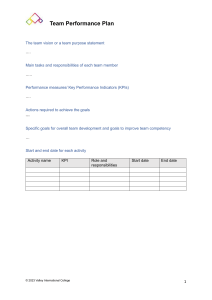
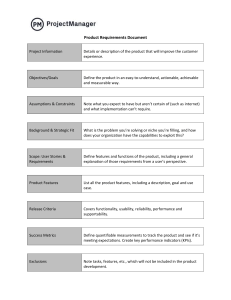
What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an organization, department, or individual is achieving key business objectives. Organizations use KPIs at multiple levels to evaluate their success at reaching targets. High-level KPIs may focus on the overall performance of the enterprise, while low-level KPIs may focus on processes in departments such as sales, marketing, HR, or support. The Importance of KPIs 1. Aligning Goals with Business Objectives: KPIs help ensure that individual and team goals are aligned with the broader business objectives. This alignment is critical for driving the organization forward cohesively. 2. Enhancing Performance: By setting clear and measurable targets, KPIs motivate employees to perform at their best. They provide a benchmark against which performance can be measured, encouraging continuous improvement. 3. Data-Driven Decision Making: KPIs provide quantitative data that can be used to make informed decisions. This data-driven approach reduces guesswork and allows for more strategic planning and resource allocation. 4. Identifying Issues Early: Regular monitoring of KPIs helps in identifying performance issues early on. This allows for timely interventions and corrective actions, minimizing potential negative impacts. 5. Accountability: KPIs foster a culture of accountability by clearly defining what success looks like. They make it easier to track progress and hold individuals and teams responsible for their performance. Developing Effective KPIs 1. Relevance: KPIs should be relevant to the specific goals and responsibilities of the role or department. Irrelevant KPIs can lead to wasted efforts and resources. 2. Measurable: KPIs need to be quantifiable. This allows for objective assessment of performance. 3. Achievable: While KPIs should be challenging, they must also be attainable. Unrealistic targets can demotivate employees and lead to burnout. 4. Time-Bound: Effective KPIs should have a clear timeframe. This helps in tracking progress and maintaining focus. 5. Actionable: KPIs should provide actionable insights. They should help in identifying specific areas that need improvement or further investment. Implementing KPIs 1. Define Clear Objectives: Begin by defining the key objectives that the KPIs will measure. These objectives should align with the overall business goals. 2. Involve Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the development of KPIs to ensure buy-in and relevance. This includes employees who will be measured by these KPIs. 3. Establish Baselines: Determine the current performance levels to establish baselines. This will help in setting realistic and achievable targets. 4. Communicate KPIs: Clearly communicate the KPIs to all relevant parties. Ensure everyone understands what is being measured, why it is important, and how it will be measured. 5. Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the KPIs and review them periodically. Make adjustments as necessary to reflect changes in business priorities or operating conditions. Examples of Good and Bad KPIs Good KPIs 1. Mobile Solution Upsell Rate o KPI: Achieve a 30% increase in the upsell rate of mobile solutions during client presentations. 2. Quarterly UI/UX Enhancement o KPI: Successfully enhance the UI/UX of at least one product per quarter. 3. UI/UX Enhancement o KPI: Achieve 100% compliance with the implementation of planned UI/UX enhancements. 4. Sprint Deadline Compliance o KPI: Achieve 100% compliance with assigned tasks within the sprint deadline. 5. Ticket Resolution Timeliness o KPI: Maintain 100% compliance with the given turnaround time for assigned tickets. 6. Downtime Minimization o KPI: Downtime less than 2 hours 7. User Acceptance Testing (UAT) Success Rate o KPI: 95% of UAT test cases passed Bad KPIs 1. Hours Worked: o Measure: Total hours worked by employees. o Reason: This KPI focuses on effort rather than outcomes. High hours worked do not necessarily correlate with productivity or quality. 2. Number of Meetings: o o Measure: Total number of meetings conducted. Reason: While meetings are important for coordination, the number of meetings is not a good indicator of project success. It can lead to inefficient use of time. 3. Lines of Code Written: o Measure: Total lines of code written. o Reason: More lines of code do not equate to better software. This KPI can encourage verbose coding practices rather than efficient and effective solutions. KPIs are essential for driving performance, aligning efforts with business objectives, and facilitating data-driven decision-making. By developing relevant, measurable, achievable, timebound, and actionable KPIs, tech companies can ensure they are on the right path to success. Implementing these KPIs effectively, with clear communication and regular monitoring, will help maintain focus and accountability across the organization. Avoiding irrelevant or counterproductive KPIs is equally important to ensure that efforts are directed towards meaningful and impactful outcomes. If you need any assistance, the HR department can facilitate you in the development and implementation of effective KPIs, ensuring they are aligned with your team’s objectives and the company’s strategic goals.