PLANTS - The Home Unit
advertisement

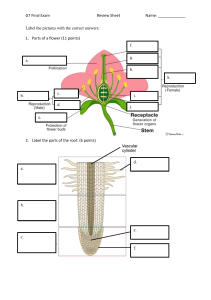
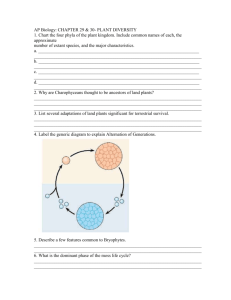
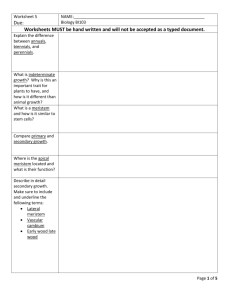
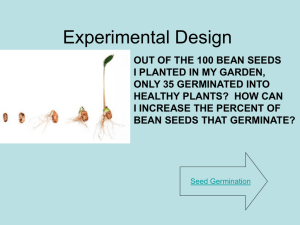
PLANTS - The Home Unit Use your textbook or any other source to learn the vocabulary, structures and function and processes associated with the plant kingdom. Write answers, make vocabulary lists, draw and label diagrams and make tables to help you understand all this information. You may use your handwritten notes on the open note test. Objectives: 1. State the basic characteristics for an organism classified as a plant? 2. Distinguish between plants and algae. 3. Explain the evolution of land plants. (Where did they come from?) 4. List the characteristics that enabled plants to colonize the land. How did plants solve the problems that living on land presented? What structures evolved? 5. State how plants store carbohydrates. What is the composition of their cell wall? What is the difference between plant and animal cell cytokinesis? 6. Distinguish between these major groups of plants: angiosperms, gymnosperms, ferns, bryophytes. Which are seedless? Which are vascular? Which are bryophytes? 7. Explain the term alternation of generations? Be sure to use simple vocabulary to describe. 8. Understand the life cycles for each major plant group. 9. State differences between a monocot and a dicot? 10. Define these terms: xylem and the phloem, meristem, apical meristem, primary growth, secondary growth 11. Plants have 3 basic “organs”- roots, stems and leaves. Structure of the root: Know these regions and their function- root cap, zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of maturation 12. Structure of the stem: Know these regions and their function - cutin, parenchyma/ collenchymas/schlerenchyma (3 types of ground tissue),vascular cambium, cork cambium 13. Structures of a leaf: Know the layers of the leaf shown in a cross section, and their functions. 14. Flower Structures – know the structure and functions of a complete flower (one flower that has both male and female parts) 15. Understand these terms associated with reproduction: double fertilization, endosperm 18. Define photoperiod and phototrophism. 20. Explain the types of vegetative propagation. 21. Know the function of these 5 types of plant hormones: gibberellins, auxins, ethylene, abscisic acid and cytokinins. LAB PORTION: (20 pts of test) Seed Germination and Observation – Germinate a seed using a moist paper towel and a plastic bag or by placing the seed along the side of a clear jar with wet towels in the center. Observe daily. Record observations and take photos on days that there are changes, label parts (5 photos minimum, see your text for germination terminology). Observe until the epicotyl is clearly apparent, then plant and provide for growth. Bring in for credit once true leaves are seen. Be sure name is on it. It must be in by the test day. Be careful that fungus does not grow on your developing plant. You may want to start several seeds. Allow a couple weeks for plant to germinate and grow to required size.