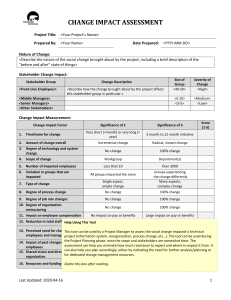
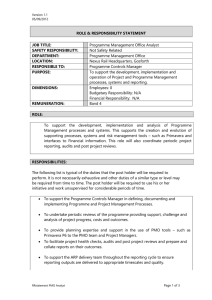
Download PMO-CP Exam Dumps for Best Preparation Exam : PMO-CP Title : PMO Certified Practitioner https://www.passcert.com/PMO-CP.html 1/5 Download PMO-CP Exam Dumps for Best Preparation 1.How many performance indicators should be used for each PMO function in each evaluation cycle? A. Only key functions should be monitored with performance Indicators, reducing bureaucracy and excessive control. B. One indicator per function, giving focus to what really matters. C. From two to four indicators, allowing the benefit of controlling to be compatible with the effort to achieve it. D. All the indicators recommended by the methodology. Answer: C Explanation: In the context of PMO (Project Management Office) functions, performance indicators serve as critical tools to measure the effectiveness and success of the PMO's activities. The best practice is to use two to four performance indicators per function during each evaluation cycle. This ensures that the evaluation is comprehensive enough to provide valuable insights without creating unnecessary bureaucracy or excessive control, which can hinder flexibility and innovation. A balanced number of indicators allows organizations to monitor the essential aspects of each function while maintaining efficiency and adaptability. By focusing on 2-4 indicators, PMOs can achieve a manageable level of control without overwhelming the team with too much data or analysis, which can be counterproductive. This approach aligns with the principle of tailoring and agility in project management, where processes and metrics should be adapted to fit the context of the work, providing maximum benefit with the least effort. This recommendation is derived from the PMBOK Guide and related frameworks like Ricardo Vargas' PMO methodologies, which emphasize focusing on value, minimizing waste, and maintaining a lean and effective governance structure. 2.The PMO Expectation Adherence indicator (pmo-EAl) is: A. The sum of 20% of the functions capable of generating 80% cumulative contribution probability. B. The sum of the selected functions' contribution probabilities. C. The sum of the results of executed projects. D. The sum of 80% of the functions capable of generating 20% cumulative contribution probability. Answer: B Explanation: The PMO Expectation Adherence Indicator (PMO-EAI) measures how well the PMO adheres to its expected contributions within an organization. The selected functions of the PMO are analyzed based on their contribution probabilities, which reflect how much they are expected to contribute to the overall project success. The correct approach to calculating the PMO-EAI involves summing the probabilities of the contributions from these selected PMO functions. This method allows a clear assessment of the effectiveness of the PMO in meeting its objectives. It aligns with the principle of focusing on measurable outcomes in PMO performance evaluation, as seen in the application of frameworks like the PMBOK Guide and project evaluation models. 3.What is the ideal type or model of PMO? A. The Strategic PMO. B. The Agile PMO. 2/5 Download PMO-CP Exam Dumps for Best Preparation C. The Center of Excellence. D. None of the answers. Answer: D Explanation: There is no one-size-fits-all ideal type of PMO (Project Management Office). The type or model of PMO that works best for an organization depends on its specific needs, culture, and strategic goals. The PMBOK Guide and various other methodologies emphasize that PMOs can take different forms based on the organization's maturity, complexity, and focus areas. A Strategic PMO may be ideal for organizations looking to align projects closely with strategic objectives. An Agile PMO would be suitable for organizations that require flexibility and rapid responsiveness to change. A Center of Excellence is more focused on providing best practices, training, and support across projects but may not directly align with the organization's strategic project execution needs. Therefore, the best PMO model must be tailored to fit the specific requirements of the organization, and none of the answers is universally ideal. Each organization must determine the PMO type that works for its unique context. 4.What are the most common PMO stakeholders? A. Upper management, project managers, and external suppliers. B. Upper management, project managers, functional managers, and project team members. C. Upper management, functional managers, and external clients of the organization D. Upper management, project managers, functional managers, and all other employees of the organization. Answer: B Explanation: The most common stakeholders of a PMO (Project Management Office) include upper management, project managers, functional managers, and project team members. These stakeholders are directly involved in or affected by the PMO’s activities and performance. Upper management provides strategic direction and ensures that the PMO aligns with organizational goals. Project managers are responsible for executing projects and rely on the PMO for governance, methodologies, and support. Functional managers oversee specific departments or areas and provide resources for projects. Project team members contribute to the project deliverables and rely on the PMO for guidance and structure. The involvement of these key stakeholders is crucial for ensuring that the PMO operates effectively and meets the organization’s expectations. 5.What essential aspects should be addressed in the development of action plans for the evolution of the PMO maturity? A. Processes, people and technology. B. Short, medium and long term. C. Current maturity, target/desired maturity and maximum maturity. D. Strategy, tactics and operation. Answer: A Explanation: 3/5 Download PMO-CP Exam Dumps for Best Preparation When developing action plans for the evolution of PMO maturity, the focus should be on processes, people, and technology. These are the foundational pillars of PMO maturity: Processes: Standardizing and optimizing project management processes is essential for improving PMO efficiency and effectiveness. People: Ensuring that the right skills, competencies, and leadership are in place to drive the PMO forward. Technology: Implementing tools and systems that support project management activities, such as project tracking, reporting, and resource management. Focusing on these aspects ensures that the PMO can grow in a structured and sustainable way, continuously enhancing its ability to deliver value to the organization . 6.Why can the performance indicators of each function have different relevance? A. Because each Indicator may have different importance In measuring the generation of value perception in stakeholders. B. Because the relevancies are influenced by the importance of each function. C. Because the relevancies are influenced by the maturity of the PMO. D. Because each indicator has a different potential to generate financial returns. Answer: A Explanation: Performance indicators can have different relevance depending on how critical they are in measuring the value perception among stakeholders. Each function of a PMO contributes differently to the overall success of the project portfolio, and stakeholders may perceive the value generated by each function in various ways. For example, some indicators may be more focused on financial returns, while others may measure customer satisfaction or project efficiency. The significance of each indicator is influenced by the specific goals of the organization and its stakeholders, as well as the role each function plays in delivering value . 7.What does the Personal Competency Adherence indicator (p-CAl) mean? A. The indicator shows the need for resources for the PMO. both quantitatively and qualitatively. B. It demonstrates how much a PMO professional is prepared to perform a particular function, and therefore can vary from function to function. C. The indicator demonstrates how the PMO team is prepared to generate perceived value for its stakeholders. D. It demonstrates how much a professional is prepared to work in the PMO, regardless of the functions to which he is allocated. Answer: B Explanation: The Personal Competency Adherence Indicator (p-CAl) measures the degree to which a PMO professional is equipped with the skills, knowledge, and readiness to perform specific functions within the PMO. Since different PMO functions may require varying levels of expertise and competencies, this indicator can vary depending on the function assigned. It focuses on how prepared the individual is to execute particular roles within the PMO framework. 4/5 Download PMO-CP Exam Dumps for Best Preparation This metric ensures that the right people are allocated to the right tasks, optimizing PMO performance and alignment with the overall project goals. 8.What is the difference between the internal goals and the external goals of the PMO? A. Internal goals are agreed upon with the PMO team and external goals are agreed upon with PMO stakeholders. B. Internal goals do not suffer direct influence from stakeholders. C. Internal goals are used to measure the performance of the PMO team. D. External goals involve external stakeholders in the organization. Answer: A Explanation: The distinction between internal and external goals of the PMO lies in who sets and agrees on them: Internal goals are established within the PMO team and are related to internal performance, processes, and team-based metrics. They focus on optimizing internal operations and improving efficiency. External goals, on the other hand, are agreed upon with PMO stakeholders. These goals focus on delivering value to external parties, ensuring that the PMO meets the expectations of stakeholders such as upper management, clients, and external partners. This alignment of internal and external goals is critical for ensuring that the PMO adds value both internally and externally, maintaining a balanced approach to performance. 9.What are PMO processes? A. They are the processes established to define the functions of the PMO and resources to be allocated. B. They are the processes established for project planning and control. C. They are the established processes to manage projects, programs and portfolio D. They are the processes established for each function performed by the PMO. Answer: D Explanation: PMO processes refer to the specific processes established for each function that the PMO performs. These processes include governance, reporting, resource management, risk management, and supporting project, program, and portfolio management functions. They are designed to ensure that the PMO operates efficiently and consistently while supporting project delivery and aligning with organizational objectives. By establishing clear processes for each PMO function, the organization ensures that there is consistency in how projects are managed and delivered, which leads to better oversight and control. 5/5