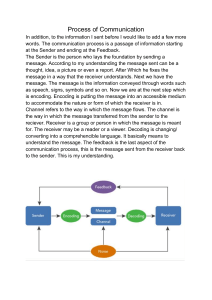
lOMoARcPSD|44391781 Purposive Communication Marketing Management (Polytechnic University of the Philippines) Scan to open on Studocu Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 Purposive Communication Unit 1: Communication Process, Principles and Ethics Communication Sharing thoughts, ideas and opinion The meaning of the latin word “communis” means “common” Communication Process Communication Cycle Decodes Encodes Sender Levels of Communication Channel Message Receiver Encodes Decodes Noise Elements of Communication Sender - it’s the one who encodes the message - the one who first initiate a conversation Message - the ideas and feelings of the sender - make up the context of a communication process Receiver - It’s the one responsible for decoding and understanding the message Feedback - it’s the response of the receiver to the sender Noise - it’s the barrier in effective communication Communication Channel - it’s the means of the sender to transfer or transmit the message to the receiver Context - it is the setting of the sender and receiver Types of Communication according to MODE Verbal Communication - it’s the use of words and texts in communicating with other people Non-Verbal Communication - It’s the use of body language, tone of the voice, gestures, and facial expressions Visual Communication - it’s the use of pictures, images, posters, and illustrations in conveying a message to the people examples are signs and warning Informal Communication - it’s unstructured - it is used when meeting your friends or family - it is unplanned and doesn’t make any considerations - it doesn’t have a set place time, anywhere or anytime they can communicate Intrapersonal Communication - communication with one self - also known as “self-talk” Interpersonal Communication - the process of communication with two or more people - functions among relatively of small people Public Communication - one speaker, many listeners - your communicating with more people Example : graduation and speech Mass Communication - it’s the use of mass media to transmit message to a large number of audience/people Example : news flash Organization/ Business Communication - it only exist in a certain organization - takes note of the flow of communication - can be vertical or horizontal communication Vertical Communication - can be upward or downward - downward - the superior or head communicates or transmit a message to the lower people - upward - the people with lower position transmits a message to the higher people Example : Principal - faculty staffs (downward) Faculty Staffs - Head Chief (Upward) Horizontal Communication - the people involve has the same level of position or status, it could be your peers or family - it’s a communication with the people same position as you in an organization Models of Communication Models of Communication - how the flow of communication is done 1) Aristotle’s Model (Linear Model) - has three elements of communication - the person at the end of the communication process which is the “Listener” makes the process successful or not - it’s in the listener’s hand the success of communication process Two Types of Communication Formal Communication - must be aware of the languages you will use - it is structured and make considerations - it is usually planned and used in business formal meetings - there is a set time and place Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 2) Berlo’s Model - it has four elements of communication - the source refers to encode the message and this message is transmitted through channel and the receiver decodes it 3) Osgood-Schramm’s Model - It does not come in linear form but circular form - it’s a continous cycle of communication 4) Schramm’s Model Source Communication skills - the ability of the source to communicate properly, write, read and speak clearly Attitude - the source must be aware of his/her own attitude towards the receiver to avoid conflict Knowledge - the source must know the in and out of the topic Social System - the source must be aware of the cultural beliefs and religious of the audience to avoid boredom and misunderstanding Culture - it refers to the cultural background of the community or the listeners when the speakers is communicating or delivering speech Message - the sender and receiver must have the same field experience for them to have effective communication - both must have same experience in order for them to communicate 5) Helical’s Model Content - everything that the speaker said is the content Elements - refers to the gestures, facial expressions and body language a speaker uses Treatment - the way one treats his message and is conveys to the listeners. It has something to do how you convey or deliver your message for your audience to understand Structure - present ideas logically for the receiver to understand the message Code - all the elements should be delivered well cause if not there will be no effective communication Channel - the use of “five senses”: Hearing, Seeing, Tasting, Smelling and Touching Receiver - the same with source Note: Berlo says “For effective communication to take place the source and receiver must be on the same level of communication” - It is unrepeatable, continuous, dynamic, and additive - unrepeatable - the topic you had when you where a toddler will change as you grow - continuous - because the communication continues and never stops - additive - it add knowledge as you grow - dynamic - because it’s from birth to perish in the earth Principles of Communication Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 Clarity of Thoughts (Clear) - it’s the responsibility of the sender to send a clear message to the receiver by using simple words for the receiver to understand - do not use any language that is not known to them Coherence - there should be a slow smooth idea - logically order and organized - important principle of communication Concise - you have to be concise in the message you will transmit or share - short but complete message Go direct to the point of the message you want to convey but with complete details - avoid flowery words and just go straight to the point Correctness - the proper use of grammar, spelling, and punctuation - a particular mistake in the word you will use might change the meaning into the word you want to convey - one mistake will make the context be misunderstood - use proper tone and level of communication Completeness - there is a need for you to look necessary or important information - the sender must send a complete information for the reader to fully understand and will not ask any questions anymore - make use of complete detailed information Concreteness - being very specific with the words you will use - may contain facts and figures - specific with figure Courtesy - very important in communicating - is being polite to other people whenever you communicate - must be observe in any context of communication - maintain respect with other people - in order for you to understand one another you must be courtesy Ethical consideration in Communication 1. 2. 3. 4. Respect Audience - be respectful with your audience - consider the audience ideas and the speaker also - respect each other to have good interaction Consider the Consequences pf their communication - consider the words you will use because it might hurt the feelings of your audience - considering the feelings of other people and the words we use reduce the conflict and misunderstanding Values Truth - share only the truth - a deal of ethnics involves respecting the truth - give the exact information and truth your audience 5. 6. - When you borrow idea from another person, author or in the internet do not forget to cite and give credits - Using information correctly is important so it will not mislead the audience Do not Falsify Information - do not make false information because we might fail to our goal - this will to you misleading your audience from the truth Do not sugar coat and go directly to the point Respect the right of others to information - it means respecting the rights of others will learn the access of information of other people - you must not use the information you collected in a bad way - do not deprive others to know the information - give access to other with the information use Unit 2 : Local and Global Communication in Multicultural Setting LOCAL COMMUNICATION It’s being able to communicate with the members of your local area It can be either in your area where you grew up (mother tongue) or a common dialect your speak on your town A communication within your local area GLOBAL COMMUNICATION It’s used to describe ways to connect, share, relate, and mobilize across geographic, political, economic social and culture divides A communication within global or around the world with use of universal language (English) MULTICULTURAL It refers to a society that contains several cultural or ethnic groups A communication with people with different races, language, dialect, views, religions, and opinions A communication in a one place with people with different values, beliefs, religions, races, or ethnics can be either ilocano, itawes, bisaya or ilongga Common Cultural in Multicultural Setting It’s the process of communication by people having different cultural backgrounds, ideologies, beliefs, and practices To facilitate communication, understanding and acceptance of cultures of parties involved in the communication process is necessary Note: Use the common language we are familiar with when communicating with other people that has different language or dialect or cultural background from us to understand one another and avoid misunderstanding. INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION Use Information Correctly Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 - refers to the interaction with people from diverse cultures - maintaining what is true and avoid spreading false information - share information that is only true when communicating Forms of Intercultural Communication 1. Interracial Communication - it’s communicating with people from different races. Ex. A Filipino interacting with an American 4. Maxim of Manner - in the local culture, the manner of saying the word is more regarded than its content - “body language meanings vary greatly from culture to culture” - the meanings of body languages to a certain culture may vary from other cultures 2. Inter-ethnic Communication - it’s interacting with people with different ethnic groups. 3. Intracultural Communication - it’s interacting with the same members of the same racial or ethnic group or co-culture. It’s communicating with the same dialect. Ex. Bisaya-Bisaya, Ilocano-Ilocano, and etc. 4. International Communication - it is where each nationalities represents their nation. Ex. Miss Universe and Summits INTERCULTURAL COMPETENCE - it’s ability to function effectively across cultures, to think and act appropriately and to communicate and work with people from different cultural backgrounds - able to communicate and understand them - understand whom they are communicating with - know what to say and not to say COMMUNICATION STRATEGIES IN MULTICULTURAL SETTINGS ASSIMILATION - i which members attempt to fit in with the member of that dominant culture ACCOMODATION - in which members maintain their cultural identity while striving to establish relationships with the members of the dominant culture SEPARATION - in which members resist or refuse interacting with members of the dominant culture Four Maxim of Grice’s Principle of Cooperation Conversation 1. Maxim of Relation - a norm that dictates the needs of the interlocutors to become sensitive in the communication process - they communicate considering the norm of the participant in the communication process - consider the feelings to whom we are communicating with 2. Maxim of Quantity - every interlocutor should observe a “fair-share-talk” of time - Everyone must be given the opportunity to talk - one should not be dominating the communication process and give others a chance to talk 3. Maxim of Quality - every interlocutor should maintain what is true in a given conversation VARIETIES AND REGISTERS OF SPOKEN AND WRITTEN ENGLISH LANGUAGE Varieties of English Language Is the various types of English dialects that are practice by people from all the world Language Register Is the appropriateness of writing and speaking styles Word Englishes American English British English Canadian English Indian English Jamaican English South African English New Zealand English Australian English Varieties of English Language British English Phonology /r/ - quicker brother mother sister /r/ - stronger brother mother sister /i/ - /al/ financial advertisement /i/ - /i/ financial advertisement /t/ - /not flap/ city computer ability /t/ - flap /d/ city computer ability British English Spelling /re/ calibre goltre centre litre fibre lustre American English Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) American English /er/ caliber golter center liter fiber luster lOMoARcPSD|44391781 British English /ence/ defence licence practise American English /ense/ defense license practice /our/ colour favourite neighbour /or/ color favorite neighbor /t/ dreamt leanrt burnt /ed/ dreamed learned burned VOCABULARY American English apartment college vacation schedule airplane Mail box cookie sweater LANGUAGE REGISTER Defined as the appropriateness of the level of the style of speaking and writing 1. /que/ banque checque chequer /k/ bank check checker /ise/ analyse criticise recognise /ize/ analyze criticize recognize /l/ enrolment fulfil skilful /ll/ enrollment fulfill skillful /ogue/ analogue dialogue catalogue /og/ analog dialog catalog Common Words American jewelry program mom tire whiskey mustache plow British jewellery programme mum tyre whisky moustache plough British English Grammar Prepositions (days, season) I’m going to a party at the weekend. What are you doing at Christmas? American English Prepositions I’m going to a party on weekend. What are you doing on Christmas? Present perfect tense when describing something that has recently occurred I’ve eaten too much. I’ve been to the shop. Past simple tense - when describing something that has recently occurred I ate too much. I went to he shop. British English flat university holiday Time table aeroplane Post box biscuit jumper 2. 3. FORMAL REGISTER - it’s the style of writing or speaking for unfamiliar audience/readers or for superiors in an office INFORMAL REGISTER - it’s otherwise called the “casual” or “intimate” register is recording when writing and speaking to friends and familiar persons FROZEN/ STATIC REGISTER - when the language is literally “frozen” in time and form and it does not change. OBTAINING, PROVIDING, INFORMATION AND DISSEMINATING INFORMATION Facts provided or learned about something or someone Knowledge obtained from investigation study or instruction The news and knowledge we receive To what is given to someone A summarize data “CONTEXT” - the event idea happened and the circumstances talked about the event “CONTENT” - the information directed towards to the end user “MEANING” - meaning or messaged conveyed by the information Characteristics of INFORMATION RELEVANT - if they are useful or applicable to the reader VALID - it must be credible and accurate and well founded RELIABLE - it is supported by sources and trusted and consistent FACTUAL - it is confirmable and documented ACCURATE - related to factual COMPLETE - share complete infos that the reader will understand TIMELY - share information shortly but must be complete Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 TOPIC 1: Types of INFORMATION Modes of Information Dissemination FACTUAL - is an information that solely deals with facts - it is short , non-explanatory, and rarely gives indepth background on a topic Synchronous - (Rich) two way communication with virtually no time delay. Allowing real-time response ANALYTICAL - is the interpretation of factual information - what does the factual information mean? What does is it imply? This is the type of information that the researchers generate in the their studies Examples: Conversation Presentation Telephone Door-to-door Meetings SUBJECTIVE - information from only one point of view - opinions are always subjective OBJECTIVE - information that is understood from multiple viewpoints are presents all sides of an argument TOPIC 2: Obtaining INFORMATION INTERVIEW - informational interview - a discussion with someone who has the information you want to know Observe the following when doing an INTERVIEW: Keep the interview concise Be respectful Prepare the questions early and do not asks personal questions Take note the answers of interviewee Asks permission first before interviewing someone and discuss why you are doing an interview OBSERVATION - by watching purposely according to the information - observe equally and do not be bias. Be objective when observing SURVEY - used for collecting data - is to be able to set information from your respondents TOPIC 3: Disseminating Information INFORMATION DISSEMINATION Means spreading of information, knowledge, opinions widely to a certain person, people or to a bigger group of audience The purpose of dissemination is to influence people’s behavior, so that they will adopt or at least become aware of a new idea, product or service which is being disseminated Asynchronous - (Reach) two-way communication with a time delay, allowing response at user’s convenience Examples: E-mail Website Notice Report Newsletter 1. New Release - a written recorded communication directed at the members f the news media for the purpose of announcing something ostensibly newsworthy 2. Blog - a regularly updated website or web page, typically one run by an individual or small group, that is written in an informal or conversational style 3. Emails - messages distributed by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network 4. Text Message - a written message, often containing short forms of words, sent form one mobile phone to another 5. Social Networking Websites/ Social Media - an online platform whch people use to build social networks or relations with other people who share similar personal or career interests, activities, backgrounds or real-life connections 6. Public Service Announcements - a message in the public interest disseminated without charge, with the objective of raising awareness of, and changing public attitudes and behavior towards a social issue 7. Door-to-Door - a canvassing technique hat is generally used for sales, marketing, advertising, or campaigning, in which the persons walk from the door of one house to the door of another, trying to inform, announce, sell or advertise a product or service to the general public or gather information 8. Community Meetings - a small-group method collecting information from community members. It is used to provide a directed but highly interactive discussion. Similar to but less formal than a focus group, and it is usually includes a larger group Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph) lOMoARcPSD|44391781 Downloaded by FRANCISCO, ELJAY A. (xt202001491@wmsu.edu.ph)