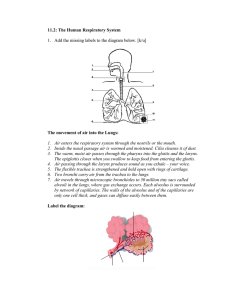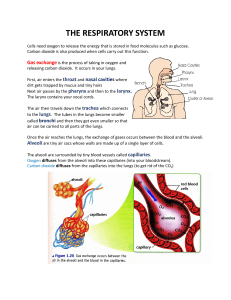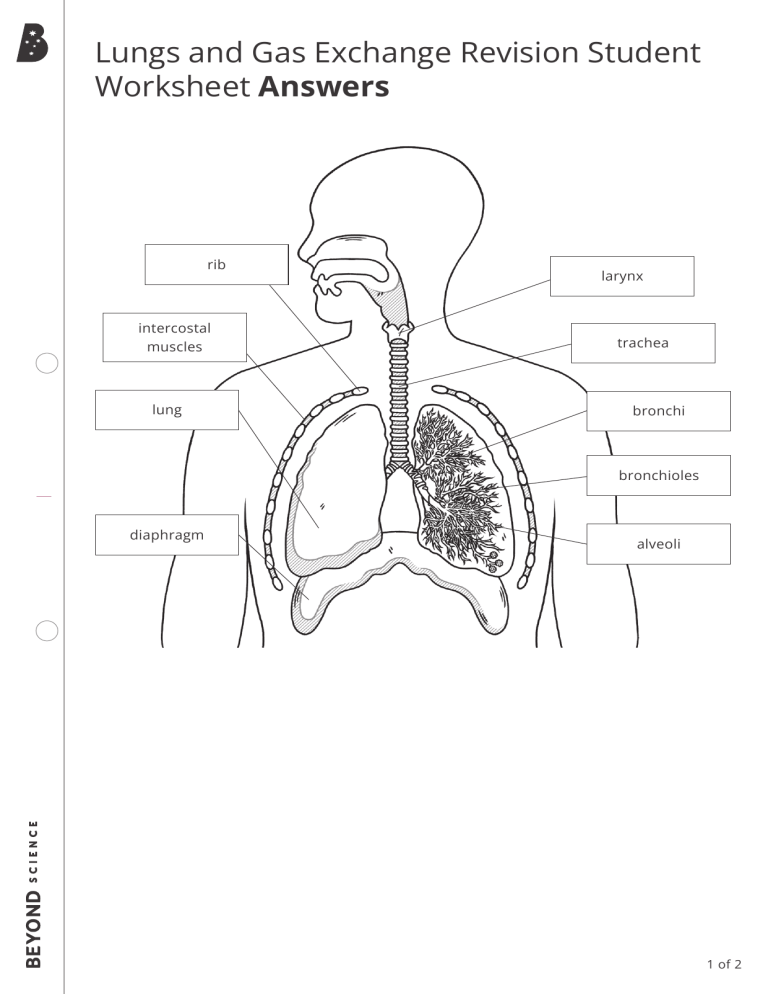
Lungs and Gas Exchange Revision Student Worksheet Answers rib intercostal muscles lung larynx trachea bronchi bronchioles diaphragm alveoli 1 of 2 Lungs and Gas Exchange Revision Activity Student Worksheet Answers Respiration The lungs are protected by the rib cage. The intercostal muscles move the ribs when you breathe, however, the muscle responsible for moving air in and out of your lungs is the diaphragm. The body takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The process of taking air in is called inhalation and removing air is called exhalation. As you trace the path of airflow, the air moves down the trachea and into the bronchi and then to the bronchioles. The bronchioles then further branch out to structures that look like a bunch of grapes. These are the alveoli. Each alveolus (singular of alveoli) is surrounded by capillaries which is a vessel so small that only red blood cells fit through. As the blood moves past the alveoli, oxygen is absorbed and attaches to each red blood cell. Carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and back into the alveoli where it can travel back up through the lungs to be exhaled. Gas Exchange at the Alveoli 1. Label the gases identified as A and B. A = carbon dioxide B = oxygen 2. Describe what is happening in the image above. The circles are red blood cells; as the blood cells move through the capillary and along the alveolus, carbon dioxide is released back into the alveolus to be exhaled via the lungs. As the blood cells continue to move, oxygen from the alveolus moves onto the red blood cells to be transported to other cells around the body. 3. Explain two ways that alveoli are adapted for gas exchange. Any two of the following: • Large surface area that allows more gas to be exchanged at once. • Thin walls that allow for a short diffusion pathway. • Moist walls that help gases pass/diffuse across the membrane. • Permeable walls that allow gases to pass/diffuse through them. • Large blood supply that maintains a constant concentration gradient. • Large diffusion gradient that allows oxygen to pass/diffuse from the lungs into the blood and carbon dioxide to pass/diffuse from the blood into the lungs. 2 of 2