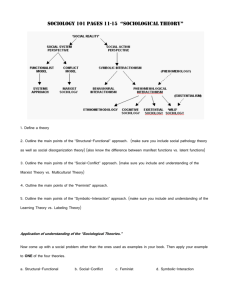
Introduction to Sociology 110 Major Theoretical Approaches in Sociology Structural-Functional Approach (Emile Durkheim; Herbert spencer; Robert Merton) What is the level of Macro-level analysis? What image of Society is a system of society does the interrelated parts that is approach have? relatively stable. Each part works to keep society operating in an orderly way. What core questions does the approach ask? Members generally agree about what is morally right and morally wrong. How is society held together? Name: Student ID: Social-Conflict (Karl Marx), Gender-Conflict (Harriet Marineau), and Race-Conflict Approaches (W.E.B. Du Bois) Symbolic-Interaction Approach (Max Weber; George Herbert Mead; Erving Goffman) Macro-level Micro-level Society is a system of social inequality based on class, gender (gender-conflict theory and feminism, and race (race-conflict theory). Society is an ongoing process. Society operates to benefit some categories of people and harm others. People interact in countless settings using symbolic communications. The reality people experience is variable and changing. Social inequality causes conflict that leads to social change. How does society divide a population? How do people experience society? What are the major parts of society? How do advantaged people protect their privileges? How do people shape the reality they experience? How are these parts linked? How do disadvantaged people challenge the system seeking change? How do behaviour and meaning change from person to person and from one situation to another? What does each part do to help society work? What are the drawbacks or critiques of the approach? (Macionis, Jansson , Benoit, & Burkowicz, 2017, p. 20) Introduction to Sociology 110 Name: Student ID: Structural-Functional Approach Q: What are the manifest and latent functions of education in society? Manifest functions – the recognized and intended consequences of any social pattern Latent functions – the unrecognized and unintended consequences of any social pattern Social-Conflict Approach Q: How does the institution of education reproduce (class, gender, sexual orientation, or race) inequality? Symbolic-Interaction Approach Q: How do interactions in the classroom shape students’ social reality? How do you experience education? How is your experience different from how another person (different socio-economic class, gender, race, nationality) might experience education?