Natalie Adeeleh
1191018
BUSA3371
PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT 1
Module A - Decision Modeling:
Dr. sahar Jallad
● Operation managers are decision makers. They should know how to make good
decisions. ----> decisions based on logic and data.
● Steps for making good decisions: (decision making process)
1- observe the issue 2- set objectives 3- create a model 4- evaluate alternative
5-select best option 6-implement and analyse
● Good designers need data that can be analysed and transferred to information. This is
done through the use of big data: huge amount of data collected in digital form
● Important terms:
➢ Alternative: choosing between two options (whether to wear an umbrella or not)
➢ State of nature: something out of your control, cannot choose, an occurring
situation. (tomorrow's weather)
● Decision tree vs table: tree is used to show the alternatives and state of nature while the
table is used to analyze the outcomes(favorable or unfavorable)
● Decision making environments: depending on amount of knowledge we have about
state of nature
1. Uncertainty: no knowledge about expected state of nature
➢ Maximax: optimistic, choosing the maximum of the maximum (highest number)
➢ Maximin: pessimistic, choosing the maximum of the minimum.(lowest number)
➢ Equally likely: average, equal probabilities, pick highest average. ((fav-unfav)/2)
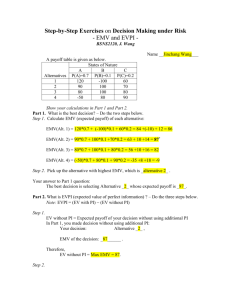
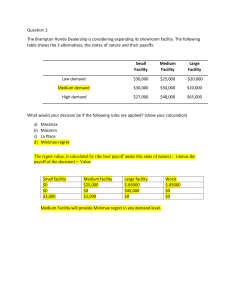
2. Risk : probabilities of several options of state of nature
➢ Expected monetary value: how much money (value) you expect to gain from a
certain decision.
EMV= ∑payoff*probability {summation of alternatives}
Payoff= money probability = chance (all probabilities must sum to 1)
➢ After calculating EMV, compare and choose the alternative with the highest value
3. Certinaity: complete knowledge on state of nature.
➢ Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI) is the price that one would be
willing to pay in order to gain access to perfect information: is when we know
everything we need to make the best choice.
➢ EVPI=difference between value under perfect info (certainty) and value under risk
= EVwPI-EMV {∑ best outcome payoff*probability}
● Decision trees are used to display and analyze sequential decisions and state of nature.
➢ Constructing a tree:
Define the problem, draw the tree, assign probabilities, estimate payoff, calculate EMV
backwards.