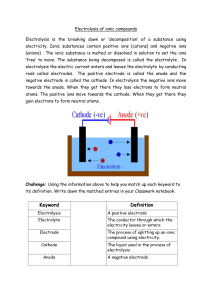
GCSE IGCSE AS A Level O Level IB AP Other My account CIE IGCSE Chemistry Revision Notes IGCSE Chemistry CIE Revision Notes 4. Electrochemistry 4.1 Electrolysis 4.1.1 Electrolysis Principles 4.1.1 Electrolysis Principles Download PDF 1. States of Matter Test Yourself 2. Atoms, Element… 3. Stoichiometry Electrolysis: General Principles When an electric current is passed through a molten ionic compound the compound decomposes or breaks down 4. Electrochemistry The process also occurs for aqueous solutions of ionic compounds Covalent compounds cannot conduct electricity hence they do not undergo electrolysis 4.1 Electrolysis Ionic compounds in the solid state cannot conduct electricity either since they have no free ions that can move and carry the charge 4.1.1 Electrolysis Principles 4.1.2 Electrolysis of Molten Compounds 4.1.3 Electrolysis of Aqueous Sodium Chloride & Dilute Sulfuric Acid Particles in ionic compounds are in fixed position in the solid state but can move around when molten or in solution 4.1.4 Electrolysis of Key terms used in a simple electrolytic cell Aqueous Solutions Electrode is a rod of metal or graphite through which an electric current flows into or out of an electrolyte 4.1.5 Ionic Half Equations Electrolyte is the ionic compound in a molten or dissolved solution that conducts the electricity Anode is the positive electrode of an electrolysis cell 4.2 Applicatio… Anion is a negatively charged ion which is attracted to the anode Cathode is the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell Cation is a positively charged ion which is attracted to the cathode 5. Chemical Energ… 6. Chemical Reacti… 7. Acids, Bases & S… 8. The Periodic Table 9. Metals 10. Chemistry of th… 11. Organic Chemis… The basic set-up of an electrolytic cell 12. Experimental Te… Metals and hydrogen form positively charged ions and so either a metal or hydrogen gas is formed at the cathode Non-metals form negatively charged ions and so non-metals (except hydrogen) are formed at the anode Exam Tip Use the PANIC mnemonic to remember which electrode is the positive and which is the negative: Positive (is) Anode Negative Is Cathode Electrolysis: Charge Transfer EXTENDED During electrolysis, current needs to flow around the circuit In order for this to occur, charge must be transferred around the circuit (current is a measure of the rate of flow of charge) by charge carriers The power supply provides the cathode with a supply of electrons, causing it to become negatively charged Positive ions (cations) in the electrolyte move towards the cathode where they gain electrons Negative ions (anions) in the electrolyte move towards the anode where they lose electrons The electrons move from the anode back towards the power supply So, in a complete circuit: Electrons are the charge carriers in the external circuit Ions are the charge carriers in the electrolyte Diagram showing the direction of movement of electrons and ions in the electrolysis of NaCl Test yourself Did this page help you? Next topic Yes No Author: Alexandra Alex studied Biochemistry at Newcastle University before embarking upon a career in teaching. With nearly 10 years of teaching experience, Alex has had several roles including Chemistry/Science Teacher, Head of Science and Examiner for AQA and Edexcel. Alex’s passion for creating engaging content that enables students to succeed in exams drove her to pursue a career outside of the classroom at SME. Resources Members Company Quick Links Join Launchpad About us Past Papers Help Center Account Contact us Biology Archive Log out Jobs Chemistry Terms Physics Privacy Maths Geography English Literature Psychology Missing a Subject or Exam Board? Tell us © Copyright 2015−2024 Save My Exams Ltd. All Rights Reserved. IBO was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, the resources created by Save My Exams.