MOOSA KHAN
Page 105
Chapter
ACID, BASES AND
SALTS
Page 106
AcIDS
BASES
SALTS
and
,
·
CIDs
Old
when
definition
Acids
are
the
Aqueous
Acid
Solution
H
Ht
Non-metal
HCL
,
ions
,y6
↳
+
H
&
Hydrogen
I
-
Ch
H20
HCL
Nat CL-NaCh
+
N
Hydrogen for (Protons)
Atom
H
1
P
1
E
0
N
=
C
+
! H
=
any into water
is
1, V, 11
↓
E
substance
.
H - C + H2O
=
(water)
forms Agreous solu.
it
that
substances
in
Hydrochloric
P
Solutive
dissolved
Htions
give
Aqueous
=
1
=
O
=
0
Acids
Acids
are
Profoe Donors
(H +)
Hydrochloric
Acid
HCL
,
H20
HCL
0345 2494359
&
H
+
@chemwithmk
+
MOOSA KHAN
Page 107
C
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 108
Nitride
02-Nitric
Acid
H20
C (
CH NO
1H
>
HNOz
,
+
**
INO
NOs
N3=
Nitrate
NOz
;
Sulfate
+
;
504
;
PO4
Phosphate ;
-
2-
3-
Carbonat ;
CO32-
Hydroxide
OH-
;
Ammonium
NHyt
I
For
-Sulfuric Acid H2SO4
03
,
H2w
1 H2SO4
acid
2H
·
Phosphoric
+
-
1904
Aluminium Sulfate
③
A
Soy
>
-
ALz(504)
H2COs
,
1 H2 (03
os
.
2HT
-
Carbonic
04-
2
acid
2
+
+
s
↓
2Al3
-
1C03
#
+
50
,
HaPO4
,
+
DO
HCL
,
=
H
acid ;
HNOz
=
HNO3
Vos-Sulfuric
acid ;
H2SO4
=>
H2SO4
04 -Carbonic
acid ;
H2COs
=>
H2COs
H3PO4
=>
HyPO4
H3 PO4
-
·
3H
+
Mineral acids
-oi
Hydrochloric
02-Nitric
os
acid
-Phosphoric acid;
Organic Acids/Carboxylic
o
Ethanoic acid ;
0345 2494359
OR
H
>
H
+
+
+
(5
+
Noj
>
2HT + So?
>
2H
-
-
>
+
CO2
3H + +
PO
+
Acids
-
CH3COOH-
CHyCOzH
@chemwithmk
>
-
CH3COO
Ht
+
Ethanoate ion
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
.
1
02-Propanoic acid ;
CzHsCOoH
Propanoic
C2HSCOOH
C2Hscoo-
-°
-
+
+
Propanoate ion
acid.
Reversible
Reaction
Irreversible
H
Reaction
&
-
OF
ACIDS
01-
STRONG
ACIDS
Acids
that
LYPES
Aqueous solution
ionizes/dissociates completely
.
/
IOHCL
Eq
HCL
H
&
1
+
0 mo
>
-
ACIDS
02-WEAK
Acid
solution
.
10 mol
Eq
/
incompletely /partially
ionizes/dissociates
that
aqueous
unionized
CL-
+
I
Unionized
in
in
2
Zmol
1CHz COOH
CH3Coo-
+
molHt
#H
+
⑧ mo
=
10 erLHCL
10
S
CH
0345 2494359
+
moL
CHzCOOH
2HT
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 109
Page 110
BASES
Bases
to
o>
that
Substances
are
salt
produce
and
.
[IONIC
Dodium
Na
Oxide
Potassium
Oxida
Calcium
Oxida
Magnesium
Oxida
Jeun (11)
Oxid
+ 1
K
O
+
COMPOUND]
-
02-
=>
NazO
=>
KzO
Catt on =S Cao so e
-
Febt of
[Definition]]
TYPES
-
=>
=>
Bases
OF
BASES
WATER
group
other
FezOz
Acceptors
proton
are
I
L
All
acids
water
Metal Oxides
.
Bases
with
reacts
INSOLUBLE
WATER
SOLUBLE
metal Oxides
than
group (I) metal
Oxides
Eg. Mg6
,
Car ,
FezOs
->
All
group [S
Eg. NazO
Water
form
@chemwithmk
K2O
soluble
dissolve in
0345 2494359
,
/chemwithmk/
metal Oxides
.
Bases
water
Metal
to
Hydroxides
(Alkalis
/chemwithmk
AIKALIS
Alkalis
01-Alkalis
React
with
acids
02-Alkalis
are
Conic
Compounds
03-Alkalis
are
metal
Hydroxid
,
hydroxides
-
NazO
Bases
But
other
-
OH-1
NaOH
=
alkalis
Hav
>
H2G
->
-
Her
CaW
we
2+
Hed
&
G
>
-
-
K20
Mg
OH-
Nat
hydroxide
Magnesian hydroxide ; Mg
Bases
,
Insoluble
H26
Salt
produce
to
Of
Sodium
wate
acceptors
proton
are
MOOSA KHAN
Page 111
-
NaOH
KOH
X
X
&
MgLOH)2'
can
prepare
Reactions.
Mg(OH)2
Lalotle
by
Bases
d
↑ata Soluble
dissolve
ir
G
S
water
Resoluble
Alkalis
Haw
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 112
*
O >
-
Are
Ionic
L
Compounds
&
Cation <+ )
-
Metal Ions
·>
mmonium
-
ANION
·-
ion
NHyt
L-)
Nor metal
&
ion
Chloride ,
Bromide
Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfide
MgS
Lithium
Sulfate
From (11)
Carbonate
all
metal Oxicks
of
But
all
Metal
-
All
Jonic
0345 2494359
are
hydroxide
Compounds
Metal Oxides
92-
FezKUz)s
But
o>
,
LizS
o >
-
,
Soy2
No
,
Sulfide
Call
Br
,
Nitrate
Calcium Chloride
/ Molecular in
(Bases)
@chemwithmk
Bases
Not
Salts
alkalis
Not
Salts
are
Except
and
Metal
.
hydroxides Calkalis)
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
REACTIONS
ACIDS
OF
01
Acids
+
Metals
>
Salt
+
02
Acids
+
Bases
&
Salt
Hydroge gas (He)
+
Water
-
(H20)
(Metal Oxides)
03
Acids
-
Alkalis
+
04
Acids+
-
01-ACIDS
HCL
Metal
Carbonates
METALS
+
Na
+
H2O
-
+
+
Ha
+
Ha
CO2
1
I
Cation ( + )
Anive(-)
Metal
Acich
a
L
+
Nach
>
Nat c
d
-
Salt
Water
Salt
>
-
-
Salt
*
&
+
=>
-
2HCh
Salt
·
hydroxides)
(Metal
>
-
MOOSA KHAN
Page 113
+
2
H
=
>
-
*2
C =
H
=
+
C=
2
Na = 2
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
=
Ha
2
1
Na
0345 2494359
2
2 Nach
/chemwithmk
. .
Page 114
HE
Mg
+
Mgclz
>
Ha
+
falt
↓
Cation
ENON
Metal
acid
Mg
2t
x
L
-0
&
MgCl2
HCL
Ea
↳
+
-
H
=
c
=
My
1Mg
12
/
H
* 2
c
1
(g
=
125 04
,
1 Mgcz
·
+
2 Na
=
=
2
&
1
=
NazSO4
&
2
H
S
1
8
=
0 I
4
0
=
Na
=
=
+
H2
2
=
Na
1
IHz
2
H
=
+
1
4
Salt
2
↓
=
lon-metal
Metal
↓
Acid
NatD
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
so
Nas S04
/chemwithmk
2 PO4
+
Le
>
2ALPO4
+
MOOSA KHAN
Page 115
3 H2(g)
H
=
G
ALs(POy)s X
Salt
AL3(pop3 X
H3DOy
X
alDY
Anion
Cative
Pop-
AQPO4 X
-
L
c -)
c+)
acid
HL
Poy
.
⑭
Al
Al
-
-
,
(PO4)
,
ALPO4
02-ACIDS
BASES
+
&
SALT
NATER
+
Oxide s Sodium Chlorid
Hychochloric acid t
Nag2-
I
that
+
1)
Ic + 2)
2HCL
-
H 12
Na
0
2
=
=
=
+
Hao
2
1
0345 2494359
cl X 2
No X 2
0
=
1
@chemwithmk
-
c
3)
-
(
=
=
[c + 3)
#
H= 2
=
C
S2NaCL
Nazo
-
Nat c
/chemwithmk/
2)
/chemwithmk
1)
1
Page 116
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Sodium Oxide
+
+
NazO
>
2H
+
MgO
Mg2
Acid
+
H2O
I
Mg(NO3)a
Alkalis
+
MgCNO3)2
>
NO-
H2O
+
-
-
+
-
NazSOy
>
Na "So,
Socioen Sulfata > Hat
Salt
·
+
Wate
.
[Metal Hydroxides]
Sulfreic acid
+
Calcium
Lychoxide
Ca2 of
+
H2
4
>
+
E
-
(OH)2
&
Calcio
CaSOy
+
+
He
2H20
c So
Ca"90
1
,
Casly
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
HCL
2HNOz
H
=
NaOH
+
H
2
Mg(OH)2
+
=
2 = H
Nall
&
·
H2G
+
MgC)2
4
=
H
0 =2
3H2)
WH
=
+
8
0 =
8
Mg
1
Mg
1
=
FeCOH)3
3
H
&
+
-
FeCOH)
=>
Fe
Iron (III)
1
hydroxide
Inve (11)
hyckoxick
Metals
have
+
.
2+
two
-Zinc
02-Silver
0345 2494359
3H20
=
c
metals
=
WH 6
Feb
charges
+
3
=
=>
2
Fells
-
Fe(OH) 3
transition
4
O=
Fe3
In
=
1= 2
N= 2
0=6
2H20
+
@chemwithmk
,
S
fixed
+
Ag
+
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 117
Page 118
04-Acids
Metal
+
Salt +
>
-
H2O
CO2
+
Carbonate
HCL
Sodium Carbonate
+
atD
&
-
COs
,
NazCOs
2H21
NazCO3
+
92NaCl
-
1
H= 2
c=
2
C= 2
Nc
2
Na 2
=
2
.
=
c
CU
+
-
~
H
H20
+
=
=
1
c
1
0= 3
0= 3
N2
+
H2
>
Nz Hy
>
NHz
-
-
2H)
=
Mgl0s
+
Hydrochloric
+
MgCl2
-
Calcien
&
+
Salt
+
H20
H20
102
+
+ 102
Carbonate
acid
Climestons]
2-
Ca2 + COs
2HCL
+
0345 2494359
CaCOs
@chemwithmk
&
Call2
/chemwithmk/
+
H20
+
/chemwithmk
102
WH2SOy
H2SOy
+
+
0345 2494359
CaCOs
MgCOs
>
>
-
@chemwithmk
CaSOy
MgSoy
MOOSA KHAN
Page 119
+
H2O
+
CO2
+
Hew
+
CO2
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 120
Bases/Alkalis
React
that
Substances
with
acids
to
produceSalt
and water
def
New
"Bases/alkalis
proton
are
acceptors"
Bases
L
Soluble Bases
->
->
-
Also known
as
ALKALIS
into
form
metal
water
to
hydroxides
alkalis /Bases
.
NazO
Kz8
.
o>
Metal
o-
All
-
.
Group (1) metal Oxides
dissolve
Insoluble Bases
H20
other
Oxides
Nazo
,
Ca8
KOH
Ago
He &
&
Oxides
group
metal
[Base But Soluble)
Bases
FezOz
CaCOH)
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
2
/chemwithmk/
,
Mg(OH)2
/chemwithmk
Reactions
REACTION
NEUTRALIZATION
Of
Base
Acidh
+
Co
↳+
Bases
of
2HNO >
>
-
=
>
Salt
H20
+
Cu CNO3)2
+
·
Salt
H2o
>
Na2SOy
-
H2O
GO
e
02-
Alkalis
+
Acids
+
H2SOy
2 NaOH
Ammonium Salts
·_
Ammonium Chloride
-
NHyT CL => NHyCL
>
+
t2H2O
Salt
A
Ammoeirm
in
NHyt
02-Ammonium
i
CL-
SoB
92 NOT
Nitrate
,
NHy" NO3 => NH4NO3
Ammonia
.
NH3
03
-
Ammonium Sulfate
NHyt
0345 2494359
SO4,
->
MOOSA KHAN
Page 121
(NH4) S04
@chemwithmk
=
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 122
heat
01
Ammonium
Salt + Alkali
Salt
>
- >
Water
+
Ammoniaga
Sodiren Chlorick
+
H20 > NHz
+
heat
Ammonium Chlorida
NHYCL
Socivenhydroxick
+
NaOH
+
>
-
NaCL
&
H20
+
+
-
NH3
(alkali)
heat
-
2 NHyNOz + CaLOH)2
=>
CaCNOs)
&
(alkli)
Ca
2t
NO
+
2
2H20
+
INHz
1
3
heat
2NH4CL
+
CaO
Callz
-
H2O
+
+
2NH3
Base
(9)
-
Ammonium
-
Potassium
-
Potassiven + H20
Sulfate
Hydroxide
Sulfate
NHy"SO -
K "Of
k
(NH4) 2904
+
KOH
k
0345 2494359
=
1
@chemwithmk
7
+
So,
-
K2SO4
K
=
NHz
+
2H2O
+
INH3
+
L
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
.
Acids
Alkalis
NaOH
HCL
ALKALLS :n
Metal
01-
or-Jonic
03
Alkalis
Compounds
Ofives
NaOH
Strong
Of
+
+
Lof
ionizes
completely
in
Aqueous
NaOH
&
Solutive
Nat
+
OH-
kt
-
OH-
Batt
+
20H
.
KOH
>
-
>
-
ALKALIS
02-WEAK
ionizes/dissociates
that
Aqueous
OH-
t
Batt
&
BaCOH)2
in
.
+ 1
K
>
-
z
Solution
Alkalis
that
Alkalis
Alkali's
.
Nat
>
Ba(OH)
Eg
acceptors
Aqueous
in
-
KOH
01
protoe
are
hycoxick
Give
.
MOOSA KHAN
Page 123
Solution.
Ey.
0345 2494359
MgCOH)
@chemwithmk
2
incompletely /partially
Mg2
Reversible
/chemwithmk/
.
+
+
20ft
/chemwithmk
Page 124
A
His
Both
HCI
Hit
doe to
acidity is
Alkalis
alkalinity is doe
acidity
and
alkalinity
,
I
H
concentrated
with acich
&
order
e
:
It
-
,
is
we
a
measure
pH
2
=
-
0
Stronge acid
of
strength
pH
scale
to
of
solution.
>
-
concentrated
acidity
a
acidity and
measure
alkali
·
.
city
*
I
7
.
D
H
MgLOH)
with alkali
[
+
,
of
more
acidity
·
c
.
alkalinity
#
water
Or
the
Measure
alkalinity
and
PH
to
Off
to
NaOH, KOH, BaCOH)
,
H
more
Needs
HNOz H2SO4 CHzCOOH
,
.
14
-
OH
H
A
Neutral
H
=
+
0
<OH-
PH
OH
.
=
6
ge
-
0
weaker alkali
d
PH
=
6
.
0
acich
0345 2494359
Weaker
pH
@chemwithmk
=
13
.
0
stronger alkali
/chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
MOOSA KHAN
Page 125
INDICATORS
Indicators
whether
us
the
solution
is
acidic
alkaline
.
or
01
tell
-
Paper
Litmus
Acid
Alkali
&e
acids
Blue
Litmus
turns
Red
in
color
&e
alkalis
Red
Litmus
trees
Blue
in
color
OR
Liquid
Litenus
I
Acid
0345 2494359
.
@chemwithmk
,
!
Alkali
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 126
02-
THYMOLP THA LEIN
Acid
Alkali
>
=
>
=
Coloneless
Blue
-METHYL ORANGE
03
04
-
Acid
=>
Alkali
=>
Rech
yellow
PHENOLPTHALE IN
Acid
=>
Colorless
Alkali
=
Pink
0345 2494359
.
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
PH
MEASURING
Meter
PH
of
of
02-UNIVERSAL
INDICATOR
i
.
PH 2
=
-
PH
0
COLOUR
CHART
Ack)
few drops
solution
with
value
a
,
=
Solution
a
S
pH meter
,
-
L
PH
60
=
of universal
colon
of solutive
80
PH
130
in
a
=
indicator
is
compared
provided toread the
of pH against
specific colom
colour
0345 2494359
MOOSA KHAN
Page 127
chart
a
@chemwithmk
.
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 128
Indical
O
Universal
pH
Colour
Green
7 =>
=
.
Neutral
Salts
Compounds
Ionic
o-
All
compounds
metal oxides [Bases]
on
ionic
NaCl
MgClz
,
,
CaSO4
.
are
salts
and
metal
Cative
Nat
,
Mght, Fe3+, Al
+
Except
hydroxides [allalis]
BaSO4
,
Ammonium
So
Salts
- Ton
Salts
d
Anion
and
Cation
;
Cation
Ammonium
5
,
NHyt
92-Br
SO4
,
-
-
NOs
CL-8
2
&
-
-
2-
Soy Noj
I
Salts
Soluble
Water
&
Water
Insoluble
H20
H2O
Nall(s
,
>
NaCLgag ,
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
BaS04 (5
/
/chemwithmk/
B
>
BaSO4LS
,
/chemwithmk
Soluble
Water
H2O
&
Nacks
Mayor
<Laq
,
Nat
&
,
+
(ag)
cizag,
Agreous
state
when
Substance
is
dissolved
comes
in
Aqueous state
a
water
it
()
Gas
(ag)
into
States
solic)
(S)
0345 2494359
Liquid
MOOSA KHAN
Page 129
@chemwithmk
(g)
/chemwithmk/
Aqueous
(ag)
/chemwithmk
.
Page 130
GENERAL
SOLUBILITY RULES
Salt
Chloride
of
Eg. NaCl MgCl2
All
chloride
Salts
-Nitrate
NaNOs
All
03
Nitrates
NazSO4
All
NO
,
CuCL et
.
,
Ag
AgCL
Zu
+1
2+
PD212
ALCNOs)s
,
FeCNOzI2
,
FeCNOg)
,
,
Soluble
are
904-
MgSO4
Sulfate
,
CaSO4
Salts
Except
01
-
Us
.
0345 2494359
,
:
salt
,
or
Cullz
soluble
water
are
.
,
-Solfate
NHuCl,
,
Lead (11) chloride
-
MgNNO3)2
,
FeClz
,
-Silver Chloride
02
02
FeCz
,
Except
CL
,
,
SALTS
FOR
,
are
K2SO4
soluble
Solfate
Bariren Sulfate
Lead (11) Sulfate
Calcium
,
CaSOy
BaSO4
,
@chemwithmk
etc
.
,
PbSO4
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
04
-
All
Carbonate
Carbonate
Salts
Salts
CO22-
,
insoluble
are
[Solble]
ept
Group [Flmetal
01-
for
Carbonate
Sodium Carbonate
Eg.
NHy
All
Ammonium
NH4CL
,
COs
Salts
(NHu)SOy
Liz Cos
,
(NH4)2 CO3
=>
NHyt
Salts
Ammonium
.
T
K2 COs
,
Carbonate
Carbonate
02-Ammonium
NazCOs
,
Potassium Carbonate
Lithium
05
MOOSA KHAN
Page 131
Soluble
.
are
,
NHyNOz
etc
.
-NH4CL
NHL Tag
NaCl(s
,
Chan
Ammonium Chloride
Ital
Chop,
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
Nach
.
/chemwithmk
Page 132
Hec
Nac
H
=
C
Precipitate
When
:-
an
produced
Silver chloride
AgCcs
,
Bromide
,
Silver Iodide ;
is
chemical
in
SALTS
=>
white
/
ppt
NazO
=
METAL
MgG
Yellow
OXIDES
All
(1) metal Oxides
group
NazO
all
Aluminium Oxide ; AlzOy
Oxides
Fe
@chemwithmk
Soluble.
water
are
(11)
;
Iron (11) Oxide ; FezOs
0345 2494359
ppt
AgI(s)
Sodium
Magnesium
Oxide
Iron
Salt
,
ppt off white ppt
OF
Oxide ;
a
C
+
196
AgBr(s) => Cream
SOLOBILITIES
Oxide ;
,
t
Solution
INSOLUBLE
MORE
Tag,
<
+
insoluble
in
agreous
a
Silver
f
-
(ppt)
SOME
Natas,
&
other
are
/chemwithmk/
KzO
,
group
metal
water
fesoluble
/chemwithmk
.
SOLUBILITIES
Sodium
METAL
OF
hydroxide NaOH
CaCOH)
Calcium
hydroxide
(OH)
,
hydroxide
0345 2494359
.
ALLOH)3
@chemwithmk
group
hydroxicks
z
Magnesium hydroxide Mg
Aluminium
All
,
,
HYDROXIDES
z
(1) metal
an
water
Soluble
NaOH
/chemwithmk/
,
KOH
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 133
Page 134
Salts
01
Chloride
,
SOLUBLE
INSOLUBLE
Silver
ALL
CL
Chloride
,
Lead (11) chloride
NO
=
ALL
Sulfate So-
ALL
Nitrate
,
03
,
.
·1
Ammonium NHi,
ALL
05
.
Group (1) metel
ALL
Carbonate
NazCO3 Kz 203
COz2-
(NH) 2 CO3
-
-
03
,
PbCIz
-
02
04
,
AgCL
Calcium
Sulfate ; CaSoy
Lead (11) Sulfate ; PBSUy
-Barium
Sulfate ; BaSO4
-
-
Salts
of
.
07-
All
,
ALL
Group (I) metal Oxides
NazO
soluble
K20
,
0345 2494359
are
.
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
REACTION
Acid
01
ACIDS
OF
metal
+
2 HClag) + 2Na(s)
Acids
=
Alkalis
=>
Soluble
Salt
Insoluble
State
with
Salt
>
-
>
-
Symbols
Ha
+
2NaCLg)
Symbols
.
Agreous
Solid
Salt>
(9)
State
.
=>
H2
+
Aqueous
Aqueous
MOOSA KHAN
Page 135
.
solid
(S)
Liquid
(4
Gas
(9)
(dissolved into) Agreous e
H2S04(9) + NaOHaq)
CaCO3(s) +
Helpg)
Naz
>
-
CaClegt
>
-
H20(4
Soyagst
H2Op
+
(0219)
Precipitation Reaction
A
Reaction
01-Soluble Salt 1
AgNOs(ag)
0345 2494359
Resoluble
in
which
+
Soluble Sath
+
NaCLag)
@chemwithmk
&
>
Salt
Insoluble
is
+
formed
.
Soluble Sat3
falt
AgCls)
ppt
/chemwithmk/
+
NaNOs lag
/chemwithmk
,
1
Page 136
AgNOs A
&
Nall
Agt : Noz
-"
--
-
..
t
Na :..
④
Soluble
+
Asid 1
Insoluble
>
-
Salt
Bacium Nitrate
Acid &
Salt
+
Sulfrisicid
BaCNOs)2)I, H2SO4(aq
0345 2494359
+
@chemwithmk
> Barium
-
Sulfate
>
-
,
Nitric
+
BaSO4(s)
acid
+
.
HNOs
ppt
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
(9)
Page 137
OF
SALTS
&
L
SOLUBLE SALTS
02
-
.
Acid + Metals
Acid + Base
Salt +He
02
Salt + H2O
03
>
-
>
-
04
03
04
-Acid talkali
-
Acid
Metal
+
Salt
>
-
SALTS
INSOLUBLE
01
01
MOOSA KHAN
PREPARATION
-
>
-
Acid + Metals
-
.
Acid + Base
Acid
+
+ H2O +
Metal
Salt
>
-
Salt
+
Her
+ H2O +
CO2
Carbonates
+ Her
Salt
>
-
Salt +He
Salt + H2O
>
-
-Acid talkali
-
>
-
os-Precipitation Reaction
CO2
Carbonates
SALT
INSOLUBLE
Barium Sulfate
BaO(s) +
H2SO4(aq)
>
-
BasOy(s)
Resides
[H2SO4
-..
.... :
&
-
-..
-
--........
&
-
,
+
aq
Ha
>
---
:..
-
&
BaCNOs)
:
HeSOy (99,
-
.
~
:
-
AgNOs(aq)
0345 2494359
-
-
-
--
->
-
P
+
2
Lay
Hackaq)
+2HNO3 (9)
-
↑
,
Go
Not e
Sgt
BaSO4(
@chemwithmk
.
P
BaSO4(s)
2/
...
-filta
filtrate
Ba(NOs)
d C
Or
2
B
H20
Excess
Babs
&
/
-
.
wa
Bac
/
-
H2O
+
>
-
Agcls
/chemwithmk/,
Insoluble
NaNOs19/
/chemwithmk
+
0345-2494359
Page 138
Separative
of
Insoluble
Salt
Filtration
Process
from
which
in
we
solution
.
a
separate
Insoluble
Residue
filter paper
↳↓
-
ppt
--
-
.......
-
-
-
>
-
Stopped
filth paper
a
BaCNOs)
Filter
H2SO4(ag
+
2
the
the
it
in
solution
that
>
-
,
and
BaSO4s
,
.
+ 2HNOs
Sulfuric acid
.
solution
distilled
water
over
Distilled
purc
0345 2494359
passes
through filte paper
Residua
03-Wash L wit ↓
04-Dry
flask
a
Barium Nitrate
01-Mix
02
-
conical
Filtrate
solid
By
funnel
Filtrate
Residue
& nsoluble
Filter
-
.
.
>
-
solid
a
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
water
wate
,
H20
/chemwithmk
1
Separation
of
MOOSA KHAN
Page 139
Salt
Soluble
a
Exaporation and crystallisation
Sallis
-
X
ma_ Nach
et
&
s
coolings
-
de
Theat
Evacorating
heat until
Bunsen Burner
NaClag,
Nall
is
>
>
(aq ,
achieved.
Ankyckous Salt
NaCk
powdered
NaCl
eH2O] Hydrated
>
-
Crystallization
Solution
saturated
nu
.
W
water
of
Salt
crystallisation
Magnesium
Chloride ,
q
↳
↓
Cation
0345 2494359
Mg2
Bas
@chemwithmk
Clz
m
Tire
+
/chemwithmk/
go
Cl
-
Acidh
HCL
/chemwithmk
Page 140
Preparation
Separation
and
Magensiven Chloride
Reactants
=>
,
of
a
Oxide
Hydrochloric
,
acich
Pay +1gOp
>
-
,
>
MgCl2
+
H
I
>
HCIag [Remaining)
Mg <12 (99)
,
(Excess)
-
[fusol
,
HCLag)
-
MgO
.
2H <
·
Salt
MgClz
Mageesive
Sos
Soluble
TH26
~
--
>
Theat
↑
>
-
Cas
Mg
H2)()
,
Mg(OH)2
1
-
>
0345 2494359
Helgay/
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Magnesium Chlorida
& MgO(s
,
.
Remains
-
01
MgO(s,
to
of
Excess
01-Add
acid.
Hydrochloric
the
solutive
03
-
Heat
the
filtrate
exaporate
water
,
in
until
a
Evaporating
solution
saturated
solution
os-Wash
the
crystals
with
Day
it
in
oven
dish
saturated
the
-
/
mjo
remaining Mgt
ecenove
04-Leave
solvent
HCh
~
n
to
Filter
/
- (ag
L
Magessiven Oxida My
,
02
-
06
-
MgCl2299)
-
-
MOOSA KHAN
Page 141
to
cold
is
cool
to
achieved
for
distilled water
crystallization
/organic
.
-x
↑
MgClz(
.
,
Anhychous
.
Selt
Hydrates
Salt
without wate of crystallisation.
0345 2494359
MgCl2 7 H28
@chemwithmk
-
Wate of
/chemwithmk/
crystallisative
/chemwithmk
Page 142
IONIC
MgOs)
+
EQUATIONS
2H(Lag)
V
Mngos
e
MgOc
Hig
2
,
+
H2O
d
↓
funs
day
2y
s
,
2 Hag
+
MgCl2(g)
<
arcity,
,
Spectator ins
ions
or
left' Right
H2OK
+
,
Y
tow
Same
MgYE
>
-
/
inga
Ag.
Sick
of the
Equation
.
Eg 2
CaCO3(s
,
H2SO4(g)
+
d
&
Ca(03(5)
2
+
Hag
CaCO3(s) + 2HTq +
,
CaSO4
>
↓
-
60y199/
SunTag
,
+
&
>
casons
,
Here t
CO2
(9)
↓
↓
H20(
102(9)
Casoy(s) + H20g) + (02(9)
Stepsn Equation
of
-Balanced
us-State
·
-
Symbols
Only Agreous
05-Cancel
Substance
funs
gives
Spectatue Suns [Same
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
.
on
left
/chemwithmk/
Sick
"Right Sick)
/chemwithmk
Eg3
Gra
Mgcoxs
Mgloss
+
,
Mg(03(
·
Eg
#4
/
27
+
Mgri
>
FOR
&QUATION
IONI
+
,
Ho
+ 202
H2O4 + (02(9)
NEUTRALIZATION
REACTION
HCL
↓
H
Ng
225
2HT
(,
+
,
↓
/
2
,
Mg Cleapt H2O + 102(9)
·
in
↓
MOOSA KHAN
Page 143
29 (
NaOH
-
/<
↓
+ Ci
NaCl
>
Na
OHjag,
t
k
24
aq &
T
0345 2494359
2KOHyg
/
+
2 H
+
+
I
(
H20(
Basulalkali
,
>
K2904(9) + 2H20(4
sit -
or
Lof
+
H2O
-
+
·
MglOH)2
He SU4)
+
[Base) Ja
MgO
& #5
,
ko
/(
↓
of
Not
Haq
>
(99)
↓
2H20
2 H20
-
.
I
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
>
H1
- 0HT91
H2O(Y
-
-
(of /
Page 144
of
Types
01-Basic
Oxides
Oxides
Behave
=>
with
>
-
Metal
NazO
Oxides
,
>
-
>
-
Junic
Compounds
Group (I) metal
Oxicks
02-AcIDic
salt and water
produce
CaU
K20
,
Non-metal
Oxides
Dissolve
wate
in
H20
+
903
+
H20
NO 2
+
Haw
Covalent
>
-
2
Insoluble
Hao
H2O
acids
as
,
NO2
freen
,
acids
H2SOs
>
-
>
H2SO4
>
HNO3
-
-
>
-
SO2
Do
not
dissolva
.
.
Bunding
0345 2494359
CO2
to
+
MgCl2 + H2O
>
-
.
solable
Nall
>
-
Behave
OxiDES
Sio
>
React
NaOH
>
-
H1)
+
802
-
,
water
are
HC1
+
Mgo
-
to
they
as
.
NazO
0>
Base
a
acids
MgO
,
NazO
>
as
.
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
03
Neutral
-
Neither
>
-
Oxides
Noe
acidic
Basic
Non-metal Oxid
>
-
Covalent
>
-
Bunding
-Carbon monoxide
Amphoteric
04-
02-Water
co
,
,
Oxides
Belo
=>
as
Heo
acidic
as
well
Basic
as
Metal Oxides
o-
Jonic
·-
o
MOOSA KHAN
Page 145
>
-
01
-
Bonding
Aluminivan Oxick
,
Al2O3
+
AlzOs
GHC)
·
>
-
2_
Zinc Oxid
2A1C13
,
ZuW
+ 3H20
Acid
Basc
isit
/
& Al2O3
Acid
>
Both
+
Nao H
lad
tolearn
alkal ;
Amphoteria
0345 2494359
>
-
Oxides
@chemwithmk
an
/chemwithmk/
Wate
Resoluble.
/chemwithmk
Page 146
Preparation of Salts
1
the
Mix
Nitrate)Ag No s to
Silver
1 . Filter
&Hx)acid
hydrochloric
with
residue
*
Aq
the
Beaker
a
solution
distilled water
.
and
containing
and cast
it
dry
in
the
over
.
(
t
la
citq, > Agcl(s
+
,
-
2
-
-
-
-
-
MixBackamb
H2SO4
the
Residue
Bai
,
0345 2494359
+
distilled water
with
50y
Filter
,
@chemwithmk
solution Wash
the
.
.
s
and
day it in over
Basoy (s)
/chemwithmk/
Junic
.
Guative
.
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 147
3
A
sislyalkeli
>
-
4
-
↳ solfmis acid " socive hycoxide
- - -
Sodium Sulfate
L
Acid tal
O
T
d
Yo ,
O
Not
Noof
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
H2SO4
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 148
Titration
Method
& MgOs
-
-
MgO
↓
,
laoHag 1HIK
2
*
7
,
+
,
>A
-
C
*
Smol
*
&
occurette
=>
i
.
↑
-
-
V
=
25cm
,
Nach
>
-
,
Smol
NazU
Salt
(Excess)
NazO + Hakay
I
Soluble
a
..
-
-
Prepare
to
- conical
flask
O
q, +
I&
HCL
Remaini
⑭ X
-
Evaporation
NaoH
·
Crystallisative
*
Nach
Page 149
#B
te
x
e
+ Na0H
HC1
NacI
>
-
n
Methyl orange
&
+
H2O
↑
acid
licatur
=>
alkeli=
/
-
Rec
yellow
NcOl
[Hc1]
L
flask
& Conical
-
(
**
Nocl
Har
+
50
3 NCOH
m
& 30cm Hel
1
-
to
-
#
Titration
Acid
-Measure
of-Add
03
few drops
without
a
the
Salt
of
acid
in
conical
a
flask
.
indicator
of
alkeli
from
a
volumes
Burette
until
a
Cystallisation
the
U7-wast
in
saturated
setrated
solutive
in
a
dist
achieved
is
to
to
.
cool
.
crystals
over
.
with
organic
.
Separate Becker
in
Exoporating
solution
solutive
the
it
-
Soluble
indicator
or-feas
Day
of
uncasured
wate , until
-
Prepara
Ho
changes. colour; and record volume of alkali used
these
05-Heat
+
Alkali
volume
addition
indicator
08
and
known
a
-Deep wise
04-Mix
to
Method
Using
01
Nach
>
-
Solvent
for
Exoporate
Page 150
alkeli
acid
↑
Take
known
a
ofSulfreic
volume
in
a
few drops of indicator. Deopwise add
form Breake until indicative changes
voluene
record the
of alkali added·
Mix
the
without
measured
H2SO4 4 , >
, +
-
the solution
saturated
cool
to
with
.
Sodium
hychotick
and
colom
acid
,
and alkeli
indicator .
NaOHag
Heat
of
volumes
flask Add
solutive
for
organic
in
is
NazSOy
4,
+
HO
Exeporating disk until
achieved·
Leave
the
solutive
Wash the
crystallisation
crystals
and
.
solvent
d it
in
over
.
5
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 151
FOR
TEST
IONS
I
P
#
Ib
TEST
L
#(3 +
-
>
-
-
↓
Reagents
~
Aqueous Sodium
Agreous
,
ol-
few deeps
Is
Excess
white
3
of
NOOH
NCOH
ppt
ppt soluble giving
colomless
a
.
OH
hydroxid,
Ammonia
NaoH
02
-
!
CATIONS
FOR
Testing
NH3
I
Analysis
Cation
Anion
Test rubes
↓
Qualitative
OH
NH3(9)
,
<,
precipitate
(ppt)
Page 152
Notes for use in qualitative analysis
Tests for anions
anion
test
carbonate, CO32−
add dilute acid, then test for carbon dioxide
gas
effervescence, carbon dioxide produced
chloride, Cl −
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then add
aqueous silver nitrate
white ppt.
bromide, Br −
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then add
aqueous silver nitrate
cream ppt.
iodide, I−
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then add
aqueous silver nitrate
yellow ppt.
nitrate, NO3–
[in solution]
add aqueous sodium hydroxide, then
aluminium foil; warm carefully
ammonia produced
sulfate, SO42−
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then add
aqueous barium nitrate
white ppt.
sulfite, SO32−
add a small volume of acidified aqueous
potassium manganate(VII)
the acidified aqueous
potassium manganate (VII) changes
colour from purple to colourless
Tests for aqueous cations
cation
test result
⑰Of
effect of aqueous sodium hydroxide
3+
effect of aqueous ammonia
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving a
colourless solution AL(OH)
white ppt., insoluble in excess
ammonium, NH4+
ammonia produced on warming
—
calcium, Ca2+
white ppt., insoluble in excess CaCOH)z
no ppt. or very slight white ppt.
chromium(III), Cr
green ppt., soluble in excess Cr(0 H)y
green ppt., insoluble in excess
copper(II), Cu2+
light blue ppt., insoluble in excess
light blue ppt., soluble in excess, giving a
dark blue solution
iron(II), Fe2+
green ppt., insoluble in excess, ppt. turns
brown near surface on standing FeCOH)2
green ppt., insoluble in excess, ppt. turns
brown near surface on standing
iron(III), Fe3+
red-brown ppt., insoluble in excess Fe(OH)3
red-brown ppt., insoluble in excess
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving a
colourless solution
Zu(OH)
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving a
colourless solution
aluminium, Al
=
3+
zinc, Zn
2+
3
G(OH)2
z
=
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
coloured [Transitive metal
& on]
W ↳ colourless
-
2| Identification of Salt and Gases
21.
A
I
&
As
present
Transition metal
-
ion
HHz
/El
-
-
>
-
-
·
Green
ppt
ppt
insoluble .
is
.
*
I
Green ppt
·
-
- -
-0
ppt
soluble.
with
Acidify
Nitric Acid
dilute
Agreous
Add
Barium Nitrate
then
0345 2494359
white pp t
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
O/A LEVELS CHEMISTRY MOOSA KHAN
Page
PAGE 153
41
>
-
Page 154
22.
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
MOOSA BH KHAN
Page 155
43.
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 156
Q1.
Q2.
MOOSA KHAN
Page 157
Page 158
MOOSA KHAN
Page 159
Page 160
Q4.
.
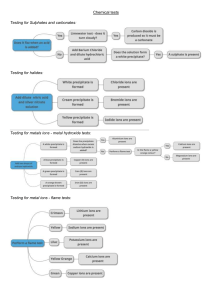
Notes for use in qualitative analysis
Tests for anions
anion
test
2–
test result
add dilute acid, then test for carbon
dioxide gas
effervescence, carbon dioxide
produced
chloride, Cl –
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then
add aqueous silver nitrate
white ppt.
bromide, Br –
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then
add aqueous silver nitrate
cream ppt.
iodide, I–
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then
add aqueous silver nitrate
yellow ppt.
nitrate, NO3–
[in solution]
add aqueous sodium hydroxide,
then aluminium foil; warm carefully
ammonia produced
sulfate, SO42 –
[in solution]
acidify with dilute nitric acid, then
add aqueous barium nitrate
white ppt.
sulfite, SO32 –
add a small volume of acidified
aqueous potassium manganate(VII)
the acidified aqueous potassium
manganate(VII) changes colour
from purple to colourless
carbonate, CO3
Tests for aqueous cations
cation
effect of aqueous sodium hydroxide
effect of aqueous ammonia
aluminium, Al 3+
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving
a colourless solution
ammonium, NH4+
ammonia produced on warming
calcium, Ca2+
white ppt., insoluble in excess
no ppt. or very slight white ppt.
chromium(III), Cr 3+
green ppt., soluble in excess
green ppt., insoluble in excess
copper(II), Cu2+
light blue ppt., insoluble in excess
light blue ppt., soluble in excess,
giving a dark blue solution
iron(II), Fe2+
green ppt., insoluble in excess,
ppt. turns brown near surface on
standing
green ppt., insoluble in excess,
ppt. turns brown near surface on
standing
iron(III), Fe3+
red-brown ppt., insoluble in excess
red-brown ppt., insoluble in excess
zinc, Zn2+
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving
a colourless solution
white ppt., soluble in excess, giving
a colourless solution
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
white ppt., insoluble in excess
–
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 161
Page 162
Tests for gases
gas
test and test result
ammonia, NH3
turns damp red litmus paper blue
carbon dioxide, CO2
turns limewater milky
chlorine, Cl 2
bleaches damp litmus paper
hydrogen, H2
‘pops’ with a lighted splint
oxygen, O2
relights a glowing splint
sulfur dioxide, SO2
turns acidified aqueous potassium manganate(VII) from purple to colourless
Flame tests for metal ions
metal ion
flame colour
lithium, Li+
red
sodium, Na+
yellow
potassium, K+
lilac
copper(II), Cu2+
blue-green
calcium, Ca2+
orange-red
barium, Ba2+
light green
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 163
Chapter
METALS
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 164
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 165
XMETALS
IV
I
,
II
,
TE , III
[Se Pb]
I
C
,
,
> Non-metal
-
Si
Ge
I
Metalloids.
Ev]
Reactivity
of
Metals
Metals
always
React
Oxidation
.
I
#a
1g
Al
>
-
Al
Fe
+
22
Fe
+
=
2,
.
le
+
Nat
8
Electrons
+
+
,
>
-
-
>
F
2+
+
F3
+
+
20
32
3e-
-
Oxidation
Metals
· -
Mg2
>
-
2
=
Losing
By
Nat
>
-
Na
Mets
:_
=>
By losing
Act
as
a
e
/Oxidis
Reducing gent
Reactivita
y bitMetalend
(Peoup I
Li
>
-
Na
metel
K
④
>
-
Rb
⑭
.
CsV
↑r -
O
-
Down
-
the
upon
.
i
the
group
increases
Down the
groupof
losing ability
.
increases
Reactivity of
Elections
metals
Page 166
PHYSICAL
PROPERTIES
Bonding
Steucture
=
Metallic
=
Giant
OF
METALS
Metallic
Lattice
Sucium/Coppa /Gold
O
④
④
& ④
④
metal
positive
-
-
-
irns
④
④
-
In ametallicBondingd
Sea
>
-
electrons
metal
in
of delocalised
positive
of
saa
a
ion
layers
delocals e
electrons.
01 Why
A :.
Metals
Wave
high
Lave
Giant
Metallic
Metals
Amount
of
huge
Break
many strong
of -Metals
Ble
they
-
of
Conducte
Electricity
Elections/mobile
of delocalised
Ekations
Elections
.
of
See
delocalised
Electrons
are
ReplacedBy
New
e
·>
e
L+
O
-
.
-
-
to
-
-
-
so
B
Sea
④Q④⑦Q
④- ⑰ Q-④
⑦④
④④
④
Energy eequired
ruck
metallic
free
Wave
Caltics
is
good
are
Point
melting
-
ne-
->
Electrons
Metal
positives
unchanged
Ekatons
Pous
stay
of
Page 167
03
-
Metals
Malleable's
are
Ductile
.
Ductility
--
-
metals
Abilitybe of
deare into
⑰⑰GGQ
④④⑦④
④
④
④
④
-
-
- -
-
-
--
-
-
-
to
-
E
wires
-
-
-
-
Malla
Ability
hammered
S
bility
metals to be
of
different
into
hopes
Di-Why
Metals
Metal
positive
arrang
when
&
22
furc
su
is
are
Malleable
& Ductile
[I)
Regulae
rly another
are
laye
they
ive
/
aclied
.
Page 168
Properties
Group I Elements – The Alkali Metals
These are metals which react with water to form alkaline solutions. The solutions
turn red litmus paper blue.
• most reactive metals in periodic table
• have one outer shell electrons
• shiny, silvery solids
• soft, easily cut with scalpel
• low densities & melting points which increases down the group
• reacts easily in air. So they’re kept in oil
• reacts vigorously (may catch fire or explode) with cold water
• they make ionic compounds of +1 charge. They have similar formulae
• they become more reactive down the group
Name
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Rubidium
Caesium
Symbol
Li
Na
K
Rb
Cs
Density (g/cm3)
0.53
0.97
0.86
1.5
1.9
Melting Point (oC)
180
98
64
39
29
Element
Lithium
Chloride
LiCl
Nitrate
LiNO3
Sulphate
Li2SO4
Oxide
Li2O
Sodium
NaCl
NaNO3
Na2SO4
Na2O
Potassium
KCl
KNO3
K2SO4
K2O
Table 12.1: The physical properties and formulae of Group I metals
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Transition Elements
Properties
• First transition series are all metals
• Transition elements have high melting points
• They have high density
• They have variable oxidation state, e.g. Iron (Fe) appear as Fe2+ or Fe3+
• They form coloured compounds, e.g. CuSO4 is blue, FeSO4 is green
• They form complex ions, e.g. MnO4 - , Manganate(VII) ions
• They act as catalyst
MOOSA KHAN
Page 169
Uses of Transition Elements
Most transition elements and their compounds act as catalysts which speed up
chemical reactions
• Iron is used in Haber Process for manufacture of ammonia
• Vanadium(V) oxide is used in contact process to manufacture sulphuric acid
• Nickel is used in hydrogenation of alkenes to form saturated fats (e.g. margarine)
Advantages
• Since transition elements speed up chemical processes in industries, they
save time in manufacture
• Less energy is needed for manufacture in industries, hence lower cost
• Since less energy is needed, more energy resources can be conserved, e.g. oil
to generate electricity in producing iron.
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 170
General Properties of Metals
Physical properties
• Ductile (can be stretched to form wires)
• Malleable (can be bent and beaten into different shapes)
• Good conductors of electricity and heat
• Shiny
• High melting points and boiling points (except mercury and sodium)
• High density (except sodium)
• Strong
Metallic lattices
metallic lattice consists of ions surrounded by a sea of electrons. But in a metallic bond, the attractive forces between the metal ions and the de-localised electrons act in all directions. So when the layers slide, new metallic bonds are easily
re-formed between ions in new lattice positions and the de-localised electrons.
The de-localised electrons continue to hold the ions in the lattice together. The
metal now has a different shape. This explains why metals are malleable (they
can be hammered into different shapes) and ductile (they can be drawn into
wires). The high tensile strength and hardness of most metals is also due to the
strong attractive forces between the metal ions and the de-localised electrons.
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 171
MOOSA KHAN
Alloys
An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals or a metal with a non-metal. The
metal added to create the alloy becomes part of the crystal lattice of the other metal. Brass is an alloy of copper (70%) with zinc (30%). It is stronger than
copper but still malleable. For these reasons it is used for musical instruments,
ornaments and household items such as door handles. But why is brass stronger
than pure copper? Zinc ions are larger than copper ions. The presence of different-sized metal ions makes the arrangement of the lattice less regular. This stops
the layers of ions from sliding over each other so easily when a force is applied
Uses of Alloy:
• Steel (mixture of iron, little carbon and trace elements)
• Brass (copper and zinc) – tough and corrosive-resistant
• Coin metals (copper with other metals e.g. nickel) – tough, resistant and
stand up to wear
Uses of Stainless Steel
is an alloy of iron containing chromium or nickel. Is the most expensive way
Applications for:
• Cutleries
• Medical instruments for hospital operations
• Kitchen sinks
• Steel objects in chemical factories and oil refineries
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 172
& ::
-
Why alloys
Because
less
are
I
malkable
metal
of
Irreg y arranged
another
slick
al
one
a
ductile
and
positis in s
they
so
donut
.
O 000000
⑳
O 000000
>
-
Two
mixing
different sizas
*
Alloys
>
-
>
-
>
-
>
-
Alloys
an
to
Alloys have high
Steel
Brass
is
fron
Physical Mixture
Conduct
an
Coppa
Fr %
Lace
must
Elements
an
alloy
-
.
Electricity (cocised
mp-
alloy
-
of
Zinc
30 %
See
.
Page 173
(
Li
Be
Na
K
i&
E
Rb
Fe
Ba
s
Rb
Reactivity
> Nc
Series
of
Metals/Electrochemical Series
of
Potassium (Most Rective) K
Sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Zinc
Iron
Lead
Hydroge
OPP
er
Gold
Platinium
.
·
°
⑩
-
[ least Reactive
Metals
Down
the
Reactivity
Decreases
Series
of Metals
PSCMAZIL
Could
Hardy
Solid Gold
make
Perfectl.y
Page 174
1) Reaction with Cold Water & Steam:
Room
temperature
Steam
{
K + H2 O
Na + H2O
Ca + H2o
KOH + H2
Reacts explosively
NaOH + H2
Ca(OH)2 + H2 } Reacts readily
}
{
Mg + H2O
MgO + H2
Al + H2O
no reaction due to oxide layer
Zn + H 2o
ZnO + H 2
(Red hot)Fe + H 2O
FeO + H 2
Pb + H2O
PbO + H2
Very slow reaction
H
Cu
Ag
Au
Pt
}
Below Hydrogen No reaction with water as they can’t
displace Hydrogen from H 2O due to being less reactive
than it
NOTE: It is a displacement reaction, all displacement reactions are redox.
2) Reaction with dilute acid: e.g: HCl
Explosive reaction
Readily Reacts
Very Slow with
warm acid
Don’t react
with dilute
acid
{
{
{
0345 2494359
K + HCl
Na + HCl
Ca + 2HCl
KCl + 1/2H2
NaCl + 1/2H2
Mg++HCl
2HCl
Al
CaCl2 + H2
MgCl2 + H2
No reaction due to oxide layer
Zn
2HCl
Fe ++ 2HCl
{ Pb + 2HCl
H
Cu + HCl
Ag + HCl
Au + HCl
Pt + HCl
ZnCl2 + H2
PbCl2 + H2
PbCl2 + H2
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
O
C G
/
L Al2O3 [Non-poeous]
Page 175
Had
(12)
d
-
d
Impermash
Le
&
:-
Al
Why
Oxyge
A :
-
Al
Al
Was
on
anything
orde
to
powdered
Al (
powdered
/
to
which
&
pass
AL
form
+
.
Non-preous
Surface
React
React with
not
. acids
a
its
allow
in
does
wate
on
metal
formed
&n
metal
through
we
oxide
.
it
Need
.
Hio
>
-
(9)
layer
does not
AGOsc
Page 176
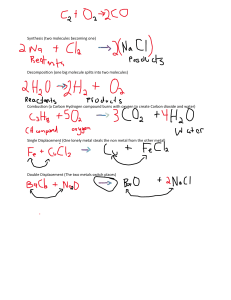
3) Displacement Reaction:
Metals higher in the reactivity can displace other metals from their
compounds which are lower in their reactivity series.
Example: CuSO 4 + Zn0
(aq)
(s)
ZnSO4 + Cu0
(aq)
(s)
Ionic equation: Cu+2 + Zn0
(aq)
(s)
Zn+2 + Cu0
(aq)
(s)
Apparatus:
Cu2+ + Zn
2+
Cu(s) + Zn (aq)
Observation:
1. Blue colour of solution changes to colourless
2. Zn rod gradually dissolves
3. Pink deposits of copper are seen
Cu + Zn2+
No Reaction
Note:
1) ZnSO4 + Cu
2) 2Al + Fe2O 3
0345 2494359
No Reaction (because copper is less reactive than zinc)
Al2O 3 + 2Fe
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 177
Reaction of
Displacement
>
A
from
o>
-
-->
Reactive
more
its
metal
salt
Solutive
Metals
displaces
a
Reactiv
less
>
-
K
Na
Reactive
Less Reactive
More
Metal
Oxidises
Metal
for
ca
Mg
Rec luces
AL
-
·
It
Cu
su,
metal in
t
E
En
En
Ze
G
If
↳
z>
-
>
-
+
+
En
2
-
+ Ze
>
-
Zu L
G
Fe
in
.
Ag
G, Sou
(Blue)
En
+
(s)
Zine dissolva
-
An
PE
CSOn
>
-
Enjoy
Gils
pink
.
Blug
+
19
>
-
colorless
,
solic&
/Beowe
.
Page 178
Reactions
Displacement
Elemental
of Metals
)
A Reaction
displaces
its
which
in
Reactive
less
a
Reactiv
more
a
fever
ives
I
Solution
salt
&
Cusorlation
K
Zn(s,
Na
ca
Get Zu
-
>
-
So
y
o>
Metals
>
--
More
-
G
Ze
React
+
By Losing
metal
.
oxidiss
2
-
-
-
Ze
P
.
+
+ 22-
zn2 +
Agt
Af
>
+
2
+2
+
Displacement
-More
02-Less
Gi
be
<Reduced
>
-
ar
o >
>
-
Au
C
. Coxidation)
↑ 0-S
-
O
En
&n
Fe
e
Ef + 2 -
>
-
+
CSO4
2-
Reactive
En
Mq
Al
.
N
ZnS04
+
Reactive
Reactive
Metal
Reactive Metal Con
Oxidises
Reduces
.
*
Page 179
More
Reactive
Displacement Reactive of Metals
metal
displaces less Reactive metal in from its
=>
salt
Solution
zeSS
Reduce
zn
904)as/ +
>
-
+
2
-
-
Ze
+
>
Ge
2
o>
More
East
ze
pink solid
·>
less
Reactive metal Oxidises
Reactivs
Reduces .
En
(SC
-
.
-
A
deposited
2+
>
-
2+
-
Reduce .
Oxidise
q
GS04(99)
+
Oxidisc
z1
2+
.
metal
ive
K
Na
cc
Mg
Al
⑭
,
K
Page 180
N
/
/
- -
X
-
-x
-
Blue
va
Fe
+
Fe
4
>
·
Cu
·
It
wewelle
-
Fe
CusOy
-
CuSOy > FeSOy
-
Fe2 + + 25
>
-
+
> green
-
+ 2
-
>
-
CaSOn
+
O2
Fe
is
E
Gr
>
-
Caw
X
Page 181
Thermal
of
Decompositive
/
Heat
T
Carbonates
Metal
n
I
Break down
Calcium Carbonate
.
Ca2 + cos2
CalOs
=>
Sodium Carbonate
Nat cos
NazCOz
-
Iron (111) Carbonate
2
Fe3 + (03
Thermal
Carbonates
Decomposition
heats
CaCO3 (s)
-
=
Group (11) metal
of
Caocss
CO2
+
Fez((Os)s
19)
heat
Mg(03(s
>
,
Stability
of
Ability of
Metal
Metal
Carbonate
Stable Metal Carbonate
CO2 (9)
+
Carbonates
Carbonates
More Thereala
less Thermal
MgO(s)
=>
to
Metal
Resist
Carbonates
Decomposed
=> Metal
decomposition.
at
that
a
Carbonates
Decomposed
at
higher temp
that
a
are
lower
.
are
temp
.
Page 182
Q:
the
following metal Carbreaks
Arrange
to
least stable
stable
-
from
most
.
-
>
-
NazCOs
cos
↳
↑
m
u
22(CO3)s
C 103
03
Rb (O 3
Metal
more
a
-
2
Carbonates
with
thermally
Stable
<
Ag2COs
MglOs
↳
Co
-
more
Reactive
metals
CS
I
Stadk)
Theremaly
No
Decompose & highest Kay3
L Most
S2CO3
Rb 2 C03
K
"C
Na COs
"cos
Rb I
Ca
s
Mg 103
3
PbCo 3
Decomposes & lowest temp
COz [least thermally Stabl]
> Aga
least
Reactive
L
.
↑
My
A L
Zo
Fe
Fez((03)
C 103
are
Rb
Most
Reati"l
-
.
T
Ar
Pt
Page 183
MOOSA KHAN
Extraction of Metals
Metals from Rocks
Minerals – elements/compounds that make up rocks
Metal ore – rock containing metal
Extracting these metals
• Metal ores are removed from ground.
• The ores contain useful and unwanted materials. Unwanted materials are
separated to obtain concentrated mineral.
• Metal is extracted from the mineral.
Occurrence of Metals
Metal ores are compounds, usually as:
• Metal oxides – metal + oxygen, eg: Al2O3
• Metal sulphides – metal + sulphur, eg: HgS
• Metal carbonates – metal + carbon + oxygen, eg: MgCO3
Some important metals ores:
Mineral Metal
Name of Ore
Sodium
Rock Salt
Calcium
Limestone
Magnesium
Aluminium
Zinc
Iron
Copper
0345 2494359
Magnesite
Bauxite
Zinc Blende
Haematite
Magnetite
Chalcopyrite
Chemical Name
Sodium chloride
Calcium carbonate
Formula
NaCl
CaCO3
Magnesium carbonate
Aluminium oxide
Zinc sulphide
Iron(III) oxide
Iron(II),(III) oxide
Copper(II) sulphide +
Iron sulphide
MgCO3
AL2O3
ZnS
Fe2O3
Fe3O4
CuFeS2
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 184
Methods of Extraction from their ores:
Reaction of Metal Oxides with Carbon
The lower the position of metal in reactivity series, the easier for carbon to remove oxygen from metal oxide by heating. At higher position, stronger heat is
needed.
E.g. CuO reacts with C can be reduced by bunsen burner flame temperature
CuO(s) + C(s)
Cu(s) + CO2 (g)
For iron oxide to be reduced, it needs very high temperature
Reaction of Metal Oxides with Hydrogen
The lower position of metal in reactivity series, the easier hydrogen remove oxygen from metal oxide by heating. At higher position, stronger heat is needed.
E.g. PbO reacts with H2 can be reduced by bunsen burner flame temperature
PbO(s) + H2 (g)
K
Na
Ca
Mg
Al
Pb(s) + H2O(l)
Extracted by electrolysis of their molten ores
because they are reactive metals and have
strong bond strength
[C]
They can be reduced
by H as reducing
agent
e.g:
CuO+H2
Cu+H2O
0345 2494359
Zn
Fe
Pb
[H]
Cu
Ag
Au
Pt
They can be extracted from there ore by suitable Reducing agent like C,CO from their ore.
E.g: Fe2O3 + CO
Fe + CO2
ZnO + C
Zn + CO2
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 185
EXTRACTION
IRON
ORE
Hematite
=
Mineral
(11) Oxida
=
Blast
furnace
Raw materials
=
CONSTRUCTION
-
WORKING
Coke
[c]
o
&
(2)
&
Molten
slag
Molten
Iron
↑
air
,
+
02)
10219
>
-
/
3200 , 9 ,
02-4s , + 10219 ,
(02)
·
Carbon monoxide
[Reducing Agent]
03
- Fez03cs 310(g)
,
+
s2F2(y +3(0c9)
wolten
Iron
.
Decomposition
heat
04
-Si0z
Silicon (IV) Oxide
(Acidic)
Cs
formance
If
04
REACTIONS
CHEMICAL
Blast
air
Fe
>
Reducing agect
=
and
Fe2O3(s)
&2
Fezos
FezOs
CaCOs
[Carbin]
CalOz
+
.
Fe2O3
Occ
02-Limestone ;
03-Coke
/ Haematite
Iern
Es
-Hematite
one
9
=
Equipment
IRON
OF
-CalOsIs)
>
-
CaOs
,
Base
os
SiDz
acidiz
+
CaO
Basic
>
-
CaS
+
10291
i832
Calciven Silicate
Molten
Page 186
Importance
-
ImpuritiesPrevents Removed
O2
Molter
slay
gas coming
molter
with
Inve
are
USEs
in
02
Used
in
03
Used
in
Pore
of Glass
manufacture of Cement
is
in
they
so
Fron
of
veryits
layers slik
as
crockery
making
Alloys
=
Irre
contact
Manufacture
Used
STEEL
in
SLAG
Of
0
-
Slag
Molten
Sand
01-
02
of
Slag
Malkable
.
metallic
over
one
ductile
and
lattice
eegularly arranged
are
another
0000
O
O
888
&e
order
[Hard
Alloy
of
to
and
less
Malleable
we
make
allvys
Mild
Steak
Iron
make
Briltle] ;
and
ductile
Feon
01
-
02-Stainless
[Irve
Steel [Irre
+
+
Carbon]
Chromiven Nickel
Carbon]
Page 187
USEs
01
-
OF
METALS
Aluminium
Corrode
01-Does not
02
-
It
has
03-Good
;
Containers
food
low
density
of
Conductor
;
to
weight
aircraft/light
Overhead Electrical
make
Electricity
Cables
;
02-Copper
Of-Good
conductor
Corrosion
of
It
is
Rusting
of
of
=>
Rust
=>
Beowe
>
-
F
+
02
+
of
+
solid/Reddish
Hydrated Iron (11)
Fe
.
Metals
.
Corrosion
Fron
Fe
Rust
wiring
Metals
oxidative
of
electrical
Electricity ;
/ Steel
32
+
Powder
Brown
Oxida
Heo
Iron
,
Fez 83. H20
>
Fez0z xH2O
.
Page 188
CONDITIONS
Iron/Stech
RUSTING
FOR
000
01-Water
00
00O O
O
; Haw
02-Oxygen ; Oz
02
Y Hec
//
A
-
/
-
Oz
X
Hac
Her
~
Oz
-
m
-
-
~
-
↑
Aos
↑
-
-
t
Boiled water
No
No
Oz
↑
Moist
air
gas
Rusting
.
.
F>
-
-
Rust
No
Rust
Deying
agentoi
Collz
Page 189
Prevention
a-Paintin
↓
-
H2O
-
Protection
-Surface
01
Rusting
From
on
q
Plastic
-Grease
d
Plating [Electroplating]
Metal
-
02
Protective
-Sacrificial
A
Reactive
more
Reactive
metal
metal
in
<g
Mg
+ 2
E
↳
Fe
less
.
From
Fe
of
place
corrodes
Mg
>
-
>
-
+
-c
+ 32
-
-
Fe
z
zn
↑
-C
01
Galvanised
02-ships
=
os-Underground
Iron
Zinc
steel
>
-
Steele
is
3c
- -
+
coated
the
Fe
>
.
with
Zinc
.
Blocks
pipes
In
>
-
3 +
are
attached
to
.
↓ -Mg
T
>
-
.
from
of
ships
.
Page 190
Conditions for Rusting
After a few days, only nail in tube A rust. This shows that air and water is needed
for rust. In boiled water, the nail doesn’t rust in B as boiled water removes
dissolved air while in C, CaCl keeps air dry so there’s no water.
Other factor
dissolved salt
Preventing Rusting
• Surface protection
• Sacrificial protection
• Use of stainless steel
Surface Protection – covers metal with a layer of substance
1. Paint
2. Grease or oil (also help to lubricate)
3. Plastic
4. Metal Plating – covering metal with thin layer of another metal (e.g. tin,chromium, silver)
Advantage – These methods are cheap (except metal plating)
Disadvantage – If the layer is broken, air and water an reach metal to rust
Sacrificial Protection
is to sacrifice more reactive metal to corrode with water and air by layering it
over less reactive metal (e.g. iron covered by magnesium). If layer is broken, water & air reach underneath layer, overlying metal still protect it.
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
MOOSA KHAN
Page 191
ƉƉůŝĐĂƟŽŶƐ͗
1. 'ĂůǀĂŶŝƐĞĚ/ƌŽŶʹŝƐƐƚĞĞůĐŽĂƚĞĚǁŝƚŚnjŝŶĐ͕ƵƐƵĂůůLJƵƐĞĚŽŶƌŽŽĨƐ͘
2. WƌŽƚĞĐƟŶŐƐŚŝƉƐʹďůŽĐŬƐŽĨnjŝŶĐĂƌĞĂƩĂĐŚĞĚƚŽŚƵůůƐƚŽĐŽƌƌŽĚĞŝŶƐƚĞĂĚŽĨ
ƐƚĞĞůǁŚŝĐŚŝƐƚŚĞƐŚŝƉŵĞƚĂů͘
3. hŶĚĞƌŐƌŽƵŶĚƐƚĞĞůƉŝƉĞƐʹƚŚĞƐĞĂƌĞĂƩĂĐŚĞĚƚŽŵĂŐŶĞƐŝƵŵďůŽĐŬƵƐŝŶŐŝŶƐƵͲ
ůĂƚĞĚĐŽƉƉĞƌĐĂďůĞƐ͘DĂŐŶĞƐŝƵŵĐŽƌƌŽĚĞƐĮƌƐƚƚŚĂŶƐƚĞĞů͘
Ang
-
i
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 192
Uses of Metals
The choice of metals over another depends on 3 factors:
1. Physical properties (e.g. melting point, strength, density, conductivity)
2. Chemical properties (e.g. resists corrosion)
3. Cost
The Uses of Some Metals and Their Reasons
Metal
Uses
Reason for the Choice
• Low density, non-toxic, cheap
Aluminium • Drink cans
• Window frames
• Resists corrosion, strong
• Electrical wires
• Ductile, good conductor of electricity
Copper
• Water pipes
• Strong, malleable, resists corrosion
• Jewellery
• Shiny and attractive, very malleable
Gold
• Protective coating • Good reflector of heat and light
• Supersonic aircraft • Light but strong, resists corrosion
Titanium
• Spacecraft
Recycling of Metals
=>
=>
How Much is Left?
There are many iron on the surface but copper and tin are seriously reducing.
If you say you have only mined the surface, why don’t you mine deeper for
more?
High temperatures and pressures and greater depth increases hazards that prevent mining up to the lower part of crust, although there are more metals further down
Conservation of metals- Recycling
• Use alternative materials to replace the use of iron (e.g. use of plastic pipes
instead of iron, use of glass bottles for soft drinks instead of aluminium)
• Recycle unused metals by melting them to produce new blocks of clean metal
How aluminium cans are recycled?
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Steel
STEEL is an alloy of Iron along with other elements like Ni, Cr. etc
• Iron made from blast furnace is not good as:
• it contains impurities which makes it brittle (can break easily)
• it cannot be bent or stretched
MOOSA KHAN
Page 193
Most iron is converted into steel which is an alloy of iron and carbon with small
amounts of other elements. Advantages of steel:
• it is strong and tough
• it can be bent and stretched without shattering
Making Steel:
• Impurities of iron is removed by blowing oxygen into molten iron to change
the impurities into oxides. They are then combined with CaO and removed as
slag.
• Carbon and other metals are added in certain amount to make steel.
Different Types of Steel:
• Mild steel – is a low carbon steel with 0.25% carbon
• it is strong and quite malleable. It is used for car bodies, ships, railway lines and steel rods to reinforce concrete
• Hard steel – is a high-carbon steel with about 1% carbon
• It is harder than mild steel and less malleable. It is used to make
tools
• Stainless steel – is iron with large amounts of chromium and nickel
• It is hard, shiny and doesn’t rust. It is used to make cutleries, medical instrument and pipes in chemical industries.
Rusting
Rusting – corrosion of iron and steel
Rust – brown solid product formed during rusting
Rust is hydrated iron(III) oxide Fe2O3.xH2O where water molecules varies
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk
Page 194
0345 2494359
@chemwithmk
/chemwithmk/
/chemwithmk