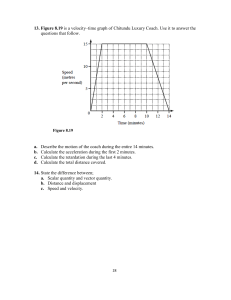
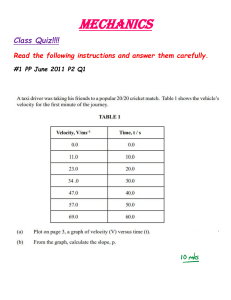
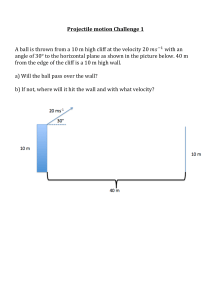
SRI CHAITANYA EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS, INDIA. A.P,TELANGANA,KARNATAKA,TAMILNADU,MAHARASHTRA,DELHI,RANCHI JR PHYSICS IPE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS Very Short Answer Questions : QUESTION NO: 1 1. What is Physics? 2. What is Raman Effect? 3. What are the fundamental forces in nature? 4. What is the contribution of S. Chandrashekhar to physics? 5. What is the discovery of C.V. Raman? QUESTION NO: 2 1. Distinguish between accuracy and precision 2. Distinguish between fundamental and derived units 3. How can systematic errors be minimized or eliminated ? 4. What are significant figures? How many significant numbers in 0.350? 5. The percentage error in the mass and speed are 2% and 3% respectively. What is the maximum error in kinetic energy calculated using these quantities ? 6. Express unified atomic mass unit in Kg. QUESTION NO: 3 1. A = ˆi + ˆj ,What is the angle between the vector and x-axis 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. If P = 2i + 4 j+14k and Q=4i+4j+10k , find the magnitude of P+Q The vector component of a vector is equal to its horizontal component. What is the angle made by the vector with x-axis. Two forces magnitudes 3 units and 5 units act at 600 with each other. What is the magnitude of the resultant ? When two right angled vectors of magnitude 7 units and 24 units combine, what is the magnitude of their resultant? What is the acceleration of a projectile at the top of its trajectory? QUESTION NO: 4 1. A bats man hits back a ball straight in the direction of the bowler without changing its initial speed of 12 m/sec. If the mass of the ball is 0.15 kg. Determine the impulse imparted to the ball (Assume linear motion of the ball) 2. What is inertia? What gives the measure of inertia? 3. A horse has to pull harder during the start of the motion than later. Explain 4. What happens to the coefficient of friction, if the weight of the body is doubled? 5. Can the coefficient of friction be greater than one ? 6. When a Bullet is Fired from a gun, the gun gives a kick in the backward direction. Explain. 7. What is Rolling Friction? Write the units for coefficient of friction. 8. If a bomb at rest explodes in to two pieces, the pieces travel in opposite directions. Explain. Sri Chaitanya Page 7 QUESTION NO: 5 1. Give the expression for the excess pressure in air bubble inside the liquid. 2. What is the principle involved behind the carburetor of an automobile 3. What are drops and bubbles spherical? 4. What is magnus effect ? 5. If the diameter of a soap bubble is 10 mm and its surface tension is 0.04N/m. Find the excess pressure inside the bubble? 6. When a water flows through a pipe, which of the layer moves fastest and slowest? QUESTION NO: 6 1. What is angle of contact? What are its values for pure water and mercury? 2. Mention any two applications of Bernoulli’s theorem. 3. Define the average pressure. Mention its units and dimensional formula. 4. Define Viscosity. What are it’s units and dimensions? 5. Give the expression for the excess pressure in a liquid drop. 6. What is a Hydrostatic paradox? QUESTION NO: 7 1. State Wien’s displacement law? 2. Why utensils are coated black ? Why bottom of the utensils are made of copper ? 3. Why gaps are left between rails on a railway track? 4. Can a substances contract on heating? Give an examples. 5. What are the lower and upper fixing points in Celsius and Fahrenheit scales? 6. What is Thermal Expansion? 7. Why is it easier to perform the skating on the snow? QUESTION NO: 8 1. Distinguish between heat and temperature ? 2. What is latent heat of vaporization? 3. The roof of buildings are often painted white during summer. Why? 4. What is green house effect ? Explain global warming? 5. Why do liquids have no linear and areal expansions? 6. What is specific gas constant? It is same for all gases. 7. If the maximum intensity of radiation for a black body is found at 1.45 micro meter, What is temperature of radiating body?(wien’s costant =2.9*10−3 mk) 8. Ventilators are provided in rooms just below the roof. Why? QUESTION NO: 9 1. State Dalton’s law and write its equation 2. Define mean free path. 3. When does a real gas behave like ideal gas? 4. State Boyle’s and Charles’s laws. 5. What is the expression between pressure and kinetic energy of a gas molecule? Sri Chaitanya Page 8 6. Two Thermally Insulated vessels 1 & 2 volumes V1 & V2 are joined with a value and filled with air at temperatures (T1, T2) and pressures (P1, P2) respectively. If the volume joining the vessels is opened, What will be the temperature inside the vessels at Equilibrium. QUESTION NO: 10 1. If the absolute temperature of a gas increased to 3 times, what will be the increase in RMS velocity of the gas molecule? 2. When pressure increases by 2%. What is the percentage decreases in the volume of a gas, Assuming Boyle’s law is obeyed. 3. Explain the concept of degrees of freedom for molecules of a gas. 4. What is the law of equipartition energy? 5. Name two prominent Which provide conclusive evidence of molecular motion. OR 1. 2. 3. 4. 7. Is it necessary that a mass should be present at the centre of mass of any system? Why are spokes provided in a bicycle wheel? By spinning egg on a table top, how will you distinguish a hardboiled egg from raw egg? If the polar ice caps of the earth were to melt, what would the effect of the length of the day be? What is the moment of inertia of a rod of mass M, Length about an axis perpendicular to it through one end? What is the difference between in position of a girl carrying a bag in one of her hands and another girl carrying a bag in each of her two hands? We cannot open or close the door by applying force at the hinges? Why? 8. Why do we prefer a spanner of longer arm as compared to the spanner of shorter arm? 5. 6. Sri Chaitanya Page 9 Short Answer Questions : Motion in a straight line 1. Derive the equations S = ut + 1 2 at 2 using graphical method. 2. A particle moves rectilinearly with uniform acceleration. It’s velocity at time t=0 is V1 and at time t=t is V2. Average velocity of the particle in this time interval is V1+V2/2. Is this statement true or false substantiate your answer? 3. Can the velocity of an object be in a direction other than the direction of acceleration of the object. Explain? 4. A ball is dropped from the roof of a tall building and simultaneously another ball is thrown with some velocity from the same roof. Which ball lands first explain ur answer? 5. Car travels the first third of a distance with speed of 10Km/h. the second third at 20km/h and the last third of 60 Km/h. What is its means speed over the entire distance? 6. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 20m/sec from the top of multistory building. The height of the point from where the ball is thrown is 25m from the ground. a) How high will the ball rise? And b) How long will it be before the ball hits the ground ? (g=10m/sec) Motion in a plane 7. State parallelogram law of vectors. Derive an expression for the magnitude and direction of resultant vector? 8. Show that the maximum height and range of projectile are u 2 sin 2 θ 2 g and u 2 sin 2 θ g 9. Define unit vector, null vector and position vector? 10. Show that the trajectory of an object thrown at certain angle with the horizontal is a parabola? 11. Show that the maximum height reached by a projectile launched at an angle of 45ο is one quarter of it’s range. 12. If a + b = a − b prove that the angle between a and b is 90ο . Laws of Motion 13. Define the terms momentum and impulse state and explain the laws of conservation of linear momentum. Sri Chaitanya Page 10 14. Why are shock absorbers used in motor cycles and cars. 15. Explain the advantages and disadvantages if friction 16. Mention the methods to reduce friction? 17. Why is pulling the lawn roller is preferred than pushing the lawn roller. System of particles and rotational motion 18. Define the vector product. Explain the properties of a vector product with two examples? 19. Distinguish between center of mass and center of gravity? 20. Define angular acceleration .and torque. Establish the relationship between angular acceleration and torque. 21. Define angular velocity. Derive v= r ω ? 22. State and prove the principle of conservation of angular momentum. Explain the principle of conservation of angular momentum with examples? Gravitation. 23. What is orbital velocity? Obtain an expression for it? 24. What is escape velocity? Obtain and expression for it? 25. What is geostationary satellite? State its uses? 26. State Kepler’s law of planetary motion? 27. Derive the relation between acceleration due to gravity(g)at the surface of a planet and gravitational constant “G” Mechanical properties of solids 28. Describe the behavior of a wire under gradually increasing obtain the expression for it? 29. Define stress and explain the types of stress. 30. Define strain energy and derive the equation for the same. 31. Define strain and explain the types of strain Thermal properties of matter 32. Two identical rectangular strips one of copper and the other of steel are riveted together to form a bimetallic strip. What will happen on heating? 33. Pendulum clocks generally go fast in winter and slow in summer. Why? 34. In what way is the anomalous behavior of water advantages to aquatic animals. 35. Write the short notes on triple point of water? 36. Explain the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales of temperature an obtain the relation between them. Sri Chaitanya Page 11 37. Explain conduction, convection and radiation with examples. Thermodynamics 38. Compare the isothermal and an adiabatic process? 39. State and explain the first law of thermodynamics? 40. Define the two molar specific heats of a gas and deduce the relation between them? 41. Define the two principle specific heats of a gas, which is greater and why? Long Answer Question. 1. State and prove the law of conservation of energy in case of freely falling bodies. A machine gun fires 360 bullets per minute and each bullet travels with a velocity of 600m/s. If the mass of each bullet is 5 gm, fine the power of machine. 2. State and prove work energy theorem. Obtain equations for potential and kinetic energies. 3. Show that the motion of simple pendulum is simple harmonic motion and obtain an equation for its time period. What is the second pendulum? Calculate the length of the seconds pendulum. 4. Define simple harmonic motion. Show that the motion of point of projection of particle performing uniform circular motion of any diameter is simple harmonic. 5. What are collisions.? Explain types of collisions. Develop the theory of one dimensional elastic collision. A body freely falling from a certain height ‘h’ after striking a smooth floor rebounds and h rises to ‘h/2’. What is the coefficient of restitution between the floor and the body. 6. Explain the reversible and irreversible process. Describe the working of Carnot engine. Obtain an expression for its efficiency. 7. State two laws of thermodynamics. How is heat engine different from refrigerator. 8. State and explain Newton’s law of cooling. State the conditions under which Newton’s law of cooling is applicable. A body cools from 60° C to 50° C in 5 minute and to 40° C in another 8 minutes. Find the temperature of surroundings. 9. State Newton’s second law of motion. Hence derive the equation of motion F=ma from it. Sri Chaitanya Page 12