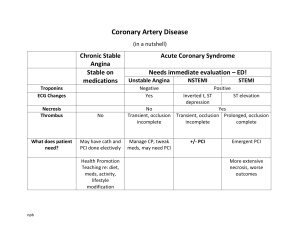
ACS Pathophysiology Worksheet Type Causes Pathophysiology BRING COMPLETED WORKSEET WITH YOU TO CLASS Clinical Manifestations Stable Angina* *Not considered a part of ACS Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Include any cultural perspectives or alternative therapies or complimentary interventions as necessary ACS Pathophysiology Worksheet Type Complications Treatments Diagnostics ECG Changes BRING COMPLETED WORKSEET WITH YOU TO CLASS Troponin Nursing Diagnosis Stable Angina* *Not considered a part of ACS Unstable Angina NSTEMI STEMI Include any cultural perspectives or alternative therapies or complimentary interventions as necessary Points to Ponder Glycoprotein IIa/IIIb (anti-plt) • • • • Reopro, Integrilin, Aggrastat, only available IV Used with ASA, Heparin, Plavix Used in UA and with NSTEMI for medical MGMT and for those undergoing PCI Used in STEMI at time of PCI ADP Inhibitors • • • • Plavix, Effient, Brillinta Used for UA, NSTEMI & STEMI right before PCI Will take for 1 yr following placement of coronary stent OK to Give w/ ASA (Dual Antiplatelet Therapy, DAPT) to prevent thrombosis of stent placed during PCI Fibrinolytics • • • • If PCI is not possible w/i 120 minutes, fibrinolytic therapy should be initiated within 30 minutes of patient arrival at the hospital Anticoagulation w/ UFH, LMWH Plavix ASA Treatment for STEMI • • • • Complete and persistent occlusion of blood flow. Immediate reperfusion Before PCI, patients should receive dual antiplatelet agents, including intravenous heparin infusion as well as an thienopyridine (Plavix) If percutaneous intervention is unavailable within 90 minutes of the diagnosis of STEMI, reperfusion should be attempted with an intravenous thrombolytic agent. NSTEMI • • • Stable, asymptomatic patient may not benefit from emergent percutaneous coronary intervention, managed medically with antiplatelet agents. PCI can be done within 48 hours of admission In NSTEMI patients with refractory ischemia or ischemia with hemodynamic or electrical instability, PCI should be performed emergently. Discharge Meds • • • Before discharge for acute MI, patients may routinely be given aspirin, high-dose statin, beta-blocker, and/or ACE-inhibitor. If PCI is contemplated, it should be done within 90 minutes in a PCI capable hospital or 120 minutes if transfer is required. If PCI is not possible w/i 120 minutes, fibrinolytic therapy should be initiated within 30 minutes of patient arrival at the hospital. Parenteral anticoagulation, in addition to antiplatelet therapy, is recommended for all patients.