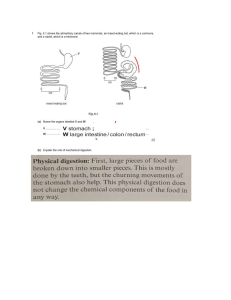
IGCSE Biology Notes: Excretion, Temperature Control, Diabetes
advertisement

IGCSE BIOLOGY
MADE BY RIANA CORDOVA
NITROGENOUS
°
WASTE
Animals produce nitrogenous waste formed from excess proteins and amino acids
BA
broken down to form nitrogen
containing product :
-
urea
These
.
are
.
How urea is made in the Liver
E X C R E T O RY PRODUCTS
'
o
Excretion
Removal from organisms
:
( respiration )
Egestion :
*
o
Removal
¥
Egestion
Lungs
toxic materials
,
,
excess
excess water
amino
acids
high concentrations
)
urea
as
it is
a
*
Each kidney contains million
""
""
M
arteriole
they
are
.
for blood clotting
acid molecules
amino
.
.
and the ammonia is
be excreted
Small amount excreted
.
away by the blood throughout the body
energy , it is wasteful for it to be excreted
contain
.
as it is
tiny
structures called nephrons
loop down the medulla and
There are thousands of renal
0
'
a'IEEE
'
{
kidneys
Foiled
.
.
capsules in the cortex of each
Inside the renal capsule
ill aries called the
/
are
glomerulus
tangle of blood
cap
-
.
blood in glomerulus cannot get away
tubule
&
e-
a
Afferent arteriole is wide and efferent arteriole is narrow
L
First coiled
builds up
collecting
easily
High pressure
.
blood in glomerulus pushes against
so
so
capillary walls
walls have holes in them to let molecules
'
glucose and
again
t
A Nephron
capillaries
urea
.
Inside the Bowman's
0
ti on happens
cortex
Amino acids
through :
are too big to
go
water salts ,
,
through
.
capsule and glomerulus is where filler a
.
Reabsorption
meauua
.
"
n.niiiiim.mn
wrapped around each nephron are good cap, name,
that reabsorb the
use ,u,
quid,
and
:c::::: ::: :S::::::p:::::: : :S: : :::c::::: :::c: :c
salts and urea
dissolved in it
.
pass ,
"
"
.
. .. .
( Urine)
-
ureter
/::÷/%::!i/n
Reabsorbed at
Component
-
:::::÷:
on
" absorbed indium amounts
-
-
Blood passing through kidneys gets filtered and removes most of the
ONLY in first coiled tubule
Glucose
→
By active transport ; nephron has many mitochondria
-
urea as well as excess
salts
Urea
.
Not reabsorbed
cannot take place
-
°
After substances
have been absorbed
solution of salt and water
L
Flows out
kidneys , along
stored for a while
*
urea
concentration
and
L
L
more
.
urea
and exercise
→
a
lot
.
of water and
as
0
0
0
Urine from all nephrons in the
Stores urine ; has
darker
concentration
yellow / orange
-
little
.
the concentration of water in
water is lost in sweat
.
urine
.
kidney take it to the ureter
stretchy walls to
Leading out the bladder
closed
water intake will affect
temp
and into the bladder where it is
pale yellow
→
else
TH E B LA D D E R
.
ureters
→
anywhere
a
.
small quantities of urine
water
product is
being released through the urethra
before
Large quantities of urine
less
*
urine
:
the final
.
duct
L
cortex
artery
renal
the
tubule
back up
goes down to the medulla
E⑧s÷÷÷
°
.
( Bowman's capsule)
renal
artery
Hence
→
.
( broken
deaminate d
are
the renal capsule in the branch of
to
"
Ii::: III.
kidney to
Needed amino acids taken
rena, capsule
,
q
'
.
µ
so
and
.
the amino acids
Because
afferent
Loop of
,
urea
Inside the nephron , blood is brought
0
.
.
the cortex again , then
gag
behind the intestines
,
renvadin
Start in the cortex
to
.
broken down into
Fi Iteration
.
to the pelvis
in sweat
toxic substance
important functions :
( kidney tubules )
stored
Enzymes in the liver split
.
5) Urea dissolves in blood and taken to
toxic waste products of metabolism and
in excess
(
urine
converted
.
( formed in liver
and salts
be
cannot
4) Carbs converted to glycogen are stored / used in the liver
.
water content in blood
Regulate
* Excrete
L
,
by producing
Located in the back of the abdomen
*
'
,
activity
enzyme
K l D N EY
They have two
°
reducing
cells
which is important
like fibrinogen
Amino acids used to build protein
down ) into carbs and ammonia
acidic
an
are
small intestine
absorbed into the blood inside the
are
Excess amino acids in the blood
( waste product of aerobic respiration )
form
canal and protein molecules
carried to the liver through the hepatic portal vein for assimilation
.
L
because it dissolves in water to
excrete
T HE
°
anus
alimentary
.
As amino acids
3)
lowering pH of
Kidneys
in
2)
Excretion
during exhalation
from
amino acids
.
undigested food waste in faeces through
of
carbon dioxide
Lungs excrete
°
excess substances
Protein in food taken into
of metabolism
kidney
t
solution
products
of waste
and
1)
hold
and then to the bladder
large quantities
is the urethra
.
.
with a sphincter
muscle
at
top which is
tightly
-
Disease
q
M
Infection
/damagµ
-
Accidents
e-
✓
K I DN E Y
in:* ::c:: :::: :c: ::n:::n: ::: : :::::÷ :::::c::::*
Inside machine
,
blood and
.si/: ina:: :ian:a./ oi:i: :n: mo:/ on.em:a: : i:ne./
kidney Dialysis
No treatment
"
*
I
f
-
D l AL Y S IS
dialysis fluid
are
separated by a partially permeable
the kidney out
and water balance
upset
is
y
kidney
transplant
-
side of body
-
membrane
kidneys
Both
-
replace both kidneys
-
-
L
*
Blood flows opposite to the
fluid allowing exchange through concentration gradient
/*:i
*
.
are
Dialysis Fluid
i ::::÷:÷: ::÷: :: :
"
L
No urea
Fluid in machine continually refreshed so concentration
""" " blood
.
*
.
Concentration
maintained
.
one several
:::: :::::n:: ::: : ::p: : ::::
"
Anticoagulant
clotting
is added into blood
.ms/
gradients
before dialysis to prevent blood
.
-
°
No
urea
in fluid
→
diffuses from blood to the dialysis fluid along the large concentration gradient
for glucose as the concentration
o
No concentration gradient
°
Movement of salts across the membrane
TRANSPLANTS
VS
Patient has much
to move
around
more
-
freedom
,
not connected
÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷:÷÷÷i:
procedure
°
Long term solution
1mg?
only
-
dialysis
work for a
limited
.
.
This
prevents net movement
.
( low salts in blood / high salts in blood )
-
D l A L Y S lS
.
:/
÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ :÷
0
Risk of rejection
the donor
o
.
if there is an imbalance in concentration
fluid
Disadvantages of transplant
Advantages of Transplants
°
occurs
levels are similar in blood and
.
/
as a
'
as immune
foreign
'
system treats
substance
.
Not enough donors to cope with demand
.
Dialysis Procedure
#
/
Hypothalamus
°
Defined as the maintenance of a constant internal environment
°
L
your body
Internal conditions within
conc
.
,
glucose
conc
,
.
body cells
function
L
If one of the conditions
can
brought back to
properly
*
If
°
o
.
°
Endothermic Animals :
even if their
consume more
Ectothermic Animals
o
due to
energy from respiration
food
( warm blooded animals)
.
Unable to regulate body temperature
:
Take in temperature from surroundings
.
(
heat is easily
Muscles in the body
o
-
layer
o
n
less
air
.
as it takes
lost from blood into air
so hairs
contract and relax very
all over the
distributed
vasoconstriction
are upright which
heat with it
near surface dilate
.
More blood in
.
surface
.
body
Metabolism
traps a layer of
warm air
to produce heat
quickly
for insulation
This is shivering
.
.
Heat generated
.
.
Arterioles that supply blood to surface of the skin are constricted
:
may increase to produce
so not
much
.
more
heat
I:÷ :÷ :÷ ÷ ÷ f
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
consists of Three layers
Epidermis
cornified
Layer
→
contains keratin
0
.
UV radiation
conditions
iea
to normal
a
-
-
-
:÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ :÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷:÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷i÷÷:÷
.
:
0
.
Blood glucose levels
are
controlled
by negative feedback
involving production of insulin
mechanism
-
and
Dermis
Blood Vessel
→
Temperature regulation
L
.
Gland
→
secretes sebum
acts as lubricant
-
glucagon hormones
.
by the islets of Langerhans
Hormones are made
-
sebaceous
e-
mechanism
(
IGAINHEATN
change from the
Body too hot
conditions
.
erial from
Occurs when
set point and returns back
effective waterproof
-
layer
→
body
Metabolism slows down
0
.
.sn/ure'Functions-
→
to parts of
.
I
→
more
blood flows through and no heat is lost
Made up of two layers : top layer epidermis and bottom
dermis
flat and trap
Arterioles supplying the the capillaries
Vasodilation :
Erector muscles contract
The Skin
o
,
.
hair lies
so
0
.
.
)
hypothalamus sends electrical impulses along the nerves
Sweat in sweat glands evaporate to cool the skin
is
Cold blooded animals
,
Cold Temperatures
temperature constantly
Maintain their body
environment changes
They also have to
°
CONTROL
.
is I 37°C
.
Erector muscles relax
means
B O D Y TEMP
temp
.
Hot temperatures
°
deviate and not
Contains thermo receptors that sense temperature of blood running through it
water
,
.
body will not function
,
blood pressure
,
) need to be kept within a certain limit
ensure
asap
.
.
°
that controls body temp
etc
to
normal
( temp
.
the control mechanism that keeps internal temperature constant
A part of the brain at the centre of
cells in the
.
Blood glucose falls
Blood glucose rises
.
pancreas with two glands in one
#
→
Sweat Gland
→
Produces sweat
cooling agent
-
1) Insulin secreted
.
from pancreas
1) Glucagon secreted
.
.
#
Hair
→
→
Heat control
2)
-
→
Erector Muscle
→
contracts / relaxes
position
to control hair
Stimulates the liver and muscle
the stored
glycogen
.
2)
to convert
cells
glucose from respiration
stored glycogen
into
glucose
.
-
→
Receptors
→
Detects
heat temp
.
and pressure
3) Blood glucose concentration falls to normal
.
stimulates liver and muscle cells to convert
( polysaccharide) into
.
3) Blood concentration rises to normal
.
.
-
Diabetes
→
Has collagen
Elastic Fibre
→
elasticity of skin
#
-
.
Dermis
*
o
underneath the dermis is a layer of
L
Adipose Tissue :
Oil
Made up of cells
fat
called
adipose tissue
large drops of
which contain
.
*
Insulates body
*
Energy reserve
*
Provides protective
.
cells
L
type 1 Diabetes :
have
died
thought to be result of the person's own immune system
Hyperglycemia Blood glucose levels
0
Hypoglycaemia :
o
:
o
symptoms
:
treatment :
needed)
as
the islets of
Langerhans
.
When blood
absence of insulin
padding around organs
glucose levels are not able to be regulated
0
.
.
blood
are
.
too high because
glucose levels drop low
no insulin
because no
glucose
can be
produced
has been made
.
due to
.
extreme thirst , weakness
Monitor
As well as
blood
/ tiredness
,
weight loss
glucose levels , physical
activity
.
and diet
injecting insulin , checking glucose conc
( affects amount of insulin
in urine
and
exercising (
glucose
)
.
can be
even
used for
respiration
.
.
,
*
Once pectin ase is broken down
juice squeezed
*
°
want
USE OF MICROORGANISMS
Microorganisms
*
by humans to produce
can be used
fungi
Ex : Bacteria and microscopic
L
Bacteria and fungi
quickly
,
more
.
Adding pectinase to fruits also helps produce
cloudy
seem
juice
clearer
a
-
larger poly
-
.
Lactase
.
o
°
the cell walls break more easily and
saccharides like pectin makes juices
Biology involves using living organisms to carry out processes to make substances
we
,
are
it down
foods
and other useful substances
and are capable of producing complex molecules
No ethical
*
Easy to remove plasmids and
issues can arise
much space
,
reproduce
*
Milk
down
.
manipulate
.
lactose
lose the
.
can be
made
-
glucose
galactose
t
ability to produce lactase as they get older in certain
lactose intoler ht
They become
lactose
.
free by adding lactase to it and allowing it to break
.
galactose for sweets
glucose and
Also produces
L
.
lactase
Many people
regions
.
very small and easy to grow , do not take up
*
0
.
enzyme that breaks
lactose is the sugar found in milk and lactase is an
.
.
USE OF PENICILLIN
USE OF YEAST
0
Making Biofuels
°
Yeast is a single
*
Fermentation
glucose
°
1)
production of penicillin
→
2C 5 Hs OH
Alcohol
is extracted
burns well
°
fuels
treated with amylase
Advantage :
by distillation
industrial fernenter
an
Ferment ers
-
are
.
.
containers used to grow
broken down to
so starch is
.
Conditions can be carefully controlled to
quantities of exactly the
right type of microorganism
.
land used
.
.
as much
as
energy
fossil fuels so petrol is
Industrial Fer mentor
.
sustainable resource
Disadvantage :
GENETIC ENGINEERING
reduce coz from air
,
for biofuels could be used for food instead
0
.
Making Bread
even if
organism relieving genetic material
L
oxygen
transgenic organism
.
Yeast is mixed with flour and water
CO2
changing of genetic material of an organism by removing
The
ting individual genes from another organism
Yeast will respire anaerobically if it has access to plenty of
sugar
is present
*
harming human cells
produce large
.
for anaerobic respiration
but does not contain
added for vehicle engine use
L
using
2 CO2
t
and uses the glucose
3) Ethanol produced
*
scale
without
.
2) Yeast is added
o
large
on a
.
culture microorganisms in large amounts
Ethanol used as a biofuel to reduce the use of fossil
glucose
o
.
are substances which kill bacteria
ethanol t carbon dioxide
Maize crop is usually used and
*
a food source
by Alexander Fleming
o
→
CGH 1206
Antibiotics
L
celled fungus that uses sugar as
-
First anti Obi tic discovered in 1928
causes
the bread to rise
Alcohol broken down and
,
respires anaerobically
,
producing CO2
L
.
recombinant DNA
.
yeast is killed as
bread bakes
Ex :
.
changing or inSer
-
.
is said
to be genetically modified
or
a
.
organism that now has the
DNA of the
,
other organisms
'
DNA is known as
.
GM crop plants
Human insulin into bacteria ,
Process
USE OF ENZYMES
1)
Biological washing Powders
in
°
Many stains on clothes are organic molecules
°
Contain
3)
Quickly breaking down large
that will dissolve
,
insoluble molecules into smaller , soluble ones
less energy and money
Effective at lower temperatures
→
L
Be used to clean delicate fabrics
which
*
Fruit juices
5)
.
aren't suitable for high temp
extracted using an enzyme called pectinase
Pectinase is added
plant cell walls
.
and
breaks
down a
used to cut the gene out of
Gene splicing takes place
:
.
.
chemical called pectin that is found inside
the DNA strand and to cut
.
( cut out gene inserted to plasmid )
Recombinant DNA plasmid is inserted into an
new
trait
gene will begin making it 's protein and
,
it copies the
develops from original
.
embryonic
cell
of an
.
If successful , cell will make the DNA plasmid
6) when cell divides
are
are
organism getting the
L
with the trait they want to put
.
4) Transformation
.
Pectinas e
°
organism B
Open a plasmid from bacteria cell
.
Advantages
L
identify the gene in organism A
2) Restriction enzymes
.
to break down large food molecules
enzymes
Scientists
causes
a
part of it's
a new
trait
own
DNA and the foreign
.
foreign gene along with it's own DNA so organism that
cell has a
copy of the
new
gene in all it's cells
.
INHERITANCE
What is inheritance ?
inheritance : transmission of genetic information from one generation to
-
What is a genotype ?
Genotypes
-
Ihewmaudnsefwhpootaee9eeesticcommbat.MY
-
to
form a gene
EX :
Eye colour
consists of genotypes and phenotypes
Alleles : two alternative forms of
An organisms physical
Determined by
factors
,
( lowercase
Homozygous
properties
and
that
a gene
(capital letter )
Recessive :
genotype
the
genetic modification
alleles
called
are
-
#µX
H
.
X
be dominant
can
the most
usually seen
dominant
it is
as
recessive
or
father
.
( XY )
.
Y
letter
)
Only when there
is
dominant allele present
no
Heterozygous
:
( Having the same )
two identical
:
( Having different )
Two different alleles
alleles
→
Pure
skin
'
Offspring Ratio
sex
inheritance ?
carrier
*
inherited
recessive allele for a trait
not show
the trait
500/0 of
( XY )
boy
Pure
breeding
PV NN ET SQUARE
f)
chromosomes
-
/muesI
Females
www.I?da::::nm:::::anca:Yn.::7:7:::
Organism that
:
500/0 of girl ( XX )
Not
→
,
What is a sex-linked
:
y
breeding
environmental
XX and XY
nutrition
X
.
.
.
""
X
Y
X
-
-
mother ( XX )
→
- -
height
What is a phenotype ?
-
gametes
-
Dominant :
,
.
.
with two letters that
shown
another
*
-
If
the gene responsible is located
linked characteristic :
a
male has an
have two
Females
X
-
. . determining came , gender
me
condition
linked
X chromosomes
→
on a sex
pass the gene to the
likely to inherit
→
chromosome
one
.
→
daughter
XX
→
gene shows
"""
more
""
other
.
likely to show sex-linked
recessive conditions
effect of recessive allele
dominant allele that masks
Gitmo
similarity in one sex than the
of the single X chromosome
b/c
÷
.
but does
If the recessive allele is
at au
masked
they become
,
the
carrier
→
.
one dominant
.
allele that
Only able to pass the allele
.
What is w dominance ?
if offspring is male
the disease
he will inherit
→
codominance when genes have alleles that
expressed equally in a phenotype
*
equally dominant
are
:
recessive
.
masks
allele
both
→
→
.
Inherits the disease
ble inherited recessive allele
using different
Codominant alleles shown with uppercase letters in genetic diagrams
letters
.
EX
:
AB is
Blood group
co dominance
.
-
What is Putten synthesis ?
*
*
pro tiers
are
polymers of amino acids
Transcription to translation
is
→
DNA to RNA
::4" I
there are twenty amino acids
in humans
Genotype
-
IA IA
.
'
'
::: : :::
RNA
"
÷::::: : :::: :: :: :: :: : :::: :: :::::: :::÷: ::::
grab
on to
make a protien
Lt
will they
In
depth detail
what is DNA ?
*
since DNA is too big to travel out of the nucleus
,
deoxy ribonucleic acid
*
ribonucleic acid
→
*
*
mRNA
moves
a
ribosome
out nucleus
Ribosome translates
to
base code
to fold and
of each gene is transcribed
reads
→
code
acids
on the
→
to mRNA
mRNA in groups
makes
protein
of three
Nuclear division
genetically
producing
identical cells
88%-1%8
⑧⑧
*
←
growth
*
Parent cell contains
made
f
Nuclear division that produces
genetically different
cells
,
→
g
replacement of cells
,
produces
( triplet bases codes specific amino acid )
.
offspring
identical
genetically
parent
µ
asexual reproduction
→
Mitosis occurs ,
each chromosome
splits
and each
.
goes to daughter cell →
During growth
,
exact
copy is
.
production of gametes to increase variation
*
Used for
*
Reduction division occurs
*
Starts with chromosomes doubling in mitosis and lining up in the centre of the cell
Reduction Division :
chromosome
diploid to
genetically
.
during meiosis
→
.
that
to ensure
gametes are haploid cells
→
cells divide twice
.
number is halved from
→
four chromosomes
of each chromosome
passes to each
different cells
dqmeeeaged
.
Meiosis
What is meiosis ?
haploid
,
p
repair damaged tissues
O
.
f :
-
used for
"
form final protein structure
replace
!
I Pnnewdn
Mitosis
A
.
cell division
what is mitosis ?
ii :
IA lo
-
and attaches to ribosome
from ribosome
'
or
" lo
.
sequence of bases into sequence of amino
Amino acid chain released
Phenotypes
.
*
Gametes
as
gamete
.
haploid cells →
b/c of double division
,
meiosis produces
four haploid cells
.
so
only one copy of each chromosome
.
VARIATION AND NATURAL SELECTION
¥on?
Continuous variation
Variation
has
:
differences between individuals of the
:
continuous variation
a
charts
There are several numbers of
( Bell shaped )
.
-
Genes are inherited
ment
can
change it
→
environ
-
Discontinuous Variation
Depend entirely on genes
:
genes
→
are
Genetic defects ( colour blindness
:
the
there
Mutations
bird develops mutation to
give colorful feathers
N
d
breeding and the passing
of the mutation
No
* on
are
:
albinism )
,
discontinuous variations
are
intermediate
no
States
:
height
,
mass
)
.
( Ex
:
.
gender
,
blood group )
.
.
*
→
when the nucleotide sequence in the DNA changes randomly
effect on the phenotype →
rare occas sirens
protein that mutated gene
mutations lead to the
,
can lead to harmful changes
*
greater advantage of mating
increased
genetically controlled and cannot be environmentally altered
(EX
-
*
:
,
.
( step shaped )
.
WYNTON ?
Example
arranged in an order
can be
,
can be measured on a scale
graph
charts show a random
distribution
involved
.
Discontinuous variation
and
.
situation in which there are many intermediates and are usually caused by both genes and environmental factors
:
normal distribution in graphs and
*
species
same
development
sickle cell anaemia
→
works the same as
produces
of
new
alleles
→
genetic changes
phenotypes
new
's
gene
un mutated
.
protein
.
small effect on
→
organism → gives them survival adv
.
.
spontaneously and continuously due to the following
Mutations happen
random
factors :
.
-
Ionising radiation
:
damage bonds and change in base sequence
-
-
*
increased rates of mutation
-
mutagens
( Mercury
certain types of chemicals
:
lead )
and
.
sickle cell Anaemia
causes
strokes , blindness ,
:
to lungs
,
kidneys
,
heart
damage
*
Mutation changes the molecule
*
sickle cell tends to
Risk for life threatening
acute chest syndrome
haemoglobin
→
RBC 's to become sickle
causes
-
shaped when releasing oxygen
.
.
.
( A and s)
Two alleles
*
get stuck in narrow
are
co
blood vessels
dominant
→
blocks flow of blood
A is normal
→
.
S is sickle cell anaemia
and
.
Carrier Mother
→
normal Hb
¥¥¥µ,¥
HBA
cue anaemia
.
Emmy nigra
↳
and
Both Parents are carriers
Heterozygous are said to be
carriers
Abs
rant
cam ,
→
'
ke
chance they will
have
y.at:7/EIbn.y:s.yEnhi.twu#bb..maen./qcaem.er
I
-
develop sickle
→
HBA
Abs
- -
Hon
.
muggy
,
-
saw
a child
one
who suffers
.
.
-
WhH-aM ?
Adaptive Features : inherited feature that helps
probability
Fitness :
Hydrophytes
-
plants adapted to extremely wet
conditions
-
small roots
:
Thin cuticle :
-
Xerophytes
-
plants adapted to extremely dry
conditions
-
.
-
-
-
-
WW
.
extract nutrients easily
need to
no
hollow
stem and leaves
Have stomata
on
prevent water loss
closing of stomata
waxy cuticle
Hairy leaves :
Increased variation
&
Overproduction of
offsprings
to
offspring
Greater chance of survival
The process of adaptation
lower
Cuts down surface area :
-
transpiration
→
.
water loss
reflects heat
→
lowers
temperature
less water
seeks water
deep down / across wide area
's
Charles Darwin
theory of survival of the fittest
out roots :
:
surface is cooler →
.
.
of variation caused by differences in genes
Individuals show
*
Overproduction of offsprings
*
Individuals with the
a range
evaporates
less water evaporates
*
Evolution :
help the plant float for photosynthesis
quicker gas exchange from atmosphere
slows down
stomata on underside :
spread
to
traps in moisture
adapted variations
&
:
filled w/ air
:
barrier for evaporation and
:
Natural selection
&
Fittest characteristic gets
spaces
both sides :
.
on
organism surviving and reproducing in its environment
.
'
.
-
passed
of an
organisms to reproduce and survive in their environment
fittest
→
competition for food and
characteristic
→
more
resources
reproduction
.
→
allele is passed down to
.
change in adaptive features overtime as a result of natural selection
Stabilizing selection
offspring → greater number of individuals with better
:
when natural selection tends to keep populations the
same
.
from generation to generation
→
change will occur it environment changes
Antibiotic resistance to Bacteria
*
Baden as reproduce quickly
*
Variation will
-
occur
caused
→
greater chance of evolution in a short amount of time
by mutation
→
might cause some bacteria to be resistant
.
to antibiotics
→
they do not die
.
.
.FI:5/n.a:. an.w. .n i:s. . .u
natural
* An example of
Selection
*
WeA¥ng ?
Tumi:E÷:÷:n
select individuals with the
Selective Breeding :
*
*
Genes of antibiotic resistance will be passed
process has to be repealed
on
to next
-
-
-
for many successive generations to ensure a new
increased crop yield
-
Better tasting fruits
.. ..
lay large eggs
Domestic
with
dogs
sheep w/ good
-
flowers
.
chicken that
-
Hardiness to weather
Large 1 unusual
characteristic
most desirable
.
-
whole population will inherit the gene
offspring →
-
.
and
breed
breeding them together
.
.
organism with the desirable traits
.
. .mu.
gentle nature
quality
wool
Horses with fine features and
are
fast
-
AND RESPONSE
COORDINATION
~
÷ ÷ ÷¥
System
central nervous
system ( cws )
system
Nervous
all of the nerves in the
impulses
Nerve
body
signals that pass along neurons
In.
sensory Neurons : carry impulses
from
to
sense organs
Voluntary Response
CNS
and
surroundings
*
Allows
*
Information is sent through the nervous system
*
Neurons
*
Axon insulated
*
cell bodies
us
to make sense of
have
our
long fibre ( axon )
a
peripheral nervous system
and
to
.
respond to them and coordinate and regulate body functions
as
nerve impulses
.
which enables
.
less time to be wasted
by a fatty sheath w/ small uninsulated sections along it
have dendrites
in transferring
impulses
.
→
connects to many other neurons
( nodes )
( forms
→
a network
electrical
jumped from one node to the next
impulses
of connection )
impulse
←
44¥
Dendrite
qgmma.qqqzgazqq.qqqg.t
[
!¥E÷
.
⑧$
⑥
schwann cells
.
receptor cell
.¥i¥i÷:÷
.
Of
.
.
.in#nm.TEihg/:snt::hsm ?hzBE/÷
I
.
conscious
:
system
:
electrical
:
central nervous
:
:
the brain and the spinal chord
peripheral
consists of the
.
.
SENSORYNEVRONETTRELAYNEVRON.LI →
MOTORNEVRONETAyhraiandt.im
decision is made to carry out
( starts in the
sTM
→
pain I pressure /
Receptor
involve
the brain
:
does not
→
not aware
&
→
Effect
→
impulses to
RESPONDED
carries impulse to effector
connects to motor neurone
spinal chord
receptor cells
and passes impulses
REFLEX
PATHWAY
effector will react
where the stimulus
essential to basic survival
sends electrical
detected by
touch
involuntary Response
→
accordingly
touched
to stimulus
The synapse
synapse junction between two
:
*
minimum
.
gap between
is the
d
:
d
chemical messengers
""
vesicles move forward
②
bid is%km*mm
f
synapse
neurotransmitters
hi
impulse arrive at the
and
←
fuses w/
More
tosynapticlett
÷-
÷
Em
K÷÷÷h÷÷÷÷÷
¥o÷÷¥÷¥?f?
"
L÷dd Tuftsetranowsmnttaen
⑥
③
condition gradient
f
q
.ee#t.s.m::.:onnen::iomes:ea
Y
585%794 ÷÷÷÷÷÷i⑧TT"Y
was
was
.→EE
..
*
only place where drugs can
affect the nervous system
messages are chemical
because
④
•¥- mem
⑤ impulse travels
r
nwweJ
along postsynaptic
U
-
-
.tl?once7mp%7ed
Far;afsEy:gt
f÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷
*
Endocrine system
glands that
:
produce hormones
cells
or
w/ receptors found inside cells
cell membrane
on
Endocrine Glands
*
once
have
a
target organs
to
body
*
*
transmit information from
Hormones : chemicals which
ystem
to
blood
supply
bring about
hormone has been used
a
a
hormones
→
response
destroyed in the
→
shape of the hormone
bring about a change
to
.
get to the plasma in the blood stream quickly
need to
travel around the
→
.
cells with target receptors that
Hormones can only bind to
the
good
to another
part of an organism
one
liver
are
Pancreas produces hormones to
regulate
.
as
complimentary to
well as
such
as
lipase
ru
blood glucose levels
←
digestive enzymes
pancreatic
amylase
a'In'T
"
"
.
( Manisa"nH
,
II'tm%7¥yaI¥e
'
+
.
.
"
÷" - i
±:
.
-
oestrogen
controls menstrual cycle
:
and
develops sexual characteristics
in
females
.
Adrenaline
Fighter
f
t
What adrenaline does to
get our muscles to react
g
*
pupils also dilate to allow
much light as possible for
information
.
*
Produced in situations where the
*
causes a range
-
-
,
be in
body may
danger
.
of different things in the body to prepare for fight or flight :
increasing blood glucose concentration
→
Increasing pulse rate t breathing rate
gum , you aimed towards
increase respiration in muscle cells
→
mu, yes
glucose
t
.
quickly to muscle cells
oxygen delivered
oxygen is cam ed me for respiration
t
cos taken more
quickly
.
.
,
,
#
COORDINATION
THE EYE
:
-
Whory Erg and?
Receptors
detect
:
Sensory organs
specialized cells that
in the environment
-
a change
and stimulate impulses in response
-
.
-
Structure t function of Eye
-
-
:
contains a group of receptors that respond to specific stimuli
skin : sensitive to pressure
Tongue
Ear :
:
,
temperature and pain
chemicals in food t drink
sound and movement
cornea :
→
→
touch and temperature
→
Iris :
taste
.
light enters pupil
Accommodation
bring
hens :
fine
way the
:
can
,
-
change shape
depending on suspensory ligament
ciliary
Muscles
cause the
:
-
-
is attached
-
Pupil dilates
More
-
light enters the eye
eight
:
smell
→
sight
.
retina
..
£
:
.. .
radial muscles relax
-
circular muscles contract
-
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments
pulled
Pupil contracts
-
T
§⑧q_
÷aEsTgPFne7
less light enters the
eye
-
-
-
-
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligament
lens are
slack
fat
lens are thin
muscles that
Rods and
change
:
-
circular muscles relax
Rods
Blind spot
.
lens
focusing
elastic
Radial muscles contract
Eye
→
.
.
÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷
-
chemicals in air
¥¥*
.is'¥:9¥÷¥÷÷¥ao!
*÷÷
his
.
:÷÷: :: : ::: :c::÷::÷
brain
Nose :
hearing t balance
transparent lens that retracts light entering eye
controls how much
-
-
-
-
.
area
cones
receptor cells sensitive
:
to
dim
light
→
found all over retina
where the retina
to the
optic
nerve
and there are no rod cells found
cones :
receptor cells that
fovea
area on
:
retina
→
distinguish color in bright light
almost where all
cone
cells
are
→
found
3 types that
are
colour sensitive
( red
,
blue
and green
)
HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Fertilisation
Whwin ?
Gametes : sex cells
to increase
adaptations
( have
ammonium
immature em released each
egiau.msg.im
takes
a
zygote
.
Cell Membrane
Egg cells
Aarne ( contains
enzymes to digest jelly
qqgeg←
.
•
*
nuclei to create
gamete
-
.
fertilisation to prevent other sperm cells )
t§⑨&¥§zizz
coat of egg cell membrane)
mitochondrion
peace in the
Iain
C-
( telly coating
that forms a barrier after
¥Lnauids
chances of fertilisation and
development of embryo)
*
fusion of the male gamete and female
the
:
Sperm cells
ifeng.gg/
her movement )
.Jgfpµ
.
I
FEI .FI:S:Firing
the zygote )
www.FIagellu-m
My
#
c
( swim to egg )
How does the
#
Embryo
:
unborn
fetus form ?
*
After fertilisation
embryo
offspring in the
Gestation time : period of
*
Embryo
*
First
development
*
Amniotic sac cushions fetus
zygote travels to the uterus
implants itself in the thick lining of the
12 weeks
a three
→
day
period in which the zygote will divide several times
*
grows and develop es →
then
uterus
for the major development of organs
embryo gets nutrients
→
to
form an
→
gestation period is nine months
nutrients taken from
the
mother
.
by diffusion through
uterus
.
fetus
→
.
protects fetus
→
the
.
then
lining
remaining gestation time
abdomen
,
.
*
bigger
in the oviduct
#
process of development
grows
,
Atsc
e -
organs
all in peace
are
placenta formed
→
embryo is now fetus
→
.
to mother
's
* Telus surrounded
*
amniotic
by
.
's
join
Umbilical chord
sac
's blood plasma
filled with amniotic fluid made from mother
→
fetus 's blood
supply to placenta
exchange of nutrients
→
t
.
removal of waste products
.
The placenta
worth remembering two substances
*
→
→
*
waste
substance
Nutrients :
fats
:
,
urea
water
Movement of molecules
Oz
t
by
occurs
diffusion → difference in cone
gradients
Not all toxin molecules are stopped
( depends
After birth
:
uterus wall
on
molecule sire )
develops by gaining glucose
amino acids
,
vessels connects to and from the
* fetus 's blood
,
fats
,
's blood
water and oxygen from mother
placenta via umbilical chord
*
Mother's blood absorbs
waste
*
Placenta is adapted
to
diffusion by having a large surface area
*
Acts as
prevent toxins
*
umbilical chord is out after baby
*
Placenta is removed
from fetus 's blood
in the placenta
so
that
.
.
they don't accumulate in high concentrations
.
to
a barrier
and
thin wall
t
pathogens entering fetus 's blood
.
.
.
placenta detaches from
→
pushed out due to
contractions
Fetus
.
.
*
*
CO2
t
.
→
afterbirth
is born
( does not hurt
→
no
)
nerves
→
tied
to
prevent bleeding
.
Breastfeeding
*
*
During pregnancy
After birth
→
mammary glands enlarged
→
mother will
be
become prepared to secrete milk
t
stimulated to release milk due to
amounts
-
the
-
baby
contains antibodies
-
-
-
mother
t
baby bond
come
→
easily to the
-
meows father
t
postnatal
baby
to bond
-
Risk of infection increased
bottles
depression
→
infection
prevents
Does not
mother
Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
right nutrients in right
.
Bottle feeding
Advantages
-
.
sucking action of the baby at breast
Breastfeeding
Whwe?
.
Allows mother
-
more
freedom
-
t
→
it
equipment not sterilized
expensive
Responsibility with the mother
the
Antenatal
:
( before birth )
take folic acid
*
Diet :
*
Exercise
*
Health
:
to
stay fit
precautions
:
name is
to prevent
given to the
care and
advice given to expectant mothers
development issues with the fetus
t
importance
of balanced diet
.
avoiding infections
,
tobacco
,
alcohol
,
nicotine
,
drugs
along
.
with checks
.
on
fetal growth and development
.
HUMAN SEX HORMONES
secondary sexual characteristics
Whdary Sexual
M¥4.4 ?
oestrogen
sex hormone
:
in
controlled by release of hormones
*
* Emotional
girls
changes also
changes that
:
occur
occur
during puberty
.
temall
more interest
mood swings t
→
Breasts develop
-
sex hormone
in opposite gender
in boys
menstrual
.
-
Growth of facial hair and body hair
-
cycle begins
muscles develop
-
Hips get wider
-
voice
-
I
*
*
g-
-
*
Starts in early adolescence
*
Ovulation occurs
y
.
days
→
controlled
halfway through cycle
to fertilize
* Failure
*
female reproductive system
by rise and fall of oestrogen
that
makes pregnancy possible
.
.
After menstruation
lining
→
① Pituitary gland produces FSH
CONNING thlmenstmal
② Egg develops inside
cycle ?
of
-
follicle stimulating Hormone
FSH
then egg travels down oviduct to uterus
causes menstruation
egg
Whatarethehormonls
:
occurs in the
.
Menstruation lasts around
f- SH
regular t natural change that
:
#
Average menstrual cycle is 28
days long
cycle
Menstrual
cycle ?
breaks
Testes start to produce sperm
-
what is the Menstrual
penis t testes
Growth of
-
Body hair grows
-
testosterone :
Male
.
to occur
of uterus starts
→
follicle
stimulates
→
produces
the breakdown
caused by
→
.
of the thick
again in preparation for implantation in the
to thicken
development of a follicle in the ovary
oestrogen
→
lining
uterus
.
next cycle
.
.
growth and repair of the lining of the uterus wall
causes
t
inhibits
production
.
③
Oestrogen rises
④
Follicle become the corpus luteum
to
high enough level →
stimulates release of
LH from
pituitary gland
→
causes
ovulation
.
A
released by pituitary
gland
&
causes
egg to start maturing and
ovaries to start releasing oestrogen
LH :
A
levels reach
⑥
If pregnancy
Oestrogen
Luteinising Hormone
oestrogen
⑤ Ovum not fertilized
peak
:
occurs
→
→
levels rise from
starts producing progesterone
→
corpus luteum breaks down
maintains
→
progesterone levels drop
t
corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone
day I
* causes uterine wall to start
to peak before
thickening
t
day 14
→
uterus
causes
lining
.
menstruation
.
preventing uterus lining from breaking down
→
.
.
egg to mature
.
N
pituitary gland stimulated
to release
LH
µ
Causes
Progesterone
:
stays low from day I
-
14
and starts to rise once
*
Increasing levels cause uterine lining to thicken further
*
Decreasing levels
ovulation to occur t
stimulates ovary to produce
progesterone
ovulation
occurs
continues
through pregnancy until placenta has developed
.
.
causes
uterine lining to break down →
→
causing menstruation
.
.
.
#