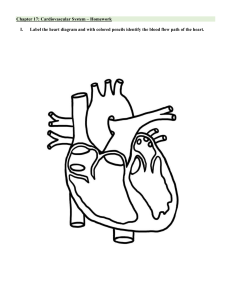
ECG What is an Electrocardiogram? Records cardiac electrical currents by means of metal electrodes placed on the surface of the body Patients should be relaxed when performing the procedure Patients should be treated according to their symptoms ECG or EKG - Electrocardiogram or Electrokardiogram - a series of waves and deflections recording the heart’s electrical activity from a certain “view.” The 12-Lead ECG 12-lead ECG paints a complete picture of the heart's electrical activity by recording information through 12 different perspectives. These 12 views are collected by placing electrodes or small, sticky patches on the chest (precordial), wrists, and ankles. PURPOSE OF ECG/EKG - To detect heart problems or blockages in the coronary arteries. - To draw a graph of the electrical impulses moving through the heart - To record heart rate and regularity of heartbeats - To diagnose a possible heart attack or other heart disorders CHEST LEADS PLACEMENT To measure the heart's electrical activity accurately, proper electrode placement is crucial. • In a 12-lead ECG, there are 12 leads calculated using 10 electrodes. V1 – 4TH ICS Right sternal boarder V2 - 4TH ICS Left sternal boarder V3 – Midway between V2 and V4 V4 – 5th ICS Left MCL V5 – 5th ICS Anterior Axillary line V6 – 5th ICS Left Mid Axillary line 3 Lead system (Cardiac Monitoring) Smoke over fire (black lead above the red lead EITHOVEN’S TRIANGLE LEAD PLACEMENTS 12 Lead groups A lead is a glimpse of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle. Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. •Lead I • Lead II • Lead III • Augmented VectorRight (aVR) • Augmented Vector Left (aVL) • Augmented vector foot(aVF) PROCEDURE Performs safety checks. Make sure that all electrical equipment and outlets are grounded. Remove patient’s accessories like jewelries, etc. 2. Review the medical record and the nursing plan of care. (check doctor's diagnosis) 3. Perform proper hand hygiene and observe appropriate infection control. 4. Performs patient evaluation. Make sure to check the identification tag of the patient before the start of the procedure. Secure consent. 5. Explain to the patient the need to lie still, relax, and breathe normally during the procedure as well as the procedure is non-invasive 6. Position the patient on semi-fowlers position. 7. Provide patient’s privacy. (expose examined area) 8. Check physician’s order . 9. Prepare equipment and other materials needed (ecg machine, cotton balls with alcohol, ky jelly) 10. Place the chest leads a. Chest skin should be dry, hairless, and oil-free. b. Electrodes should have full contact with the patient's skin. For better electrode adhesion and oil-free skin, rub the area with an alcohol prep pad. 11. Place the limb leads. 12. Turn on the machine and start recording. 13. Once done, remove chest and limb leads. Return all personal belongings 14. Document (Name, Age, Sex, Date and time performed) THE ELECTRICAL SYSTEM OF THE HEART 1. PRECAUTIONS 1. The recording equipment and other nearby electrical equipment should be properly grounded to prevent electrical interference. 2. Double-check color codes and lead markings to be sure connectors match. 3. Make sure that the electrodes are firmly attached, and reattached them if loose skin contact is suspended. 4. Don’t use cables that are broken, frayed, or bare. Conduction Pathway of the Heart ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Depolarization The electrical charge of a cell is altered by a shift of electrolytes on either side of the cell membrane. This change stimulates muscle fiber to contract. Repolarization Chemical pumps re-establish an internal negative charge as the cells return to their resting state. NORMAL COMPONENTS OF THE ECG WAVEFORM P wave P wave normal duration is 0.06 to 0.12 seconds ❑Characteristics: Concave and small ❑ Clinical Significance: Atrial depolarization PR interval PR interval normal duration is 0.12 to 0.20 seconds ❑ Characteristics: Period from the start of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex ❑ Clinical Significance: AV conduction time QRS Complex QRS Complex normal duration is 0.06-0.12 seconds ❑ Characteristics: R waves are deflected positively and the Q and S waves are negative ❑ Clinical Significance: Ventricular depolarization ST Segment Normally not depressed more than 0.5 mm and not elevated no more than 1 mm ❑ Characteristics: Isoelectric ❑ Clinical Significance: Early ventricular repolarization QT Segment Normal values for the QT interval are between 0.30 and 0.44 (0.45 for women) seconds ❑Clinical Significance: Ventricular depolarization and repolarization T wave ❑ Characteristics: Rounded and asymmetrical ❑ Clinical Significance: Ventricular repolarization The term used for the release (discharge) of an electrical stimulus is "depolarization", and the term forrecharging is "repolarization". So, the 3 stages of a single heart beat are: 1.Atrial depolarization 2.Ventricular depolarization 3.Atrial and ventricular repolarization CARDIAC MONITORING Cardiac Monitoring a non-invasive procedure that displays the electrical activity of the heart; these electrical impulses are picked by the surface electrodes and are transported and then recorded in the ECG. Purpose of Cardiac Monitoring 1. Provide a continuous graphic picture of cardiac electrical activity. 2. Monitor oxygen saturation of the arterial blood. 3. Help in diagnosis of life-threatening problems, as cardiac dysrhythmias. Indications ✓ Patients with suppressed respiratory system by a drug overdose or anesthesia. ✓ Monitor the pattern of a child’s heart rhythm pre- and postsurgery. ✓ Monitor abnormal heart rhythms. ✓ Monitor the effect of cardiac medications have on a child’s heart rhythm. Types of Monitoring Lead System ➢ All cardiac monitors use lead system to record the electrical activity generated by cardiac tissue. ➢ Cardiac monitoring systems currently on the market vary from three-electrode telemetry devices to three, four, and five electrode hard-wire systems. *Sponge with alcohol *KY gel *Scissors B. Patient Skin *Shaving (for adolescent) *Disinfectant with alcohol or soap *Keep the skin dry 3. Implementation Initiating ECG monitoring: *Explains the purpose of ECG monitoring to the patients and family. *Applies the electrodes to the appropriate location and attaches the correct cables to each electrode. Note: Electrodes are to be changed every 24 hrs and selects an appropriate lead in which to monitor the patient. *Check cables and lead wires for fraying, broken wires or discoloration. *Plug lead wires into patient’s cable. *Plug the patient’s cable into monitor. *Turn on the monitor. *Adjust the monitor. -Speed (25mm/sec) -Sets the appropriate alarm limits based on the initialrate/rhythm and ensures alarms are set to ON position. Note: Pediatrics – Alarms are set that are appropriate for the age or as ordered by the physician. Post Care A. Patient *Reassure the patient B. Environment *Discard the used items. C. Nurse *Record ECG strips from the monitor. *Evaluate the ECG pattern continually for dysrhythmia. * Wash hands. Procedure 1. Assessment Assess the patient need for cardiac monitoring. 2. Preparation A. Environment *Bedside monitor *Machine cables *Three electrodes Ongoing Care ✓ Checks the alarm limit settings at the start of every shift and continues to adjust the alarm as the patient’s rhythm and condition warrant. ✓ Reviews every shift the monitoring trends and alarms. ✓ Reassess the patient for signs of hemodynamic compromise with any significant changes in cardiac rate or rhythm (i.e. BP, oxygen saturation, RR, or myocardial ischemia). ✓ Reports to the physician: • Life threatening cardiac arrhythmias and initiates appropriate actions. • New or unexpected changes in the cardiac rate, rhythm or clinical status. 4. Documentation *Record the patient’s ECG. *Record any dysrhythmia and treatment. Special Considerations ✓ Make sure all electrical equipment and outlets are grounded. ✓ Ensure that the patient is clean and dry. ✓ Avoid opening the electrode packages until just before using. ✓ Avoid placing the electrodes on bony prominences, hairy locations, areas where defibrillator pads will be placed, or areas for chest compression. ✓ If the patient’s skin is very oily, scaly, or diaphoretic, rub the electrode site with a dry gauze pad before applying the electrode. ✓ Have the patient breathe normally during the procedure. ✓ Assess skin integrity, and reposition the electrodes every 48 hours.