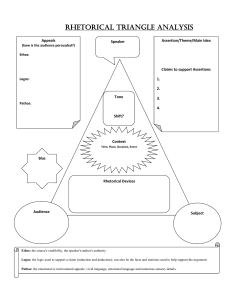
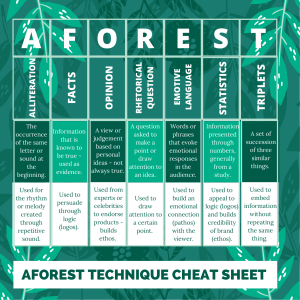
READTHEORY ® TEACHING STUDENTS TO READ AND THINK CRITICALLY "Tools of Persuasion" Reading Comprehension Assessment ReadTheory.org For exciting updates, offers, and other helpful information, follow us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/ReadTheory and Twitter at www.twitter.com/ReadTheory. Comprehension materials similar to those featured in this workbook are available online at www.ReadTheory.org -- an interactive teaching tool where students can take reading comprehension quizzes, earn achievements, enter contests, track their performance, and more. Supplementary materials to this workbook are available in printable worksheet form at www.EnglishForEveryone.org. COPYRIGHT NOTICE Reproduction and or duplication on websites, creation of digital or online quizzes or tests, publication on intranets, and or use of this publication for commercial gain is strictly prohibited. Use of this publication is restricted to the purchaser and his or her students. This publication and its contents are non-transferrable between teachers. All materials in our publications, such as graphics, text, and logos are the property of Read Theory LLC and are protected by United States and international copyright laws. © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. 1 READTHEORY Passage and Questions Name________________ Date________________ • Reading Comprehension Assessment Directions: Read the passage. Then answer the questions below. Tools of Persuasion Persuasion is the art of convincing someone to agree with your point of view. According to the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, there are three basic tools of persuasion: ethos, pathos, and logos. Ethos is a speaker’s way of convincing the audience that she is a credible source. An audience will consider a speaker credible if she seems trustworthy, reliable, and sincere. This can be done in many ways. For example, a speaker can develop ethos by explaining how much experience or education she has in the field. After all, you would be more likely to listen to advice about how to take care of your teeth from a dentist than a firefighter. A speaker can also create ethos by convincing the audience that she is a good person who has their best interests at heart. If an audience cannot trust you, you will not be able to persuade them. Pathos is a speaker’s way of connecting with an audience’s emotions. For example, a speaker who is trying to convince an audience to vote for him might say that he alone can save the country from a terrible war. These words are intended to fill the audience with fear, thus making them want to vote for him. Similarly, a charity organization that helps animals might show an audience pictures of injured dogs and cats. These images are intended to fill the viewers with pity. If the audience feels bad for the animals, they will be more likely to donate money. Logos is the use of facts, information, statistics, or other evidence to make your argument more convincing. An audience will be more likely to believe you if you have data to back up your claims. For example, a commercial for soap might tell you that laboratory tests have shown that their soap kills all 7,000,000 of the bacteria living on your hands right now. This piece of information might make you more likely to buy their brand of soap. Presenting this evidence is much more convincing than simply saying “our soap is the best!” Use of logos can also increase a speaker’s ethos; the more facts a speaker includes in his argument, the more likely you are to think that he is educated and trustworthy. Although ethos, pathos, and logos all have their strengths, they are often most effective when they are used together. Indeed, most speakers use a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade their audiences. The next time you listen to a speech, watch a commercial, or listen to a friend try to convince you to lend him some money, be on the lookout for these ancient Greek tools of persuasion. 1) As used in paragraph 2, what is the best antonym for credible? A. B. C. D. unintelligent boring dishonest amazing 2) Amy is trying to convince her mother to buy her a pair of $200 shoes. She says: “Mom, the shoes I have are really old and ugly. If I don’t get these new shoes, everyone at school is going to laugh at me. I will be so embarrassed that I will want to die.” What form of persuasion is Amy using here? A. B. C. D. pathos ethos logos a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. 2 READTHEORY Questions 3) According to the passage, logos can build ethos because A. an audience is more easily convinced by facts and information than simple appeals to emotions like pity or fear B. an audience is more likely to trust a speaker who uses evidence to support his argument C. a speaker who overuses pathos might make an audience too emotional; audiences who are too frightened or too sad are unlikely to be persuaded D. a speaker can use misleading or false information to make his argument seem more convincing 4) Gareth is running for mayor. He tells his audience: “Under our current mayor, there have been 15,000 new cases of unemployment. If he stays in office, who knows how many more people will lose their jobs? The number could go up even higher. When I was the CEO of Magnatech, I helped to create over 1,000 new jobs. I can do the same thing for this city if you vote for me.” Which form of persuasion is Gareth using here? I. pathos II. logos III. ethos A. B. C. D. I only I and II only II and III only I, II, and III 5) According to the passage, the most effective tool of persuasion is A. B. C. D. ethos, because you cannot persuade an audience that does not trust you logos, because it can also be used to build ethos a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos pathos, because human beings are most easily persuaded by emotion 6) Imagine you wanted to convince an uninformed person to take a political position that is the same as yours. What issue would you try to talk to this person about? How would you include ethos, pathos, and logos in your persuasion? Make your case below. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. 3 READTHEORY Questions 7) Some persuasive programming involves only ethos, some involves only pathos, and some involves only logos. Which of these single-tactic persuasion types do you find most effective? Which one are least effective? Why? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ 8) Sometimes ethos, pathos, and logos can be used to make people believe things that are not entirely true. Can you think of an example? How can people avoid being tricked by faulty persuasion tactics? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________ © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. 4 READTHEORY Answers and Explanations 1) C Question Type: Vocabulary credible (adjective): reliable, believable, trustworthy. In paragraph 2, the author says: “Ethos is a speaker’s way of convincing the audience that she is a credible source.” We can use context clues—hints from known words or phrases around the unknown word or phrase—to help us figure out what the word credible most nearly means. The author explains that “an audience will consider a speaker credible if she seems trustworthy, reliable, and sincere,” and then adds: “if an audience cannot trust you, you will not be able to persuade them.” The words “trustworthy, reliable, and sincere” are especially good clues about what credible means. Based on these quotations, we can see that a credible person is someone you can trust. Because the question is asking for an antonym, we are looking for a word that means the opposite of trustworthy. You would not trust someone who was dishonest, disloyal, or a cheater. We can tell that we are looking for a word that means dishonest. Therefore (C) is correct. Based on the above information, we can tell that we are looking for a word that means dishonest. Unintelligent does not mean dishonest. Therefore (A) is incorrect. Based on the above information, we can tell that we are looking for a word that means dishonest. Boring does not mean dishonest. Therefore (B) is incorrect. Based on the above information, we can tell that we are looking for a word that means dishonest. Amazing does not mean dishonest. Therefore (D) is incorrect. 2) A Question Type: Inference In paragraph 3, the author explains that pathos: “is a speaker’s way of connecting with an audience’s emotions.” The author then gives two examples: a candidate who uses fear to gain votes and a charity that makes you feel pity to get money. The second example is similar to the situation in the question. Amy wants new shoes. She tries to convince her mother by saying that if she does not get them, everyone will laugh at her. She claims that she will be “so embarrassed” that she will “want to die.” Here, Amy is attempting to make her mother feel pity for her. If her mother feels bad enough for her, she will buy her the new shoes. Amy is thus using pathos to try to convince her mother to buy the shoes. Therefore (A) is correct. As the author explains in paragraph 2, ethos is “a speaker’s way of convincing the audience that she is a credible source.” Amy is not attempting to convince her mother that she is honest or trustworthy in this example. Therefore (B) is incorrect. As the author explains in paragraph 4, logos is “the use of facts, information, statistics, or other evidence to make your argument more convincing.” Amy is not using any facts, information, or statistics in this example. Therefore (C) is incorrect. Based on the above information, we can see that Amy is not using ethos or pathos in this example. Therefore (D) is incorrect. 3) B Question Type: Detail In paragraph 4, the author writes: “use of logos can also increase a speaker’s ethos; the more facts a speaker includes in his argument, the more likely you are to think that he is educated and trustworthy.” In other words, an audience will be more likely to trust a speaker that uses facts, information, or other evidence in his argument. Therefore (B) is correct. The passage does not provide information to support choices (A), (C), or (D). Therefore they are incorrect. 4) D Question Type: Global In paragraph 3, the author explains that pathos: “is a speaker’s way of connecting with an audience’s emotions.” One of the examples the author gives in this paragraph is of a candidate who says that “he alone can save the country from a terrible war. These words are intended to fill the audience with fear, thus making them want to vote for him.” In this example, the speaker uses fear to gain an audience’s votes. In the question’s example, Gareth is also using fear to gain votes. He warns that if the current mayor stays in office, “who knows how many more people will lose their jobs? The number could go up even higher.” Gareth is trying to make the audience afraid that the unemployment rate will go up if they do not vote the mayor out of office. Because Gareth is using fear to persuade the audience, this example contains pathos. This supports option (I). As the author explains in paragraph 4, logos is “the use of facts, information, statistics, or other evidence to make your argument more convincing.” In his speech, Gareth tells the audience that “under our current mayor, there have been 15,000 new cases of unemployment.” This statistic is a fact that will help Gareth’s argument. By using this information, Gareth is trying to convince the audience that the mayor should be voted out of office. Because Gareth is using facts to persuade the audience, this example contains logos. This supports option (II). As the author states in paragraph 2, ethos is “a speaker’s way of convincing the audience that she is a credible source.” The author further explains: “a speaker can develop ethos by explaining how much experience or education she has in the field.” In his speech, Gareth says to the audience: “when I was the CEO of Magnatech, I helped to create over 1,000 new jobs. I can do the same thing for this city.” Here, Gareth tells the audience that he has a lot of experience creating jobs. By highlighting his experience, Gareth uses ethos to make his speech more persuasive. This supports option (III). Therefore (D) is correct. 5) C Question Type: Detail In the final paragraph, the author writes: “Although ethos, pathos, and logos all have their strengths, they are often most effective when they are used together. Indeed, most speakers use a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade their audiences.” Here, the author tells us that ethos, pathos, and logos each have their own advantages. None of them is more useful than the other. The author then claims that they are “most effective when they are used together.” In other words, a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos is the most effective tool of persuasion. Therefore (C) is correct. Although paragraph 2 does state that “if an audience cannot trust you, you will not be able to persuade them,” the author never states that ethos is the most effective tool of persuasion. Therefore (A) is incorrect. Although paragraph 4 does state that “use of logos can also increase a speaker’s ethos,” the author never states that logos is the most effective tool of persuasion. Therefore (B) is incorrect. The passage never says that human beings are most easily persuaded by emotion or that pathos is the most effective tool of persuasion. Therefore (D) is incorrect. © Copyright Read Theory LLC, 2012. All rights reserved. 5