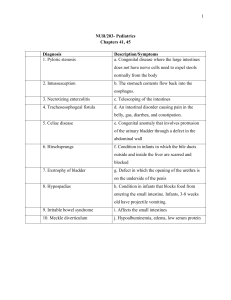
PEDIATRICS 100 ESSENTIAL ONE LINERS Must know for NEET PG 2023 Dr Meenakshi Bothra Gupta 0 1 Most common cause of short stature during childhood is constitutional delay in growth & puberty Bone age C Chr age score 2 macrocephaly Microcephaly is head circumference < - 3 z score of expected according to age and sex some synd carpenter pfeiffer sojourn 3 Craniosynostosis port leads to abnormal head shape due to premature fusion of cranial sutures 4 In Achondroplasia there is large head with short limbs, trident hand & champagne glass pelvis US IS ratio Increases Hypophosghetfisprex 5 Rett syndrome is a X linked dominant disorder with acquired microcephaly, delayed development and stereotypic hand wringing movements 6 6 6 7 13 m E E Delayed dentition is when no teeth erupts by 13 months age Emitting 7 First sign of puberty in females is Thelarche & First sign of puberty in males is Testicular Enlargement 8 In any sick child with medical emergency, ABCDE steps are performed. A- Airway B- Breathing C- Circulation DAVP U E- Eighty 9 Severe acute malnutrition in a child (6m – 5yr) is defined as presence of 1 or more of: weight for height < 70% or < -3 z score of expected, mid upper arm circumference < 11.5 cm or symmetric bipedal edema of nutritional origin. E 10 83 I i 11 Earliest symptom of vitamin A deficiency is Night blindness while earliest sign is Conjunctival xerosis L 12 Zinc deficiency can lead to growth failure, diarrhea, hypogonadism, alopecia, poor wound healing Acrodermatitis Enteropathica 13 Calculation of maintenance fluid requirement in children (per day): For 1st 10 kg: 100 ml/kg F Beyond 20 kg: 20 ml/kg 14 For next 10 kg: 50 ml/kg past 10 100 1000 4 Imitation 50 Efme 24hr 14 Intravenous fluids in neonates Daily fluid requirements during 1st wk of life (ml/kg/day) Birth wt Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 ≥D 7 <1500g 80 95 110 120 130 140 O 150 ≥1500g 60 75 90 105 120 135 150 • Initial fluids: 10% Dextrose with no electrolytes • Maintain glucose infusion rate 4-6 mg/kg/min • Na & K should be added to IV fluid after 48 hours 15 Breat milk contains more lactose & lesser protein as compared to cow’s milk & Breast milk contains adequate amounts of all vitamins except vitamin D, vitamin K (& vitamin B12 in strictly vegan mothers). 15 16 For how long can expressed breast milk be stored? • At room temp → 8-10 hours • Refrigerator → 24-48 hours • Deep freezer (-20oC) → 3 months E 16 17 In dominant disorders at least 1 of the parents is usually affected & father to son transmission rules out X linked inheritance 18 Fragile X syndrome is due to > 200 CGG repeats; Loss of function mutation of FMR1 gene is seen In o Ig DID 19 Confirm Fetal karyotype Biochemical marker used for Antenatal screening of Down Syndrome during 1st trimester: PAPP-A, HCG 2nd T s Triple AFP Quadruple test Triple test UE Init 20 Multiple fractures in antenatal USG → Most likely diagnosis: Osteogenesis imperfecta BY SNH 21 Most common chromosomal abnormality in children is Down syndrome, which is most commonly caused by maternal meiotic non-disjunction 22 Most common Glycogen storage disease in children is Von Gierke disease (type I GSD) Breastfeeding 23 al Most common enzyme deficient in Galactosemia is GALT (Galactose 1 phosphate uridyl transferase) É Galactokinese Epimerase 24 In phenylketonuria, FeCl3 test with urine gives green colour; while In MSUD, FeCl3 test with urine gives blue color and Darkening of urine on standing is seen in Alkaptonuria 25 A child with seizures and lethargy with metabolic acidosis along with skin rashes and / or alopecia → think of Biotinidase deficiency or Multiple Carboxylase deficiency É 26 Metabolic diseases in which Cherry red spot is seen: GM1 gangliosidosis, Niemann Pick disease, Tay Sach disease 27 Enzyme replacement therapy is available for: Gaucher Disease Hurler disease Pompe disease Fabry disease Niemann Pick DIsease t 28 Palpable purpura in a child with presence of one or more of arthritis/arthralgia, abdominal pain, renal involvement or any biopsy showing IgA deposition is diagnostic of Henoch Schonlein Purpura F 29 Congenital CMV is the most common non-genetic cause of sensorineural deafness in children 30 Congenital Rubella Syndrome classically presents with cataract, cit sensorineural deafness and congenital heart diseases Y PDA 31 Hypoplasia of limbs and scarring is caused due to congenital varicella 32 Hutchinson’s triad a consists of Interstitial Keratitis, Sensorineural deafness and Hutchinson’s teeth w 33 Pleomorphic skin rashes are suggestive of Varicella infection while erythematous maculopapular rash with conjunctivitis and coryza is suggestive of Measles 34 Most common Complication of Measles is Otitis media, but Most common cause of Death in Measles is Pneumonia. 35 Both f-IPV and PCV are recommended at 6 weeks, 14 weeks and 9 months in the National Immunisation Schedule 36 If the first dose of measles vaccine was given at 7 months, when should we schedule the next dose? 1st dose at 9 months and next at 16-24 months photos 37 Open vial policy i allows re-use of partially used multidose vials of vaccines like Pentavalent vaccine, OPV, IPV, upto 28 days, provided expiry date of vaccine has not passed, cold chain is properly maintained, aseptic precautions have been taken and the vaccine vial septum is not leaking. 38 Serious Adverse effects of DPT include persistent crying, fever > 40.5°C, seizures, hypotonic hyporesponsive episodes (HHEs), and encephalopathy & DPT is contraindicated in h/o anaphylaxis or encephalopathy within 7 days of previous DPT & progressive neurological diseases 39 Causes of delayed passage of meconium in a neonate include Hirschsprung disease & Cystic Fibrosis 40 Cold stress → 36– 36.4oC Moderate hypothermia → 32– 35.9oC Severe hypothermia → < 32oC nytimes. a 214.02 41 If a neonate is found to have a heart rate of < 100/minute at birth, positive pressure ventilation is recommended, but if the heart rate becomes < 60/minute, chest compressions are also recommended along with positive pressure ventilation using 100% oxygen FEE 42 In neonatal resuscitation, chest compression : positive pressure ventilation is given at 3:1 a 43 Absolute contra-indication of bag and mask ventilation is congenital diaphragmatic hernia 44 Causes of Asymmetric Moro’s reflex: Fracture clavicle Shoulder joint dislocation Congenital Hemiplegia Erb’s palsy É 45 Most common type of seizures in neonates: Subtle N Sz for phenobarbital DOC 46 Neonate is Hyperalert in Stage I HIE & Moro’s reflex is exaggerated; Seizures are a feature of stage 2 HIE while Baby is severely hypotonic in stage 3 HIE & Moro’s reflex is absent F 47 EE 48 Cephalhematoma takes 24-48 hours to appear completely & 5-7 weeks to disappear & it does not cross sutures while Caput succedaneum is present at birth in its maximum size and it disappears in 48-72 hours. 49 Advantages of Kangaroo Mother care include lesser chances of neonatal hypothermia and nosocomial sepsis, lesser duration of hospital stay and higher exclusive breastfeeding rates. ginny Most common congenital abnormality in specs most 50 Infant of Diabetic mother (IDM) is Congenital heart disease (Most common CHD is VSD, while most specific CHD is TGA) 51 Brongpogomor Most important mechanism by which phototherapy acts is structural isomerisation needed go to 52 Most important risk factor for NEC is Prematurity 53 Most common type of Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia is Bochdalek (posterolateral) variety. 54 Most common cause of Neonatal Sepsis in India: Acinetobacter (Latest update) > Klebsiella PDA 55 Continuous TOF ESM in machinery palm once mum Most common congenital heart disease, affected by Infective endocarditis is Ventricular septal defect ASD wide fixed split of S2 56 Most common heart disease in Down syndrome is AV septal defect or Endocardial cushion defect Ff tumer Noonan s Williams PS Suparah AS 57 Most common congenital heart disease causing mortality in 1st week of life is Hypoplastic left7heart syndrome 58 Condition which worsens with prolonged infusion of Prostaglandin E: Obstructed TAPVC Close Ductus arteriosus in Preterm N Indomethecin Ibuprofen 59 In fetus maximum oxygen saturation is found in umbilical vein followed by Inferior vena cava; while minimum oxygen concentration is found in Umbilical artery 60 If a child with VSD or PDA or ASD develops Cyanosis & Clubbing, think of Eisenmenger syndrome F 61 Most common cause of cyanosis in a child is Tetralogy of Fallot, while in a neonate, it is Transposition of great vessels 62 Atrial septal defect is not a component of Tetralogy of Fallot but it is a component of Trilogy of Fallot and Pentalogy of Fallot 63 Egg on side appearance is seen in Transposition of great arteries, boot shaped heart in Tetralogy of Fallot, snowman appearance in Total Anomalous Pulmonary venous connection & Box shaped heart in Ebstein Anomaly. 64 Most common primary intraocular Tumor in children is Retinoblastoma & Most common presentation of Retinoblastoma is leukocoria (white pupil) 65 Drugs used for Iron chelation in a child with Thalassemia (started when serum ferritin >1000 ng/ml) are: Desferrioxamine, Deferiprone & Deferasirox 66 Most common viral agent causing diarrhea in children is Rotavirus 67 Most common extraintestinal manifestation of celiac disease is refractory iron deficiency anemia 68 Most common cause of portal hypertension in children in India is Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction. 69 Most common cause of stridor in neonate and young infant is Laryngomalacia 70 Most common cause of Common cold is Rhinovirus 71 Most common cause of Croup is Parainfluenza virus while most common cause of Acute Epiglottitis is Streptococcus 7 72 Treatment of mild Croup includes single dose Dexamethasone while moderate to severe croup also requires Nebulised Epinephrine, inhaled oxygen along with intravenous fluids E 73 Most common cause of Bronchiolitis is Respiratory syncytial virus 74 Most common cause of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children is minimal change disease 75 Schwartz formula for calculation of estimated GFR in children: eGFR = k x length (cm) Serum Cr ingldl 40 0.47100where, k is 0.413 Ny Schistose 76 Hemolytic uremic syndrome is a triad of Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia, Thrombocytopenia & Renal insufficiency Eculizumet 77 Staging of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Stage Serum Cr 1 >0.3 mg/dl increase or 1.5-1.9 < 0.5 ml/kg/hr for 6-12 times baseline hrs 2 2-2.9 times baseline 3 > 3 times baseline or serum Cr > 4 mg/dl or need of RRT En Urine output I < 0.5 ml/kg/hr for > 12 hours < 0.3 ml/kg/hr for > 24 hr or Anuria for > 12 hr 78 Most common cause of hydronephrosis in a newborn : Ureteropelvic Pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction 79 Most common cause of urinary obstruction in boys : posterior urethral valves 80 Most common cause of pyelonephritis and recurrent urinary tract infection in children is Vesicoureteric Reflux (VUR) 81 Esan 3Mt Most common cause of gross hematuria in 1 children 1-2 days after upper respiratory infection is IgA nephropathy 82 Most common cause of congenital hypothyroidism is Thyroid dysgenesis while most common cause of congenital hypothyroidism in a child with goitre is Thyroid dyshormonogenesis 83 Most common cause of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) is 21 hydroxylase deficiency at MMFF 84 Most common cause of Cushing syndrome is prolonged exogenous administration of glucocorticoids 85 Most common cause of seizure in children < 5 years is Febrile seizures 86 Most common location of Meningomyelocele is Lumbosacral region 87 Dose of Folic acid to prevent Neural tube defects is 400 ug per day to all women of childbearing age and 4000 ug/day to high risk women, starting at least 1 month before conception Ya 88 Treatment of choice for infantile spasms: ACTH worth 89 Most common cause of an elevated CSF opening pressure is an agitated child 90 Most common neurobehavioral disorder of childhood is Attention Deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) 91 Nusinersin spindrift In a floppy child with normal social and cognitive milestones with tongue fasciculations, think of SMA; Floppy child with hypertophic cardiomyopathy and hepatomegaly → think of Pompe’s disease E x 92 Corticosteroids A male child with progressively increasing weakness of proximal muscles with Gower sign and valley sign positive and pseudohypertrophy of calf muscles and highly elevated CPK values, think of DMD It 93 Most common surgical cause of non-bilious vomiting in infants is Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis 94 Most common abdominal emergency of early childhood is Intussusception 1 dangled spring 95 Marsh grading Best screening tests for Celiac disease is a combination of anti ttG IgA and total IgA anti CRI Endo te I 0 X U LN 96 Most common cause of intestinal obstruction between 3 months to 6 years of age: Intussusception 97 Treatment of acute Diarrhea includes prevention &/or treatment of dehydration, zinc therapy and continuing normal diet 98 Rickets leads to cupping, fraying and splaying of ends of long bones É 99 Scurvy leads to gum bleeding, prominent costochondral junctions and painful pseudoparalysis of limbs 100 Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is Arthritis of one or more joints, lasting atleast 6 weeks in a child <16 yrs age. Nothing is Impossible to a willing heart!