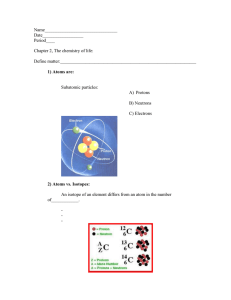
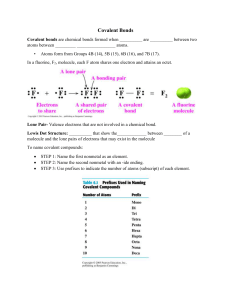
Grade 9 29,02,2024 Semester Test Subject: Chemistry 120mi ns /100 General Instructions: (i) Answer all questions. (ii) Read each question carefully before providing an answer. (iii) Section A comprises 25 True and false questions, totaling 25 marks. Section B consists of 20 Multiplechoice questions, each worth 1 mark. Section C comprises of 3 Structural questions each worth 5 marks. Section D includes 17 Direct questions each worth 2 marks, except last two 5 marks each totaling 40 marks. Section A: True or false questions: (25 questions – 25 Marks) 1. The number of neutrons may be different in the atoms of the same element. [ ] 2. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons called isotopes of that element. [ ] 3. The atomic mass in the periodic table is the average mass of the different isotopes of an element. [ ] 4. The number of electrons in an atom of an element always equals the number of protons in the nucleus? [ ] 5. Metalloids have characteristics of both metals and nonmetals. [ ] 6. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is called the atomic mass. [ ] 7. lanthanides are placed below the main table in the periodic table. [ ] 8. Actinides are not radioactive. [ ] 9. Alkali metals are the least reactive group on the periodic table. [ ] 10. Transition metals are less reactive than alkali and alkaline-earth metals. [ ] 11. Covalent bonds are formed between atoms of non-metals. [ ] 12. In covalent bonding, valence electrons are transferred between two atoms. [ 13. Covalent bonds can only be formed between atoms of the same element. [ ] ] 14. A molecule is formed when a group of two or more atoms are held together by ionic bonds. [ 15. Hydrogen (H2) is an example of a compound molecule. [ ] 16. In a chlorine molecule (Cl2), each chlorine atom shares a pair of electrons. [ ] 17. Methane (CH4) is formed by four single covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms. [ 18. Oxygen in carbon dioxide (CO2) shares two of its outer electrons. [ 20. Substances with simple molecular structures are usually soluble in water. [ Subject: chemistry ] ] 19. Substances with simple molecular structures have high melting and boiling points. [ Prepared by: Sakarye ] ] ] pg. 1 21. Most substances with simple molecular structures conduct electricity in any state. [ 22. Giant molecular structures are usually soluble in organic solvents. [ 23. Giant molecular structures have very low melting and boiling points. [ ] ] 24. Giant molecular structures are insoluble in both water and organic solvents. [ 25. Acids turn blue litmus paper into red. [ ] ] ] Section B: Matching fill in the blanks with the appropriate terms from the box (30 questions – 15 Marks). 1. What holds metal atoms together in a metallic lattice structure? a) Covalent bonds b) Ionic bonds c) Metallic bonding d) Hydrogen bonds 2. What happens to the outer electrons of metal atoms in a metallic bond? a) They gain electrons b) They become positively charged ions c) They become negatively charged ions d) They become delocalized 3. What is responsible for the high electrical conductivity of metals? a) Tight packing of atoms b) Movement of mobile electrons c) Formation of covalent bonds d) Absence of electrons 4. Why do metals have high melting and boiling points? a) Weak metallic bonds b) Absence of mobile electrons c) Strong electrostatic forces between ions and electrons d) Lack of packing density 5. What property allows metals to be hammered into different shapes? a) Ductility b) Conductivity c) Malleability d) Density 6. What happens to the arrangement of metal ions when a force is applied? a) The ions break apart b) The ions gain electrons c) The ions slide over each other d) The ions repel each other 7. What term describes the ability of metals to be drawn into wires without breaking? a) Malleability b) Conductivity c) Ductility d) Rigidity 8. What is the primary reason behind the high densities of metals? a) Loose packing of atoms c) Strong metallic bonds Prepared by: Sakarye b) Movement of mobile electrons d) Lack of electron cloud Subject: chemistry pg. 2 9. What enables heat energy to be easily transferred in metals? a) Movement of mobile electrons c) Tight packing of atoms b) Absence of metallic bonds d) Weak electrostatic forces 10. What term describes the situation where outer electrons move freely within the metal lattice? a) Ionization b) Delocalization c) Polarization d) Dissociation 11. Which solvent are substances with simple molecular structures typically soluble in? a) Water b) Ethanol c) Dichloromethane d) Both a and b 12. Covalent bonds are typically formed between atoms of: a) Metals b) Noble gases c) Non-metals d) Alloys 13. Which of the following is an example of a compound molecule? a) Hydrogen (H2) b) Oxygen (O2) c) Chlorine (Cl2) d) Carbon dioxide (CO2) 14. In a hydrogen molecule (H2), how many single covalent bonds are formed? a) None b) One c) Two d) Three 15. How many electrons are shared between two chlorine atoms in a chlorine molecule (Cl2)? a) One b) Two c) Three d) Four 16. What type of bond is formed in a molecule of oxygen (O2)? a) Single covalent bond b) Double covalent bond c) Triple covalent bond d) Ionic bond 17. How many single covalent bonds are formed between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a water molecule (H2O)? a) None b) One c) Two d) Three 18. Which element forms a double covalent bond with itself in a molecule? a) Hydrogen b) Carbon c) Nitrogen d) Oxygen 19. What is the primary reason for the low melting and boiling points of substances with simple molecular structures? a) Strong covalent bonds Prepared by: Sakarye b) Weak intermolecular forces c) Presence of metallic bonds Subject: chemistry d) High density pg. 3 20. Why do substances with giant molecular structures have high melting and boiling points? a) Due to weak intermolecular forces b) Because of strong metallic bonds bonds d) Due to lack of intermolecular forces c) Because of strong covalent Section C: Direct Questions (40 Marks) 1. What is an acid? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 2. What is the role of water in acids? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________. 3. What electrostatic force of attraction? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________. 4. What is the definition of a molecule? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 5. Can you provide examples of compounds formed by covalent bonds? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 6. What type of bond is formed when two electrons are shared between atoms of the same element? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 7. What is the molecular formula of chlorine gas? 2 marks ________________________________________________________________________________________. 8. How many electrons are needed for oxygen atoms to achieve stable octet configuration in a molecule of oxygen gas (O2)? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 9. What is the molecular formula of nitrogen gas? 2 marks ____________________________________________________________________________________. 10. what are Noble Gases? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 11. What is the molecular formula of methane? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 12. How many electrons are needed for a carbon atom to achieve octet configuration? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. Prepared by: Sakarye Subject: chemistry pg. 4 13. What is the difference between cations and anions? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. 14. Why do substances with giant molecular structures have high melting and boiling points? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________. 15. Why do atoms react? 2 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. 16. Explain ionic bonding? 5 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________. 17. Explain uses of sulfuric acid? 5 marks _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________. Section C Structural Questions: ( 3 questions – 15 Marks). Using the first example as a guide complete the diagrams below by filling in the blanks. Example: Methane (CH4) ‘Dot and cross’ diagram H H H Prepared by: Sakarye Molecular formula Model H H C H Structural formula C H H H Subject: chemistry CH4 H pg. 5 C H H Oxygen ‘Dot and cross’ diagram Structural formula Molecular formula Model O O2 Nitrogen ‘Dot and cross’ diagram Structural formula Molecular formula Model N N Carbon dioxide ‘Dot and cross’ diagram Structural formula Molecular formula Model C O CO2 Prepared by: Sakarye Subject: chemistry pg. 6