Hypertension & Diabetes Treatment Seeking Behavior Research
advertisement

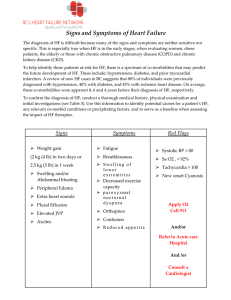
“Factors associated with low treatment seeking behavior among patients of Hypertension and Diabetes” INTRODUCTION. Hypertension (HTN) and diabetes mellitus (DM) are rapidly emerging as public health threats in developing countries.[1,2] HTN and DM are high in geriatric population across all geographical area and sociodemographic groups in uganda.[3,4] HTN and DM affect 1 billion and 422 million[6] people worldwide, respectively. Treatment-seeking behavior significantly influences the course and outcome of mental, social and physical problems associated with Hypertension and Diabetes. However, there is a dearth of information on the treatment-seeking behaviour of persons with Hypertension and Diabetes in Uganda. Understanding treatment-seeking behaviors and associated factors of Hypertension and Diabetes patients in local communities helps to improve health services via promoting prompt treatment, improving patients’ prognosis, finding information and timely treatment. 80% of people suffering from Hypertension and diabetes do not actually know they have it and this attributable to low poor treatment seeking behavior. This study therefore aims at un earthing the barriers and enablers for this behavior. Need for the study Hypertension or elevated blood pressure ̶ is a serious medical condition that significantly increases the risks of heart, brain, kidney and other diseases. An estimated 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 years worldwide have hypertension, most (two-thirds) living in low- and middle-income countries an estimated 46% of adults with hypertension are unaware that they have the condition. Less than half of adults (42%) with hypertension are diagnosed and treated References. 1. Bhardwaj R, Kandori A, Marwah R, Vaidya P, Singh B, Dhiman P, et al. Prevalence, awareness and control of hypertension in rural communities of Himachal Pradesh. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010;58:423–4. 429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] 2. Verma R, Khanna P, Mehta B. National programme on prevention and control of diabetes in India: Need to focus. Australas Med J. 2012;5:310–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] 3. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension Problem Statement: "Exploring Factors Associated with Low Treatment-Seeking Behavior Among Patients with Hypertension and Diabetes: A Multidimensional Analysis" Problem Description: Hypertension and diabetes are two of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide, posing significant health risks and economic burdens. Effective management of these conditions primarily relies on timely medical intervention, regular monitoring, and adherence to treatment plans. However, a considerable number of patients with hypertension and diabetes do not know they have it and exhibit low treatment-seeking behavior, leading to suboptimal health outcomes and increased healthcare costs. Understanding the factors associated with this phenomenon is crucial for developing targeted interventions to improve treatment-seeking behavior and overall patient wellbeing. This study aims to investigate the multidimensional factors contributing to low treatment-seeking behavior among patients with hypertension and diabetes. By examining various aspects such as individual characteristics, socioeconomic factors, healthcare system barriers, psychosocial influences, and cultural aspects, we seek to identify the underlying determinants influencing patients' decisions to seek or delay seeking treatment. Through a comprehensive analysis, we aim to provide evidence-based insights and actionable recommendations to healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders to address the gaps in treatment-seeking behavior and enhance patient care for hypertension and diabetes. Key research questions: What are the individual characteristics that influence treatment-seeking behavior among patients with hypertension and diabetes? How do socioeconomic factors such as income, education, and health insurance coverage impact treatment-seeking behavior for these conditions? What are the healthcare system-related barriers (e.g., accessibility, affordability, quality of care) that contribute to low treatment-seeking behavior among patients with hypertension and diabetes? How do psychosocial factors, including patient beliefs, attitudes, and social support, influence treatment-seeking behavior? To what extent do cultural factors, including cultural norms, beliefs, and stigmatization, affect treatment-seeking behavior for hypertension and diabetes? By addressing these research questions, this study aims to generate valuable insights into the multifaceted factors associated with low treatment-seeking behavior among patients with hypertension and diabetes. The findings will contribute to the development of targeted interventions, policies, and healthcare strategies aimed at improving treatment-seeking behavior, reducing health disparities, and promoting better outcomes for individuals with these chronic conditions. Multidimensional Analysis is a statistical technique used to examine complex relationships between multiple variables in a dataset. It allows researchers to explore patterns, associations, and interactions among various dimensions or factors simultaneously. In the context of the questionnaire on cultural factors and treatment-seeking behavior for hypertension and diabetes, multidimensional analysis can help uncover the interplay between cultural norms, beliefs, stigmatization, and other variables that may influence treatmentseeking behavior. By analyzing the data collected from the questionnaire, researchers can identify patterns and relationships among different cultural factors and their impact on individuals' decisions to seek treatment. The multidimensional analysis may involve techniques such as: 1. Factor Analysis: to identify underlying factors or dimensions that explain the variance in responses related to cultural norms, beliefs, and stigmatization. 2. Cluster Analysis: to group individuals based on their responses, identifying distinct subgroups within the sample population based on cultural factors and treatmentseeking behavior. 3. Regression Analysis: to assess the relationship between cultural factors (independent variables) and treatment-seeking behavior (dependent variable), controlling for other relevant variables such as demographics, access to healthcare, and social support. 4. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM): to examine the complex relationships among cultural factors, treatment-seeking behavior, and other variables, taking into account direct and indirect effects. By conducting a multidimensional analysis, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how cultural factors interact and influence treatment-seeking behavior for hypertension and diabetes. This analysis can provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals and policymakers in developing targeted interventions and strategies to improve healthcare access and address cultural barriers to treatment.