Business Analytics Quiz: Probability, Statistics, Decision Making
advertisement

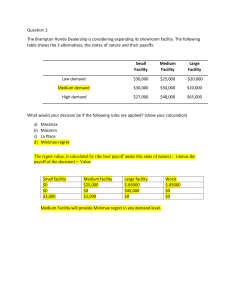
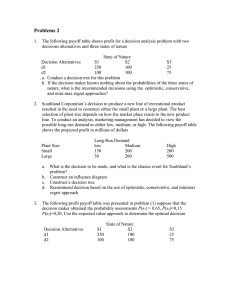
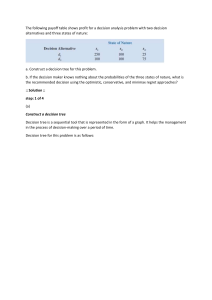
ELE BA Quiz 2 I. TRUE or FALSE. On the space provided before each number, write TRUE if the statement is correct; otherwise, FALSE. 1. A proposal that could either be approved or not approved is an example of experiment. 2. The sample space for rolling two dice is 36. 3. A three diagram is a device consisting of line segments emanating from a starting point and also from the outcome point. 4. In tossing 2 coins at a time, the probability of getting 2 heads is ½. 5. When a single die is rolled, the probability of getting a 9 is zero. 6. Empirical probability is calculated as a relative frequency of occurrence. 7. A company financial analyst calculating the cost it will take before they could reach their target profit illustrates continuous sample space. 8. The normal distribution learned in Statistics is a type of continuous distribution. 9. A probability distribution lists all of the possible values of the random variable and their corresponding probabilities. 10. Probability distributions must be nonnegative and the sum of the probabilities must sum up to 1. 11. Marginal probability is also called Simple Probability. 12. If A and B are two events, then the conditional probability of B is written as P(A/B) and read as “the probability of A given that B has already occurred.” 13. Two events A and B are dependent events if the occurrence of one event does not affect the probability of the occurrence of the other event. 14. Uncertainty means that relevant parameters such as costs, capacity and demand have known values. 15. In the decision making under risk, a widely applied criterion is expected monetary value. 16. Maximax approach as a decision criterion is also known as conservative approach. 17. A single-stage decision problem is a decision problem which has two or more sets of decision alternatives. 18. The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) is the measure of how much a decision-maker would be willing to pay in exchange for the perfect information gathered to reach certainty. 19. The minimum expected opportunity loss is also equal to the expected value of perfect information. 20. If the expected value of sample information is 1.37 and the expected value of perfect information is 2.3, then the efficiency of sample information is equal to 56.59%. II. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice on the space provided before each number. 1. For a card drawn from an ordinary deck, find the probability of getting a queen. A. B. C. D. 4/50 4/13 1/13 1/4 2. If a family has three children, find the probability that all the children are girls. A. B. C. D. 1/8 1/3 3/8 3/6 3. A card is drawn from an ordinary deck. Find the probability of getting a 3 or a diamond. A. B. C. D. 1/13 4/13 13/52 15/52 4. In tossing a die once, find the probability of getting a 5 or 6. A. B. C. D. 1/6 1/3 2/5 1/2 5. A category of probability which is based on an individual’s personal judgment or experience? A. B. C. D. Classical Diagnostic Empirical Subjective 6. Assume that 10, 20, 30, and 40 are the possible values of a random variable X, with corresponding probabilities 0.15, 0.25, 0.35, and 0.25. Compute for the probability of X less than or equal to 30. A. 0.25 B. 0.40 C. 0.75 D. 1 For numbers 7 to 10. A box contains 500 envelopes of which 75 contain $100 in cash, 150 contain $25, and 275 contain $10. An envelope may be purchased for $25. What is the sample space for the different amounts of money? Assign probabilities to the sample points. 7. Find the probability that the first enveloped purchased contains $10. A. B. C. D. 75/500 150/500 275/500 1 8. Determine the probability that the first enveloped purchased contains $100. A. B. C. D. 75/500 150/500 275/500 425/500 9. Compute the probability that the first enveloped purchased contains less than $100. A. B. C. D. 75/500 150/500 275/500 425/500 10. Calculate the mean of the probability distribution. A. B. C. D. 25 28 75 166.67 11. A manager at Moksha Yoga Center believes that 37% of female and 30% of male open house attendees she contacts will purchase a membership. What is the probability that randomly selected female contacted by the manager will not purchase a membership? A. B. C. D. 0.30 0.37 0.63 0.70 12. Which does not illustrate decision making environments? A. B. C. D. Certainty Laplace Risk Uncertainty 13. Which of the following is not a criterion on decision making under certainty? A. B. C. D. Maximax Maximin Laplace Minimum Regret For numbers 14 to 16. Given the payoff table below. Possible Future Demand Alternatives Low Moderate High Small Facility $10 $10 $10 Medium Facility $7 $12 $12 ($4) $2 $16 Large Facility 14. Determine the best alternative if it is known with certainty that the demand will be low. A. B. C. D. Small facility Medium facility Large facility None 15. What is the best alternative if it is known with certainty that the demand will be moderate? A. B. C. D. Small facility Medium facility Large facility None 16. Calculate the associated payoff with the best alternative if it is known with certainty that the demand will be high. A. $7 B. $10 C. $12 D. $16 17. Which decision making under uncertainty uses the criterion best average payoff? A. B. C. D. Maximax Maximin Laplace Minimax Regret 18. Determine the decision making under uncertainty that uses the criterion least of the worst regrets. A. B. C. D. Maximax Maximin Laplace Minimax Regret For numbers 19 to 22. An investor is considering investing in Stocks, Bonds or Real Estate under uncertain economic conditions. The payoff table of returns for the investor’s decision situation is shown below. Economic Conditions Decision Good Stable Poor Stocks 250,000 350,000 150,000 Bonds 200,000 200,000 200,000 Real Estate -100,000 500,000 300,000 19. Determine the best investment under uncertainty using the Maximax decision criterion. A. B. C. D. Stocks Bonds Real Estate Uncertain 20. Compute the payoff using the Maximin decision criterion. A. B. C. D. 150,000 200,000 350,000 500,000 21. Which is the best investment using Laplace criterion? A. B. C. D. Stocks Bonds Real Estate Uncertain 22. Calculate the Minimax regret. A. B. C. D. 150,000 300,000 350,000 500,000 For numbers 23 to 25. ABC Company is planning to manufacture its own new PC-based system, which intends to be marketed by next year under its own brand. One particular concern of the company has something to do with the keyboard that will be used in the system, which will have a special feature on function keys. The payoff table is given below. The profit contribution is in thousands of dollars. Economic Conditions Alternatives Future Low (25%) Sales Moderate (60%) Level High (15%) Manufacture -30 20 110 Buy from local 20 60 50 Buy from Japan 10 45 80 23. Calculate the maximum expected payoff opportunity. A. B. C. D. $21,000 $41,500 $48,500 $57,500 24. Determine the best decision using the expected payoff opportunity. A. B. C. D. Manufacture Buy from local Buy from Japan Risky 25. What is the expected value with perfect information? A. B. C. D. $21,000 $41,500 $48,500 $57,500 26. Calculated the expected value of perfect information. A. B. C. D. $9,000 $10,500 $11,500 $57,500 For numbers 27 to 30. 27. Compute the expected value of node 8. A. B. C. D. 7.80 7.94 13.46 18.26 28. Determine the expected value of node 10. A. B. C. D. 1.15 7.35 8.15 12.20 29. What is the expected value of node 14? A. B. C. D. 7.80 12.20 14.20 18.26 30. Calculate the expected value with sample information. A. B. C. D. 8.15 14.20 15.93 18.26