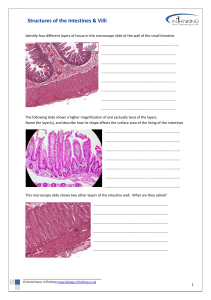
1 NUR/203- Pediatrics Chapters 41, 45 Diagnosis 1. Pyloric stenosis Description/Symptoms a. Congenital disease where the large intestines does not have nerve cells need to expel stools normally from the body 2. Intussusception b. The stomach contents flow back into the esophagus. 3. Necrotizing entercolitis c. Telescoping of the intestines 4. Tracheoesophogeal fistula d. An intestinal disorder causing pain in the belly, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. 5. Celiac disease e. Congenital anomaly that involves protrusion of the urinary bladder through a defect in the abdominal wall 6. Hirschsprungs f. Condition in infants in which the bile ducts outside and inside the liver are scarred and blocked 7. Exstrophy of bladder g. Defect in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis 8. Hypospadias h. Condition in infants that blocks food from entering the small intestine. Infants, 3-8 weeks old have projectile vomiting. 9. Irritable bowel syndrome i. Affects the small intestines 10. Meckle diverticulum j. Hypoalbuminemia, edema, low serum protein 2 Diagnosis 11. Enuresis Description/Symptoms k. Failure or an incomplete descent of the testicle(s) 12. Glomerulonephritis l. Repair is typically done at 2-3 months of age 13. Gastroesophogeal reflux disease m. The opening of the foreskin is too tight 14. Biliary atresia n. Fluid collection around the testes 15. Cleft lip o. Passage of urine at night in children that are potty trained 16. Cleft palate p. Tissue in the small or large intestine is injured or begins to die off. 17. Phimosis q. Repair done typically at 8 to 12 months 18. Hydrocele r. Caused by a recent strep infection 19.Cryptorchidism s. Common congenital abnormality where there is an abnormal connection between the esophagus and the trachea 20. Nephrotic syndrome t. The most common congenital malformation of gastrointestinal tract. It can cause complications in the form of ulceration, hemorrhage,