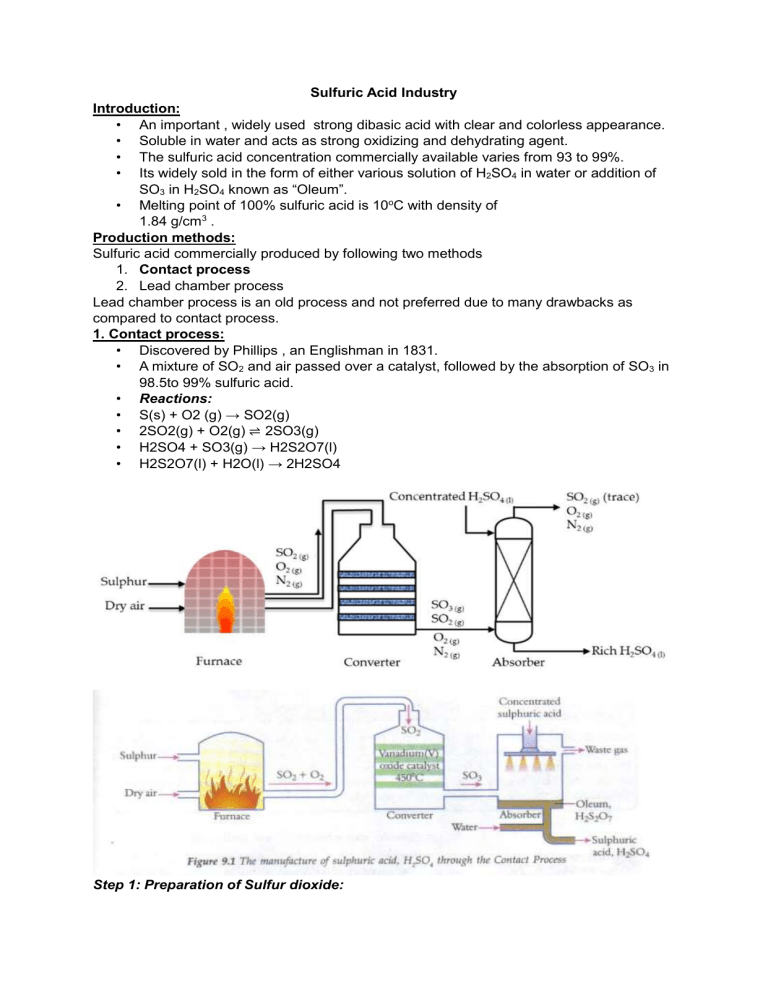
Sulfuric Acid Industry Introduction: • An important , widely used strong dibasic acid with clear and colorless appearance. • Soluble in water and acts as strong oxidizing and dehydrating agent. • The sulfuric acid concentration commercially available varies from 93 to 99%. • Its widely sold in the form of either various solution of H2SO4 in water or addition of SO3 in H2SO4 known as “Oleum”. • Melting point of 100% sulfuric acid is 10oC with density of 1.84 g/cm3 . Production methods: Sulfuric acid commercially produced by following two methods 1. Contact process 2. Lead chamber process Lead chamber process is an old process and not preferred due to many drawbacks as compared to contact process. 1. Contact process: • Discovered by Phillips , an Englishman in 1831. • A mixture of SO2 and air passed over a catalyst, followed by the absorption of SO3 in 98.5to 99% sulfuric acid. • Reactions: • S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2(g) • 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) • H2SO4 + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l) • H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4 Step 1: Preparation of Sulfur dioxide: SO2 is prepared by burning Sulfur in the presence of excess air so that the product combines with oxygen which is helpful for the next stage. S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2(g) Step 2: Preparation of Sulfur trioxide: Sulfur trioxide is formed when Sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen in a ratio of 1:1 at a temperature of 400 °C – 450°C and a pressure of 1-2 atm in the presence of V2O5 as a catalyst. This reaction is reversible in nature. 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) Step 3: Preparation of concentrated Sulfuric acid: The Sulfur trioxide formed is first made to react with concentrated Sulfuric acid. Sulfur trioxide cannot be dissolved in water directly as it leads to the formation of fog. The product obtained after this reaction is known as oleum. The oleum obtained is then dissolved in water to obtain concentrated Sulfuric acid. H2SO4 + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l) H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4 Raw materials: 1. Elemental sulfur – Can be obtained in pure form from ores via mining. – Can also be obtained from fuel gases. 2. Air Used as a source of oxygen for the conversion of sulfur to SO2 and then catalytic conversion of SO2 to SO3 Catalyst: Vanadium pentaoxide (V2O5) Major steps: 1. Melting of sulfur 2. Air drying 3. Sulfur burning 4. Heat recovery 5. SO2 convertor 6. Economizer 7. Oleum production 8. H2SO4 production (9899%). 1.Melting of sulfur: • A concrete tank with steam coils and a mechanical agitator to reduce the melting time ( steam pressure is usually 50-70 psi). • Molten sulfur transferred to settling tank where it remains for 72 hours in order to remove insoluble sulfur sludge. • The temperature is maintained at 134-140 o C.; melting point of sulfur 115 °C • Then transferred from settling tank to sulfur burner by a submerged centrifugal pump. • The transfer line is steam jacketed to maintain temperature. 2. Drying of air : • Air is dried to remove moisture in it in order to prevent corrosion and mist formation. • A turbo blower is used to blow air into drying tower and 93-98% sulfuric acid is sprayed for dehydration. • Drying tower is fabricated with steel and is lined with acid proof bricks with ceramic rings. • The moisture free air is then heated via heat exchanger and then entered into the sulfur burner. 3. Sulfur burning : • Sulfur burner consists of steel vessels lined with firebricks and insulation bricks or a refractory material. • Molten sulfur is injected into the burner along with the air and is converted into sulfur dioxide. S+O2 SO2 • The product gas consists of about 10-12% SO2 and temperature varies from 10001200oC 4. Heat recovery: • Oxidation of the SO2 upon the catalyst layer is not possible at such a high temperature. • Therefore, the temperature of the gas is reduced to 420-440oC via waste heat boiler before entering the convertor. • Also, gas is filtered once again in order to remove any traces of dust and ash via hot gas filter. • Gas filter consists of insulated steel vessel with crushed fire bricks as a filter medium. 5. SO2 convertor: • The convertor consists of single insulated vessel consists of four layers of catalyst supported upon cast iron grids. • The reaction between SO2 and oxygen is exothermic, the gas enters the first layer at temperature of 405-415oC and leaves at 595-605oC . • At this stage 70 % conversion is achieved. SO2 + 1/2O2 SO3 • The gas is removed form the convertor and then cooled to 435-430oC and then reenters the second layer of the catalyst. • The final conversion is achieved about 98% in the remaining three layers of SO2 to SO3. 6. Economizer : • The gas from convertor is passed thorough the economizer and cooled to a temperature of 105-235oC . • The hot water from economizer is fed to waste heat boiler. 7. Oleum producion (Sulfuric acid fuming) : • Oleum (H2S2O7) is an intermediate product in the sulfuric acid manufacturing process. • Oleum tower consists of two parts , top portion where the distribution of the Oleum occurs, and bottom part used to circulate the 20% Oleum continuously. • Strength of the Oleum obtained is usually 38%. • Oleum is taken out form the system continuously , cooled and stored in steel tanks. 8. H2SO4 production: • The gas leaving the Oleum tower contains unabsorbed SO3 and it is passed through the 98% acid absorption tower. • Similar in construction to drying tower. • The 98% acid tank is common for both i.e. for drying air and for absorption tower. • 98 to 99 % H2SO4 is collected at the bottom of the tower and taken to storage via the outlet of drying acid cooler at temperature of 40—50oC. • The exhaust gases might consist of traces of SO3 and SO2(0.3% by volume). SO2 conversion to SO2 SO2 convertor Rate of Reaction 𝑟𝐴 = 𝑘𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝑏 rA=[k(T)][fn(CA, CB)] At Constant Temperature (227 C) and Pressure 14.7 Atm 28% SO2 and 72% Air Equilibrium Yield Chemical reactions • • • • • S(s)+O2(g) 2SO2(g)+O2(g) SO3(g)+H2SO4(l) SO3(g)+H2O(l) H2S2O7(l)+H2O(l) SO2(g) 2SO3(g) H2S2O7(l) H2SO4(l) 2H2SO4(l) Uses of Sulfuric Acid • • • • • • Used in the production of very important and widely used chemicals like fertilizers, metal sulfates, Nitric acid, Phosphoric acid, HCl. Also used in the manufacturing of explosives materials like TNT, nitrocellulose. Used in the purification of petroleum. A major used in the production of dyes. Used for the extraction of copper and uranium form ores. It serves as an electrolyte in lead acid battery.




