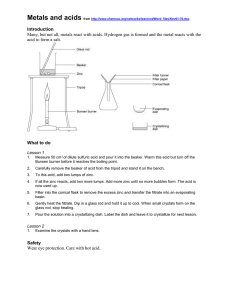
Grade 9 Term 3 Formative Assessment -2 Chemistry Total 20 Marks. 1. State whether the following changes are physical or chemical: Time : 30 minutes [2] [2] 3. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes to produce water and oxygen. The equation is: [3] a) melting of ice - …………………………. b) burning of magnesium- …………………………. c) evaporation of ethanol - …………………………. d) dissolving of sugar in water - …………………………. 2. State whether the following changes are exothermic or endothermic: a) condensation of steam to water- …………………………. b) burning of magnesium- …………………………. c) addition of concentrated sulfuric acid to water- …………………………. d) evaporation of a volatile liquid.- …………………………. 2H2O2,(g) - 2H2O(g) + 02(g) Using the following values, calculate the heat change for the reaction and say whether it is exothermic or endothermic. Bond energies: O-O= 144 kJ/mol O-H = 464 kJ/mol O=O = 498 kJ/mol ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Draw a reaction pathway diagram for the following reaction, which is exothermic. [2] [1] Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) 5. What is a catalyst? ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6. What is an enzyme? [1] ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 7. Which solid catalyst will speed up the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide? [1] ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 8. In terms of the collision theory, explain why the rate of a reaction increases with: [3] a) an increase in temperature ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… b) an increase in the surface area of a solid reactant ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c) an increased concentration of a reacting solution. ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9. Zinc reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to form hydrogen. Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 If lumps of zinc are used the reaction is quite slow, but small pieces of zinc react more rapidly. a) Explain why smaller pieces of zinc react more rapidly. Use ideas about particles and collisions. [2] ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… b) If the acid is heated, the reaction takes place more rapidly. Explain why the reaction speeds up when the acid is heated. Use ideas about collisions and energy. [2] ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c) When small pieces of copper metal are added, the fizzing becomes much faster. Copper does not react with dilute sulfuric acid and is still there when effervescence stops. Explain these observations [1] ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… End **************