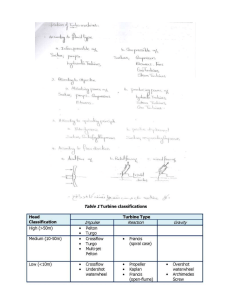
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311562395 Design and Construction of a Mini-Hydrodynamic generator Conference Paper · December 2016 CITATION READS 1 10,042 6 authors, including: Md.Sourove Akther Momin Md. Sahid Hassan Walton Hi-tech Industries Ltd. Andong National University 11 PUBLICATIONS 28 CITATIONS 2 PUBLICATIONS 7 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE Mihir Dutta Andong National University 7 PUBLICATIONS 3 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE All content following this page was uploaded by Mihir Dutta on 19 February 2019. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. SEE PROFILE International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Energy Engineering 2016 26-27 December, 2016, Khulna, BANGLADESH ICIMIE-MC-160356 Design and Construction of a Mini-Hydrodynamic generator Md. Golam Kader1,Md. Sourove Akther Momin 2,*, Mihir Dutta3 ,Md.Sahid Hassan4,Ariful Hossen5 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Khulna University of Engineering & Technology, Khulna-9203, BANGLADESH ABSTRACT In the field of power generation, hydro electrical power plant has a great contribution in the world. It is popular due to having efficient and reliable form of clean source of renewable energy. It can be an excellent method of harnessing renewable energy from small rivers and streams. The mini-hydro project designed to be a run -of-river type, because it requires very little or no reservoir in order to power the turbine. The water will run straight through the turbine and back into the river or stream to use it for the other purposes. This has a minimal environmental impact on the local ecosystem. In this project, the basic concept of hydro power generation is shown. A proto type turbine was designed by Solid Works software. The turbine power and speed were directly proportional with the site head, but there were specific points for maximum turbine power and speed with the variation of the site water flow rate. Turbine is rotated by using the thrust of water of velocity of water. Two dynamo is attached with turbine shaft and so rotation of turbine is the result in rotation of both dynamo. This concept highly increase the overall efficiency. Power generation by this mini hydro power generator is calculated. To the sum up, it can be said that if this concept will be applied in the Hydro power plant, the output of power generation will be increase. Keywords: Hydro electric power plant; Renewable Energy; Solid Works; Generator 1. Introduction Hydropower is an extremely flexible technology for power generation. Hydro reservoirs provide built-in energy storage, and the fast response time of hydropower enables it to be used to optimize electricity production across grids, meeting sudden fluctuations in demands. However, large scale hydropower projects can be controversial because they affect water availability downstream, inundate valuable ecosystems and may require the relocations of populations[3]. Despite being a mature technology, in comparison with other renewable energy sources, hydropower has still a significant potential. New plants can be developed and old ones upgraded, especially in terms of increasing efficiency and electricity production as well as environmental performance. In particular, the development of low-head or very low-head small hydro plants holds much promise. The hydro-power plants can be classified as below l. Storage plant ( a) High head plants ( b) Low head plants ( c ) Medium head plants. 2. Run-of-river power plants ( a) With pond age ( b) Without poundage. 3. Pumped storage power Plants[1]. Hydro-electric power is a form of renewable energy resource, which comes from the flowing water. To generate electricity, water must be in motion. When the water is falling by the force of gravity, its potential energy converts into kinetic energy. This kinetic energy of the flowing water turns blades or vanes in a hydraulic turbines, the form of energy is changed to mechanical energy. The turbine turns the generator rotor which then * Corresponding author. Tel.: +88-01738373182 E-mail address: sur.sor269@gmail.com converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy [5]. 2. Overview of Hydro Electric Power Plant 2.1 Historical Background Humans have been harnessing water to perform work for thousands of years. The Greeks used water wheels for grinding wheat into flour more than 2,000 years ago. The evolution of the modern hydropower turbine began in the mid-1700s when a French hydraulic and military engineer, Bernard Forest de Bélidor wrote Architecture Hydraulique . In 1880[3], a dynamo driven by a water turbine was used to provide arc lighting– a technique where an electric spark in the air between two conductors produces a light – to a theatre and storefront in Grand Rapids, Michigan, and in 1881, a dynamo connected to a turbine in a flour mill provided street lighting at Niagara Falls, New York; both of which used direct current technology. The breakthrough of alternating current, the method used today, allowed power to be transmitted longer distances and ushered in the first U.S. commercial Fig.1 Ancient concept to generate electricity from water installation of an alternating current hydropower plant at the Redlands Power Plant in California in 1893[1]. The Redlands Power Plant utilized Pelton waterwheels driven by water taken from the nearby Mill Creek and a 3-phase generator which ensured consistent power delivery. The past century of hydropower has seen a number of hydroelectric advancements that have helped it become an integral part of the renewable energy mix in the United States. Find out more about the last 100 years of hydropower with this timeline [2]. 2.2 Hydroelectric Power generation o 675,000 MW of hydro-electricity o approximately 20% of the world’s electricity o accounting for about 88% of electricity from renewable sources. 2.2.1 o o o o o o Itapúa power plant Largest hydroelectric power plant in the world Located between Brazil and Paraguay. Can generate 12,600 MW of power. Height of the dam reaches 196 meter and the length 7.76 km. Lake created by the project spreads over 1,350 sq. km and contains 29 billion tons of water. Cost of the project stands at US$20 billion. 2.2.2 Hydroelectric power Plant in U.S.A Hydroelectric power stations in the United States are currently the largest producer of renewable power in the U.S. Hydroelectric power produced 66.8% of the total renewable power in the U.S. in 2008, and 6.4% of the total electricity[3]. 2.2.3 o o o o 2.2.4 o o o o 2.2.5 o o o o Hydropower prospects in Bangladesh Flat terrain - limited potential The rivers in the CHT hold such potentials. Kaptai on Karnafuli river generating 218 MW of power. Other potential rivers are Matamuhuri and Sangu. Tipaimukh dam Located on the Barak River in Manipur State of India Multi-purpose - electricity generation and flood control Electricity generation capacity - 1500 MW Risk of dam failure Impact on haor eco-system. Karnafuli Hydro Power Station 230 MW generation capacity Reservoir size is 777 sq. km Economic development Social disruption 2.3 Advantages of hydroelectric power generation o No fuel required. o Less supervising staff is required. o Cost of electricity is constant. o o o o o No ash & flue gas problem & does not pollute the atmosphere. The plant efficiency does not changes with age. It takes few minutes to run & synchronize the plant. Can easily work during high peak daily loads. These plants are used for flood control & irrigation purpose. 2.4 Hydropower prospects in the Himalayan countries Table -1 Tabular information about the prospects in the Himalayan countries of hydropower [3]. Country Installed Hydropow Hydropo Generation er wer Capacity Developed Potential (MW) (MW) (MW) Bangladesh 4,120 218 755 Bhutan 481 469 23,670/3 0,000 India 124,287 32,300 84,000/1 50,000 Nepal 684 627 43,000/8 3,000 2.5 Disadvantages of hydroelectric power generation o Disrupts the aquatic ecosystems. o Disruption in the surrounding areas. o Requires large areas. o Large scale human displacement. o Very high capital cost or investment. o High quality construction. o Site specific. 3. Constituents of Hydroelectric Power Station Water driven structures in a hydro electric control station incorporate dam ,spillways , head works, surge tank, penstock and extra works. 3.1 Dam A dam is a hindrance which stores water and makes water head. Dams are worked of concrete or stone masonry, earth or shake fill. This sort and game plans rely on the geography of the site. A masonry dam might be based on a contract canyon. An earth dam might be most appropriate for a wide valley. The kind of dam likewise relies on the establishment conditions, local material and transportations available, occurrence of earth tremors what's more, other hazards.at the vast majority of destinations more than one kind of dam is appropriate and the one which is most efficient is picked. 3.2 Spillways There are times in which the waterway surpasses the capacity limit of the supply. Such a circumstance emerges amid substantial precipitation in the catchment territory. To release the overflow water from the capacity supply into the stream on the down stream side of the dam spillways are utilized. Spillways are ICMIEE-MC-160356- 2 developed of solid wharfs on the top of the dam. Doors are given between these wharfs and surplus water is released over the peak of the dam by opening of these doors. 3.5 Penstocks Penstocks are opened or shut courses which convey water to the turbines. They are by and large made of strengthened cement or steel. Concrete penstocks are reasonable for low heads(<30m)as awesome weight causes fast crumbling of cement. The steel penstocks can be intended for any head, the thickness of penstock increments with the head or working weight, Different gadgets, for example, programmed butterfly valve, air valve and surge tank are accommodated the insurance of penstocks. Programmed butterfly valve stop water move through the penstock instantly when it raptures . Air valve keeps up the air weight inside within the penstock equivalent to the barometrical weight. At the point when water comes up short on a penstock quicker than it enters, a vacuum is made which may bring about the penstock to collapse. Under such situations, air valve opens and concedes air in the penstock to keep up inside pneumatic stress equivalent to the outside pneumatic stress. Fig 2. Hydroelectric dam cross-section diagram 3.3 Head Works The headwork’s comprises of the preoccupation structures at the leader of an admission. They by and large incorporate blasts and racks for occupying skimming debris, sluices for by-passing flotsam and jetsam and silt and valves for controlling the stream of water to the turbine. The stream of water into what's more, through headwork’s ought to be as smooth as conceivable to keep away from head loss and cavitation. For this purpose, it is important to keep away from sharp corners and sudden withdrawals or amplifications. 3.4 Surge Tank Open channels driving water to the turbine require no security. Notwithstanding, at the point when shut channels are used, protection ended up important to restrict the irregular weight in the conduit. For this reason, closed channels are dependably given a surge tank. A surge tank is a little store of tank(open at the top) in which water level ascents or tumbles to decrease weight swings in the channel. A surge tank is situated close to the start of the channel. At the point when the turbine is running at an unfaltering load, there are no surges in the stream of water through the conductor i.e. the amount of water streaming through the conductor is only adequate to meet the turbine necessities. However, when the heap on the turbine decreases, the senator shuts the doors of the turbine, reducing water supply to the turbine. The overabundance water at the lower end of the conductor surges back to the surge tank and expands the water level. In this manner the conductor is kept from bursting. On the other hand when the heap on the turbine builds, extra water is drawn from the surge tank to meet the expanded load prerequisites. Thus a surge tanks overcomes the strange weight in the conductor when load on the turbine falls and goes about as a repository amid increment of load on turbine. Fig 3. Hydraulic turbine 4. Theory: Here, we consider that the revolution per minute(N) of the turbine blade has to determine. When our output from turbine P is fixed. We know, Overall efficiency of turbine = mechanical efficiency × hydraulic efficiency × volumetric efficiency Or, Ƞ0=Ƞm× Ƞh× Ƞv (1) Here, Ƞv is the ration of the quantity of water actually striking the wade to the quantity of water supplied to the turbine. ICMIEE-MC-160356- 3 Ƞv = , (2) in this project a little amount of water will be used. So the value of will be very low. We can neglect it. So, Ƞv = 1, and hence, Ƞ0=Ƞm× Ƞh (3) Here, before striking the blade the velocity of water is V and after striking the blade velocity of water is u. We can measure the head H. Then we can write, V= (4) Cv is the coefficient of velocity for the water tap with its value ranging from 0.97 to 0.98 .We can consider this value is 0.98. After striking the blade, a radial velocity will create. So, u = , 4. Components The components of the system are as follows: o Dynamo o Shaft o Screw o Nut and bolt o Tin sheet o Wooden basement o LED light o Resistance o Diode 5. Design & Construction 5.1 Design of Turbine by Solid Works software The output of power plant greatly depends on the efficiency of turbine. Because the shaft of dynamo is directly coupling with the turbine shaft. As much as the turbine rotate, the rotation of dynamo produce more power which is the requirement. So, design of turbine is shown below. (5) where D is the diameter of the wheel, which is constant. Let us consider water will strike the blade at normal direction. So force exerted by the jet, F= (6) , where w is the specific weight of water and a is the cross section area of water tap from where water is discharged. So, output = F × u (7) , and Input = Ƞh = (8) = Fig.3. Solid Works design of Turbine blade. 5.2 Total arrangement of the system After designing the turbine, it is required to connect the turbine shaft with the dynamo shaft. And then the basement to hold the total system. The total system is shown below. (9) Again Ƞm= (10) , where k is the factor which is less then unity. As we consider Φ = 90 degree. Finally we get, Ƞ0 = , which is again equal to = × (11) (12) Fig.4 Total arrangement of the project. Here all frictional effect are neglected for the simplicity of calculation [4]. 5.3 Construction o Sheet cutting process ICMIEE-MC-160356- 4 o o o Drilling process Welding process Grinding process Sheet cutting: The blade of turbine was created by cutting of stainless steel which is corrosion resistive. Two aluminum sheet was cut to hold the dynamo. Drilling: The turbine wheel was drilled to make it light. It was done by drilling machining. Welding: The turbine blade was attached with the wheel by welding. The shaft of turbine was also connected by welding process. Finally the two dynamo was connected with the shaft of turbine Grinding: The irregular surface on turbine due to welding was finished by grinding process. It’s make it shiny and nice. 7.Conclusion In the field of technology electric power is must needed. Day by day the requirement of electric power increasing. Hence, without power generation the whole development process is impossible. From the data it is appeared that decrease the diameter of the jet the power and performance increase. It is very important system for power development. References: [1] “Power Plant Engineering”, by G.R Nagpal, fifth edition , [2] “An Introduction To Hydropower Concept And Planning”, Canyon Hydro Publication. [3] Published on the page of (U.S Department of energy publication). [4] “Hydraulics And Fluid Mechanics Including Hydraulic Machines”, by Dr. P.N Modi & Dr. S.M. Seth, new edition, [5] Celso Penche "Layman's guidebook on how to develop a small hydro site", Published by the European Small Hydropower Association (ESHA), Second edition, Belgium, June, 1998. 6. Result & Discussion Table 2 Table for experimental data Obser Cross Output Output vatio section of Voltage, Power, P n No. jet, d V (watt) (m) (Volt) Overall Turbine efficiency, Ƞ0 01 0.01 1.2 0.2 0.81% For observation no. 04 02 0.008 1.5 0.253 1.59% Water head H=17.4m, power P=0.568 watt 03 0.006 1.8 0.324 3.64% Area A= 04 0.004 2.5 0.568 14.38% Velocity V= m/s The design of turbine blade for hydroelectric power generator was done by solid works software. The efficiency of turbine is increase with the decrease of jet dia. Because it increase the rotation of wheel and corresponding electric power is also increase. The aim of project was to design and constriction a mini-hydro dynamic power generator. It was successfully done. While designing the whole process the historical background was studied. From where the concept of power generation was came from was understood. Similar process of power generation was also studied. A proto type turbine blade was designed. The turbine efficiency which was designed was calculated. The output power get from this hydro dynamic generator was calculated. It was observed that the overall efficiency of turbine is not good. The reason behind this that there use electric motor as a dynamo. Again the dynamo is very small to produce huge energy. So output power is little. But it was observed that with the increase of rotation of turbine the power production was also increased. The efficiency calculated is quite good. It was thought that if this concept is applied in the hydro power plant, it will be very efficient. Appendix =0.000012566 sq m =0.98 =18.1 Discharge Q =AV=0.00022745 cube m/s Efficiency Ƞ0 =14.38 % ICMIEE-MC-160356- 5 View publication stats