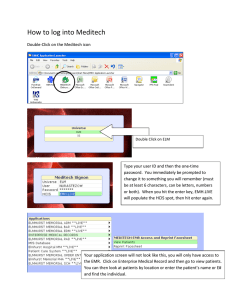
CM2 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING AND LOSS RESERVING THE EFFICIENT MARKETS HYPOTHESIS (CH-1) An EFFICIENT MARKET is one in which every security’s price equals its investment value at all times. In an efficient market information is fully reflected in the price. This means that the share prices adjust instantaneously and without bias to new information. THREE FORMS OF THE EFFICIENT MARKET HYPOTHESIS STRONG FORM EMH SEMI STRONG FORM EMH WEAK FORM EMH STRONG FORM EMH states that market prices incorporate all information, both publicly available and also that available only to insiders. SEMI STRONG FORM EMH states that market prices incorporate all publicly available information. WEAK FORM EMH states that market prices incorporate all information contained in the price history of that investment. STRONG FORM EMH implies SEMI STRONG FORM EMH and WEAK FORM EMH. SEMI STRONG FORM EMH implies WEAK FORM EMH. INVESTMENT TECHNIQUES INSIDER TRADING involves trading on the basis of information that has not been published or made known to public. FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS includes the analysis of balance sheets, consideration of company stratergy, the environment in which the company operates etc. TECHNICAL ANALYSIS is the study of chart patterns. A variety of trends, triangles and peak formations are used as bullish or bearish indicators. If STRONG FORM EMH holds then INSIDER TRAINING is on no use. If SEMI STRONG FORM EMH holds then FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS is of no use. If WEAK FORM EMH holds then TECHNICAL ANALYSIS is of no use. www.finatics.co.in FINATICS(AN ALL INDIA TOPPER INITIATIVE] 7980009365 Page 1 CM2 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING AND LOSS RESERVING TESTING THE EFFICIENT MARKET HYPOTHESIS STRONG FORM EMH STUDIES OF DIRECTOR’S SHARE TRADING. The past studies suggest that even with inside information it is difficult to outperform the market suggesting that STRONG FORM EMH hold. LEGALITY OF INSIDER TRAINING. Insider trading is banned in many countries suggesting that the lawmakers believe that the STRONG FORM EMH does not hold in their stock markets. SEMI STRONG FORM EMH TESTING INFORMATIONAL EFFICIENCY TESTING FOR EXCESSIVE VOLATILITY WEAK FORM EMH TECHNICAL ANALYSIS revealed to be no better than random stock selection. INFORMATIONAL EFFICIENCY The market for a particular security is said to exhibit INFORMATIONAL EFFICIENCY if new information is incorporated quickly and accurately into the price of the security. The main difficulties is testing Informational Efficiency are : It is empirically difficult to exactly determine when a particular piece of information becomes available (to the public or anyone). It is difficult to judge exactly how and the extent to which the market price should react to a particular event. It is difficult to determine what constitutes publicly available information. How to adjust returns for risk and transaction costs. EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE CONCERNING INFORMTIONAL EFFICIENCY Empirical evidence suggest that markets do over react to certain events and under reacts to other events and that over/under reaction is corrected over a long time period. If this is true then traders might be able to take advantage of the slow correction of the market to make excess risk adjusted returns and so efficiency would not hold. EXAMPLES OF OVER REACTION to events: PAST PERFORMANCE- Past winners tend to be future losers and vice versa. The market appears to overreact to past performance. Certain accounting ratios appears to have prediction powers, an example of the market apparently over reacting to past growth. www.finatics.co.in FINATICS(AN ALL INDIA TOPPER INITIATIVE] 7980009365 Page 2 CM2 FINANCIAL ENGINEERING AND LOSS RESERVING Firms coming to the market by INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING(IPO) or SEASONED EQUITY OFFERING(SEO) have poor subsequent market performance. EgMarkets of US and UK EXAMPLES OF UNDER REACTION to events: Stock prices continue to respond to earning announcements up to a year after their announcement. Abnormal excess returns for both the parent and subsidiary firms following a demerger. Abnormal negative returns following merger. Other examples of pricing anamolies, eg the ability of accounting ratios to indicate outperformance are proxies for risk. VOLATILITY TEST The claims of excessive volatility was first formulated into a testable proposition by SHILLER in 1981. He considered a discounted cashflow model of equities going back to 1870. By using the actual dividends paid and some terminal value for the stock he was able to calculate the perfect ‘foresight price’, the correct equity price if market participants were able to predict future dividends correctly. The difference between the perfect foresight price and actual price arises from the forecast errors of future dividend. If market participants are rational then we would expect no systematic forecast errors. Also if markets are efficient, broad movements in the perfect foresight price should be correlated with moves in actual price as both react to the same news. The various criticisms of Shiller’s methodology are: The choice of terminal value for the stock price. The use of constant discount rates. Bias in estimates of variance due to autocorrelation. Possible non stationarity of time series. www.finatics.co.in FINATICS(AN ALL INDIA TOPPER INITIATIVE] 7980009365 Page 3