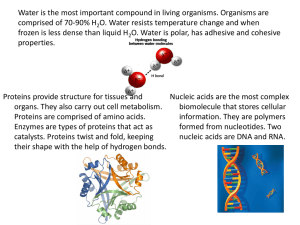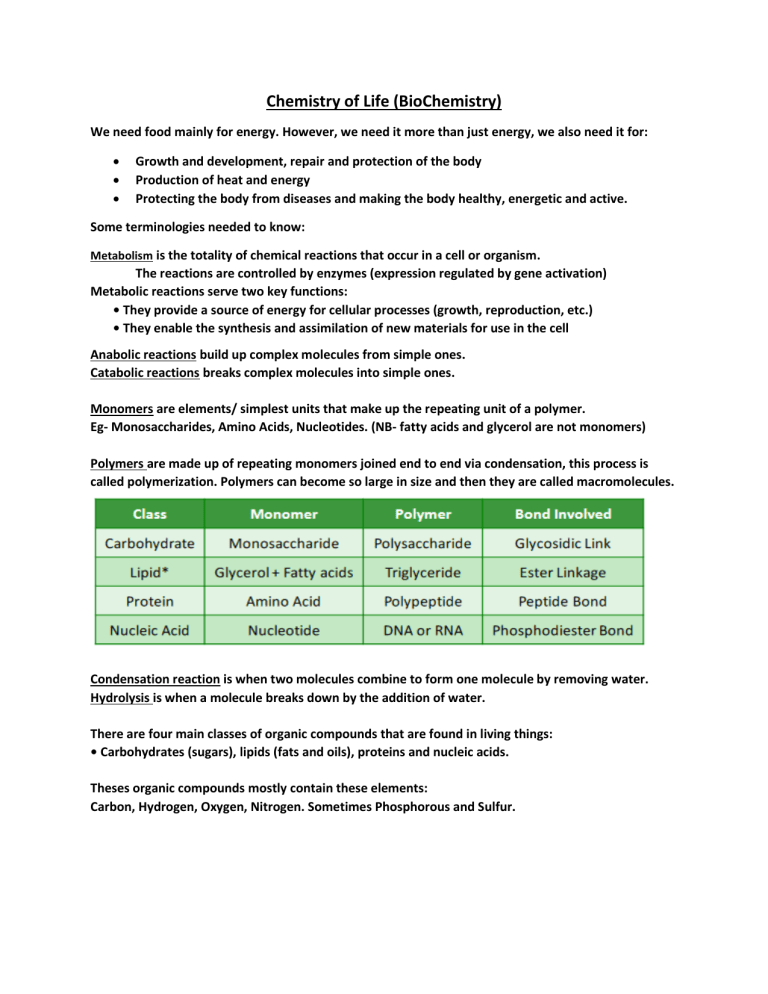
Chemistry of Life (BioChemistry) We need food mainly for energy. However, we need it more than just energy, we also need it for: • • • Growth and development, repair and protection of the body Production of heat and energy Protecting the body from diseases and making the body healthy, energetic and active. Some terminologies needed to know: Metabolism is the totality of chemical reactions that occur in a cell or organism. The reactions are controlled by enzymes (expression regulated by gene activation) Metabolic reactions serve two key functions: • They provide a source of energy for cellular processes (growth, reproduction, etc.) • They enable the synthesis and assimilation of new materials for use in the cell Anabolic reactions build up complex molecules from simple ones. Catabolic reactions breaks complex molecules into simple ones. Monomers are elements/ simplest units that make up the repeating unit of a polymer. Eg- Monosaccharides, Amino Acids, Nucleotides. (NB- fatty acids and glycerol are not monomers) Polymers are made up of repeating monomers joined end to end via condensation, this process is called polymerization. Polymers can become so large in size and then they are called macromolecules. Condensation reaction is when two molecules combine to form one molecule by removing water. Hydrolysis is when a molecule breaks down by the addition of water. There are four main classes of organic compounds that are found in living things: • Carbohydrates (sugars), lipids (fats and oils), proteins and nucleic acids. Theses organic compounds mostly contain these elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen. Sometimes Phosphorous and Sulfur. Now foods can be broken down into 6 components: Carbohydrate- It is the main source of energy for many organisms. It consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They have no smell, colour but have a sweet taste. Now, carbohydrates can be divided into three categories: Sources of Carbohydrates: Roles of Carbohydrates: • • • Source of energy in Respiration o As it contains many C-H bonds, so when broken down gives of a lot og energy. Building blocks for larger molecules o Eg- RNA, DNA, ATP, glycoproteins and glycolipids in plasma membrane. Structural Support o Eg- Cellulose in cell walls Which disaccharides form with which glucose: Another part to discuss is Starch Test and Benedicts Test. Fats is an essential component of food. It is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. There are 2 types of fatty acids in food. Now solid lipids are called fats and liquid lipids are called unsaturated fatty acids. Eg- fats of fish and meat contain saturated fatty acids while cooking oil are unsaturated fatty acids. Sources of Lipids Now role of lipids: Fats are high in calories and that is why it gives of a lot of energy when respired. Also fats are major structural component of plasma membranes and also needed for many other biological functions such as hormones. Fat test remains to be discussed. Proteins is composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. Proteins are identified by the amino acids present and so far we have 20 amino acids. Sources of Protein: Roles of proteins: • Proteins play a crucial role in building up many substances. This depends on the compound which can have many roles Proteins can be soluble and insoluble due to hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. The amino acids are responsible for it. They can be polar, non-polar and charged as well. Test for proteins remains. Vitamins are essential for normal growth and a healthy body. Vitamins are organic compounds that are needed in small amounts in the body. If they are missing the body, it can then lead to vitamin deficiency. Vitamins and minerals deficiency disease Minerals and Inorganic elements Also things to discuss are fibres.