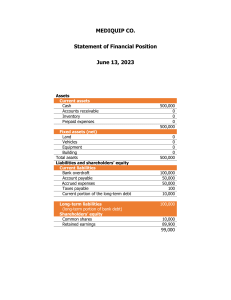
Accounting and Financial Management Dr S. Velavan, B.E., M.B.A., PhD., DoMS, NIT Trichy Book references Financial Accounting: Financial Accounting: A Managerial Perspective (6th Edition), by R Narayanaswamy (RNS) An Introduction to Accountancy (13th Edition), by SN Maheshwari, Suneel K Maheswari, Sharad K Maheshwari (SNM) Cost and Management Accounting: Managerial Accounting, 16th Edition, by Ray H. Garrison, Eric W. Noreen, Peter C. Brewer (GNB) Learning Objectives Stakeholders in a Business Accounting definition Objectives of the course Difference between Financial Accounting and Management Accounting Basic Accounting Terms in Profit & Loss statement and Balance Sheet Stakeholders Customers Vendors Suppliers of raw materials Other vendors Competitors New entrants Capital providers Own, Family, Friends Lenders Capital Market Government Society Accounting Input Process Business Transactions (monetary value) Identifying Recording Classifying Summarizing Analyzing & Interpreting Communicating Output Information to Users Objectives of the course Financial Accounting Process of creation of financial statements Understanding the terms and concepts underlying published financial statements Begin to read, analyze, and evaluate published financial statements Management Accounting Explain the concept of management accounting in making financial decisions Understand different costing methods Financial Accounting Management Accounting Provide information about the performance of the company as a whole in the form • Profit and Loss Statement • Balance Sheet Statement • Cashflow Statement Provide information about the individual departments within the company For use by the external parties like shareholders, creditors, banks, investors, and Government For internal use by Management Record of past events Data of the present, and future Mostly – Yearly, sometimes half-yearly Mostly - monthly More precise Less precise Basic Accounting Terms: Profit & Loss Statement Revenue Operating Income (Income from the core business operations) Revenue from Sales of Goods, performance of Services for a customer or a client Other operating Income Non-Operating Income (Income from non-core business operations) Interest Income Dividend Income Gain on sale of assets Basic Accounting Terms: Profit & Loss Statement Expenses Operating Expenses (Cost of services and things used for generating revenue) Cost of raw materials consumed Purchase of Stock-In-Trade Employee Benefit Expenses Rent, Electricity, Power, Fuel, Transportation, Repairs to Building, Machinery Depreciation expenses Non-Operating Expenses Finance cost (Interest expenses) Payment to auditors Consultancy charges paid Tax paid Basic Accounting Terms: Balance Sheet Equity: It is the owners’ equity in the business. It is a residual claim against the assets of the business after the total liabilities are deducted. Also known as Net-worth. Equity Share capital (Amount contributed by the shareholders towards a company’s capital) Reserves and Surplus Share premium (is the excess of shareholders’ contribution over share capital) Retained Earnings (Profit kept in the business after paying dividends) Basic Accounting Terms: Balance Sheet Liabilities (present obligation of the entity, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of the entity's resources. Obligation must be reliably measurable) Non-current liabilities (more than one year) Bank borrowings Other long-term liabilities Current liabilities (less than one year) Bank borrowings Trade payables (Amount payable to the vendors) Salary payable Other expense payable (Rent, insurance, etc) Basic Accounting Terms: Balance Sheet Assets (A resource that gives benefits to its owners; Tangible or intangible rights owned by an enterprise and carrying probable future benefits) Non-current assets Land Building Plant & Machinery Intangible Assets (Patents, Trademarks, etc) Current assets Cash & Bank Balances Inventory Trade receivables (Amount to be received from the customers) Office supplies