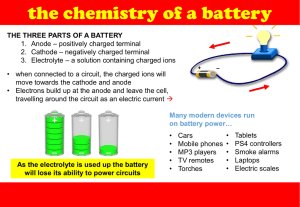
Batteries are among the most common everyday applications of chemistry. Smartphones, watches and clocks, MP3 players, toys, calculators, computers, smoke detectors, and automobiles are among the many common products that rely on battery power. Lead-acid storage batteries are most frequently used to start cars. The most common configuration within such a battery is a series of six cells, each with a potential of 2 volts, for a total battery potential of 12 volts. The name lead battery is derived from both the anode, which is a collection of lead (Pb) plates, and the cathode, lead(IV) oxide (𝑃𝑏𝑂)plates. 1. The oxidation reaction at the anode is: Anode: 𝑃𝑏(𝑠) + 𝑆𝑂42+ (𝑎𝑞) → 𝑃𝑏𝑆𝑂4 (𝑠) + 2 𝑒 − a. Write the reduction reaction occurring at the cathode between 𝑃𝑏𝑂/𝑃𝑏𝑆𝑂4 Cathode: (2 marks) b. Write the full balance redox equation Overall: (2 marks) 2. Another common battery is the button batteries used to power watches, calculators, and cameras. The overall reaction for one type of button batteries is: 𝑍𝑛(𝑠) + 2𝐻𝑔𝑂(𝑠) ⟶ 2𝐻𝑔(𝑙) + 𝑍𝑛𝑂(𝑠) Determine which species is the oxidant and which is the reductant in this case. Explain how you determined this. (2 marks) 3. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in each of the following substances? a. N2 d. NaNO3 b. NO2 c. NH3