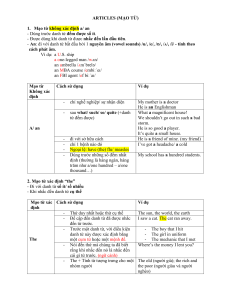
ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KỲ II TIẾNG ANH 9 A. Grammar: I. CONDITIONAL SENTENCES (CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN) TYPE TYPE 1 – Present Real Condition IF CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE Simple Present S + Vo/ Vs/es Simple Future S+ WILL + Vo CAN MAY TYPE 2 – Present Unreal Condition Past Subjunctive S + V2/Ved (BE là WERE) Future in the past S + WOULD + Vo COULD MIGHT Ví dụ: - Type 1: + If it rains this evening, I won’t go out. (Nếu tối nay trời mưa tôi sẽ không ra ngoài.) + Lan will miss the bus if she doesn’t hurry. (Lan sẽ bỏ lỡ xe buýt nếu cô ấy không khẩn trương lên.) - Type 2: + If I were you, I would buy that book. (Nếu tôi là bạn, tôi sẽ mua quyển sách đó.) + He could buy a bike if he had enough money. (Anh ấy có thể mua xe đạp nếu anh ấy có đủ tiền.) - Unless (Trừ phi) = If …not (Nếu……. không) Ví dụ: If you don’t get up early, you will miss the bus. (Nếu bạn không thức dậy sớm bạn sẽ bỏ lỡ xe buýt.) = Unless you get up early, you will miss the bus. II. CONNECTIVES (TỪ NỐI) 1. and, but, or: a. and (và): là từ nối được dùng để nối các từ, cụm từ hay mệnh đề với nhau. Eg: + We buy vegetables, bread, fish and meat every day. + Yesterday she watered the flowers and went shopping. + James said that he was never late for class and that he always did his homework. b. but (nhưng): để diễn đạt một ý trái ngược với ý nói trước đó. Eg: + He is intelligent but lazy. + I like bananas but my brother doesn’t. + She tried hard but failed. c. or (hoặc là/hay là): dùng đưa ra một sự lựa chọn. Eg: + Do you come from France or German ? + Is that good or bad ? 2. so, because: a. so (vì vậy/ vì thế). Eg: She heard the bad news, so she cried. b. because (bởi vì/ do). Eg: She cried because she heard the bad news. 3. however, therefore: a. however (tuy nhiên): được dùng để diễn đạt một ý trái ngược với ý nói trước đó. Eg: She rich and beautiful. However, she is not happy. b. therefore (do đó/vì thế): đựơc dùng để chỉ hậu quả. Eg: He’s busy. Therefore, he can’t help you. III. ARTICLES (MẠO TỪ) "a" và "an" dùng chỉ những sự vật, hiện tượng cụ thể người nghe không biết, "The" chỉ sự việc cả người nói và người nghe đều biết. 1. Mạo từ “the” - Dùng “the” khi nói về một vật riêng hoặc một người mà cả người nghe và người nói đều biết. Ví dụ: The dog is on the chair. (Con chó ở trên ghế ấy.) - “the” cũng được dùng để nói về một vật thể hoặc địa điểm đặc biệt, duy nhất. Ví dụ: The Eiffel Tower is in Paris. (Tháp Eiffel ở Paris.) The Earth revolves around the Sun. (Trái Đất xoay xung quanh mặt trời.) - Trong một số trường hợp, “the” có thể dùng với danh từ số ít và số nhiều. Ví dụ: the cat (con mèo), the cats (những con mèo) - “the” đứng trước danh từ, xác định bằng một cụm từ hoặc một mệnh đề. Ví dụ: The girl in uniform is my sister. (Cô gái mặc đồng phục là chị của tôi.) - Mạo từ “the” đứng trước từ chỉ thứ tự của sự việc như "first" (thứ nhất), "second" (thứ nhì), "only" (duy nhất) Ví dụ: The first day (ngày đầu tiên) The best time (thời gian thuận tiện nhất) The only way (cách duy nhất) - "the" + danh từ số ít tượng trưng cho một nhóm động vật, một loài hoặc đồ vật Ví dụ: The whale is in danger of becoming extinct. (Cá voi đang có nguy cơ tuyệt chủng.) - "the" dùng với một thành viên của một nhóm người nhất định Ví dụ: The small shopkeeper is finding business increasingly difficult. (Giới chủ tiệm nhỏ nhận thấy việc buôn bán ngày càng khó khăn.) - Mạo từ "the" đứng trước tính từ chỉ một nhóm người, một tầng lớp trong xã hội Ví dụ: the old (người già), the rich and the poor (người giàu và người nghèo) - Dùng trước những danh từ riêng chỉ biển, sông, quần đảo, dãy núi, tên gọi số nhiều của các nước, sa mạc, miền Ví dụ: The Pacific (Thái Bình Dương), The Netherlands (Hà Lan) - "the" + tên họ (dạng số nhiều) chỉ gia tộc... Ví dụ: The Smiths (Gia đình nhà Smiths) 2. Mạo từ “a” và “an” - “A” và “An” có cách sử dụng gần giống nhau. Tuy nhiên, dùng “An” khi chữ đằng sau bắt đầu bằng nguyên âm (a, o, u e,i) và dùng “A” khi chữ đằng sau bắt đầu bằng các phụ âm còn lại. Ví dụ: An hour (một giờ), a dog (một con chó) - Từ “A” và “An” dùng khi danh từ người nói nhắc đến không đặc biệt. Ví dụ: I would like an apple. (Tôi muốn một trái táo.) - “A” và “An” dùng để giới thiệu về thứ lần đầu tiên nhắc tới với người nghe (người nghe chưa biết gì về thứ này). Sau khi giới thiệu, người nói có thể dùng mạo từ “The” khi nhắc tới vật đó. Ví dụ: John has a dog and cat. The dog is called Rover, and the cat is called Fluffy. (John có một con chó và một con mèo. Chú chó tên là Rover và chú mèo tên là Fluffy.) - Trong một số trường hợp, “A”, “An” được dùng với danh từ số ít Ví dụ: A cat (một con mèo) 3. Không sử dụng mạo từ - Mạo từ không được sử dụng khi nói về sự việc chung hoặc nhắc tới ví dụ. Ví dụ: I don’t like apples. (Tôi không thích táo.) - Một số tên quốc gia, thành phố, các bang không dùng mạo từ đứng trước. Ví dụ: I live in London. (Tôi sống tại London.) Trừ trường hợp của The Philippines, The United Kingdom, The United States of America. - Tên các môn học không sử dụng mạo từ Ví dụ: John studies economics and science. - Trước tên quốc gia, châu lục, núi, hồ, đường. Ví dụ: Europe (châu Âu), South America (Nam Mỹ), France (Pháp) - Sau tính từ sở hữu hoặc sau danh từ ở sở hữu cách Ví dụ: The girl's mother (Mẹ của cô gái) - Trước tên gọi các bữa ăn. Ví dụ: They invited some friends to dinner. (Họ mời vài người bạn đến ăn tối) - Trước các tước hiệu Ví dụ: King Louis XIV of France (Vua Louis XIV của Pháp) - Trong một số trường hợp đặc biệt Ví dụ: In spring/in autumn (vào mùa xuân/mùa thu), last night (đêm qua), next year (năm tới), from beginning to end (từ đầu tới cuối), from left to right (từ trái sang phải). IV. RELATIVE CLAUSES (MỆNH ĐỀ QUAN HỆ) Mệnh đề quan hệ là mệnh đề bắt đầu bởi các đại từ quan hệ như who/whom/which/whose/that và các trạng từ quan hệ như where/when. Có hai loại mệnh đề quan hệ: Mệnh đề quan hệ xác định (defining) và không xác định (non-defining). 1. Mệnh đề quan hệ xác định. Là mệnh đề cần thiết phải có để làm chức năng giới hạn, làm rõ nghĩa danh từ đứng trước nó. Mệnh đề này thường không có dấu phẩy trước và sau nó. Eg: I don’t know the girl whom/that you met yesterday. 2. Mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định. Là mệnh đề không cần thiết phải có để làm chức năng giới hạn danh từ đứng trước nó, nghĩa là bản thân danh từ đứng trước nó bổ nghĩa. Vì thế mệnh đề này thường dùng sau danh từ riêng hoặc các danh từ bổ nghĩa ( Mr. Pike, Mrs. Hoa, ..), thường có dấu phẩy trước và sau nó. Eg: Mr. Pike , who is my neighbor , is very nice. 3. Relative pronouns (Đại từ quan hệ) Functions Defining Non-defining ( Chức năng) (Xác định) (Không xác định) Người WHO / THAT WHO Vật WHICH / THAT WHICH Người WHOM / THAT WHOM Vật WHICH / THAT WHICH Người WHOSE WHOSE Vật WHOSE WHOSE Subject ( Chủ ngữ ) Object ( Tân ngữ ) Posessive ( Sở hữu ) 4. Relative adverbs. - When => time Ví dụ: Monday is the day. We will come then. => Monday is the day when we will come. - Where => place Ví dụ: I never forget the village. I was born there. => I never forget the village where I was born. V. THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE (THÌ QUÁ KHỨ ĐƠN) 1. Form TO BE: (+): S + was/ were (-): S + was/were not (=wasn’t/weren’t) (?): Was/Were + S +…? ĐỘNG TỪ THƯỜNG: (+): S + V-ed/ cột 2 bảng động từ bất quy tắc (-): S + did not (didn’t) + V(inf) (?): Did + S + V(inf) Notes: Qui tắc thêm ED: - Động từ tận cùng bằng “e” câm. Thì chỉ cần thêm “d”: change => changed, love => loved. - Động từ tận cùng bằng một phụ âm trước nó là nguyên âm duy nhất, trước khi thêm “ed” phải gấp đôi phụ âm cuối: stop =>stopped, rub =>rubbed; hug => hugged. - Những động từ tận cùng bằng “y” trước nó là một phụ âm thì đổi y =>i trước khi thêm “ed”: try => tried 2. Use (Cách dùng) Diễn tả một hđ đã xảy ra và chấm dứt ở một thời điểm xác định trong quá khứ. Thường đi kèm với các từ chỉ thời gian: yesterday, ago, last/night, week, month…, in 1990… Ex: Yesterday he went home late. Kể lại một chuỗi hành động xảy ra liên tục. Ex: The man came to the door, unlocked it, entered the room, went to bed and lay down on it. Một việc làm thường xảy ra, một thói quen trong quá khứ. Thường đi với phó từ tần suất. Ex: I spoke Chinese when I was young. VI. THE PAST PERFECT TENSE (THÌ QUÁ KHỨ HOÀN THÀNH) 1. Khái niệm: Thì quá khứ hoàn thành: dùng để diễn tả một hành động xảy ra trước một hành động khác và cả hai hành động này đều đã xảy ra trong quá khứ. Hành động nào xảy ra trước thì dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành. Hành động xảy ra sau thì dùng thì quá khứ đơn. 2. Cấu trúc: Câu khẳng định S + had + VpII Ví dụ: – He had gone out when I came into the house. (Anh ấy đã đi ra ngoài khi tôi vào nhà.) – They had finished their work right before the deadline last week .(Họ đã hoàn thành công việc của họ ngay trước hạn chót vào tuần trước.) Câu phủ định S + hadn’t + VpII – hadn’t = had not Ví dụ: – She hadn’t comehome when I got there. (Cô ấy vẫn chưa về nhà khi tôi về.) – They hadn’t finishedtheir lunch when I saw them. (Họ vẫn chưa ăn xong bữa trưa khi trông thấy họ). Câu nghi vấn Had + S + VpII ? Trả lời: Yes, S + had. No, S + hadn’t. Ví dụ: – Had the film endedwhen you arrived at the cinema? (Bộ phim đã kết thúc khi bạn tới rạp chiếu phim phải không?) Yes, it had./ No, it hadn’t VII. THE PASSIVE VOICE (CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG) 1. Cách chuyển câu chủ động sang bị động Ví dụ: Mr Manh teaches English. => English is taught by Mr Manh. *Note : - Nếu trong câu có nhiều trạng từ thị khi chuyển sang câu bị động chúng được sắp xếp theo thứ tự sau : Tenses Active Passive Hiện tại đơn giản S + V_(s/es) S + am/is/are + V_(ed/3) + by + O Quá khứ đơn giản S + V_(ed/2) S + was/were + V_(ed/3) + by + O Hiện tại tiếp diễn S + am/is/are + Ving S + am/is/are + being +V(ed/3) + by + O Quá khứ tiếp diễn S + was/were + Ving S + was/were + being + V(ed/3) + by + O Hiện tại hoàn thành S + have/has + V(ed/3) S + have/has + been + V(ed/3) + by + O Tương lai đơn và động từ khuyết thiếu S + will/can/... + V S + will/ can…+ be + Ved/3 + by + O Thể cách + nơi chốn + thời gian Trạng từ chỉ nơi chốn được đặt trước By + O Trạng từ chỉ thời gian được đặt sau By + O - Nếu câu chủ động có 2 tân ngữ thì một trong 2 tân ngữ có thể làm S trong câu bị động. Ví dụ: He gave me a pen. => I was given a pen by him. => A pen was given to me by him. 2. Some special Passive form: a. Questions: Ex: Who wrote that play? => By whom was that play written? Have they read the letter? => Has the letter been read? b. Material agent: Ex: Smoke filled the room. => The room was filled with smoke. c. Negative pronoun agent: Ex: Nobody can unlock the case. -> The case can’t be unlocked. d. Sentences with two objects: Ex: Mary’s parents gave her a birthday present. => Mary was given a birthday present by her parents. => A birthday present was given to Mary by her parents. 3. Câu bị động của các thì: 4. Một số trường hợp bị động khác: a. Bị động với “ have / get something done ”: Hình thức bị động này được sử dụng để nhấn mạnh rằng hành động của chủ thể được thực hiện của người khác. Eg: Someone painted John’s flat yesterday. => John had his flat pạinted yesterday. b. Bị động với hình thức nguyên thể (infinitive) và danh động từ (gerund ). Eg: + We dọn’t want to be refused entry. + She hates being photographed. c. Bị động với các động từ chỉ quan điểm ( verbs of opinion ): believe, know, say, report, think,… Hình thức bị động này thường được sử dụng khi người nói muốn tránh đề cập tới chủ thể thực hiện hành động. It + to be + PII(ed/cột 3) + that + clause. Hoặc: S + to be + PII(ed/cột 3) + to-inf/to have + PII(ed/cột 3). VIII. ADVERB CLAUSES OF CONCESSION (MỆNH ĐỀ TRẠNG NGỮ CHỈ SỰ NHƯỢNG BỘ) 1. Although / even though / though + clause: Mặc dù… - We continued working although we were tired. = Although we were tired, we continued working. - I didn’t get the job even though I had all the necessary qualifications. = Even though I had all the necessary qualifications, I didn’t get the job. - I couldn’t sleep though I was very tired. - Though the girl isn’t beautiful,I like her voice - Even though I seee him every day,I’ve never spoken to him. 2. In spite of / Despite + noun / noun phrase - Although the traffic was bad, I arrived on time. = In spite of / Despite the bad traffic, I arrived on time. - Although it rained heavily, we enjoyed our vacation. = We enjoyed our vacation in spite of / despite the heavy rain. IX. MODALS: MAY vs MIGHT - Diễn tả một khả năng có thể xảy ra, chứ không phải chắc chắn 100% ở hiện tại. - Cấu trúc: MAY / MIGHT + Vo - Ví dụ: + What is in this box ? - It may / might be a watch. + She may / might have a cold. X. PHRASAL VERBS (CỤM ĐỘNG TỪ) account for: chiếm go on/ keep on: tiếp tục set out: khởi hành break out: xảy ra hold on: nối máy set up: xây dựng. Thành lập catch up: bắt kịp make up one’s mind = decide stand for: thay cho carry out: tiến hành live on: sống nhờ vào take off: cởi ra come in: mời vào look forward to: trông mong try on: mặc thử come back: trở về come on/ carry on: tiếp tục cut down: cắt giảm depend on: phụ thuộc fall down: giảm sút fill in: điền vào get along with: hòa thuận với give out: phân phát look at: nhìn look after: chăm sóc look up: tra từ look for: tìm kiếm look down: coi xuống look out: coi trông, cẩn thận run out of: cạn , hết turn on: bật lên turn off: tắt turn up: xuất hiện turn down: vặn nhỏ xuống turn round: quay lại wake up: thức dạy walk across: đi ngang qua work out: xây dựng put on: mặc vào put off: hoãn lại give up: từ bỏ B. PRACTICE PRACTICE TEST 1 Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word that differs from the other three in the position of primary stress in each of the following questions. 1. A. climate B. campus C. control D. capture 2. A. exhibition B. habitable C. application D. academic Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions. 3. A. stages B. finishes C. resources D. styles 4. A. celebrate B. capture C. conserve D. compose Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the follow questions. 5. When I came in, the television was on, but nobody — it. A. is watching B. had watched C. was watching D. watched 6. I love this small villages ……..I used to live for six years in my childhood. A. where B. which C. that D. whose 7. There are many other _ _ of art other than just painting and sculpture. A. means B. forms C. origins D. presents 8. The heating comes on automatically. You………..turn it on. A. mustn't B. mayn't C. don't have to D. oughtn't to 9. Sending a child with an injury into a game gives the child the the…. that health is not as important as winning. A. meaning B. significance C. suggestion D. message 10. She was an …….writer for years before she won the Nobel Prize for Literature. A. admiration B. admiring C. admired D. admire 11. Too much exercise can be….... but walking is good for your health. A. harmful B. harmless C. harmed D. harming 12. __ lending me your calculator for a moment? art rot aldizzogasw313 A. Can you B. Would you mind C. Could you please D. Why don't you 13. This exercise is very boring. I wish the teacher_ us some more interesting things to do. A. gave B. gives C. had given D. will give 14. You must explain your problems…………. A. so clear as you can B. most clearly as you should C. more clearly than you are D. as clearly as you can Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word(s) CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. 15. Luckily Susan got over her operation very quickly. A. recovered from B. looked at C. paid for D. got up 16. Students are understandably anxious about getting work after graduation. A. careful B. fearful C. excited D. worried Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word in each of the following questions. 17. After the alien spacecraft hovered over the park for a short while, it vanished. A. landed B. appeared C. attacked D. rose 18. Mathematics is a compulsory subject in all Vietnamese high schools. A. difficult B. changeable C. optional D. interesting Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the option that best completes each of the following exchanges. 19. -“May I come in?" -“……………….." A. No, you may not. B. Yes, why not? C. Yes, please do. D. No, I don't accept that 20. -"Let's meet outside the art gallery." -"…………..." A. Yes, let us do it. B. When can I go there? C. I'd like to go to the concert. D. Yes. Is 8.30 all right Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions from 21 to 25.b Polar bears on an island in Russia are scaring people in a small town. At least 52 polar bears have been seen wandering around the town of Belushya Guba. The town is on the island of Novaya Zemlya, which is in the Arctic Ocean. The situation has become serious because the bears have chased people and entered homes and offices. Local officials have declared a “polar bear emergency". Local official Alexander Minayev said: “The people are scared. They are frightened to leave homes and their daily routines are broken. Parents are afraid to let their children go to school or kindergarten." A local said: "I have been [here] since 1983, but there have never been so many polar bears in the vicinity." Officials say the polar bears are roaming into towns looking for food. They say that climate change is one reason for this. More sea ice is melting, which means the bears are moving into new areas to find food. They are attracted by the smell of food in bins outside people's homes. Town officials have asked for permission to kill the animals to reduce the danger to humans. However, Russia's environmental agency has refused this request. Polar bears are classed as a vulnerable species. The World Wildlife Fund says they are in danger because of the "ongoing and potential loss of their sea ice habitat resulting from climate change". It is helping to keep the polar bears away from the people of Belushya Guba 21. In which body of water is the island in this news story? A. The Black Sea B. The Baltic Sea C. The Caribbean Sea D. The Arctic Ocean 22. What buildings did the bears go into? A. pet shops and garages B. kitchens and restaurants C. homes and offices D. fish shops and saunas 23. One reason for the polar bears roaming into towns is. A. climate change B. more sea ice C. school children D. humans' danger 24. Where was the food that the polar bears could smell? A. in bins B. on kitchen tables C. in a warehouse D. in a restaurant 25. What is the World Wildlife Fund helping people in the town with? A. Defending their homes. B. Keeping the bears away C. Creating ice D. Conserving the environment Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct word that best fits each of the numbered blanks from 26 to 30. Greg LeMond was the first American winner of the Tour de France cycle race. He decided to (26)…. a cyclist when he was still at school and began to win a lot of prizes. LeMond missed going to the Moscow Olympics in 1980. Today he regrets having lost the (27)…… to win a gold medal. LeMond won his first Tour de France in 1986 and his future seemed to be very (28)….. but the next year LeMond had a terrible accident. LeMond wanted to take part in the 1987 Tour de France but his doctors didn't let him leave the hospital, Two years (29)….. he started training again. In 1989 he won the Tour de France on the last day of the race, and he was the winner again in 1990. LeMond (30)….. cycling in 1994 and opened a sports business with his father. 26. A. begin B. become C. happen D. develop 27. A. chance B. ability C. possibility D. option 28. A. light B. intelligent C. poor D. good 29. A. earlier B. following C. later D. shortly 30. A. started B. kept C. closed D. stopped Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the underlined part that needs correction in each of the following questions. 21. Please give me a few milk and some biscuits if you have any left. A. Please give B. a few C. some biscuits D. any left ]32. My brother decided to buy in the morning a new bike, but in the afternoon he changed his mind. A. decided to `B. in the morning a new bike C. in the afternoon D. changed 33. The study of these animals are truly fascinating, and many books have been written about them. A. these B. are C. many books D. written 34. Antarctic blue whales can be 100 foot long and weigh more than any dinosaur that ever lived. A. can be B. foot long C. more than D. ever 35. Many environmentalists fear that the earth will run out essential natural resources before the end of the twenty-first century. A. environmentalists B. that C. out essential D. before Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the sentence that is best written from the words/ phrases given 36.//go/school/my dad's car/whenever /rain A. Going to school in my dad's car if it rain is my wish. B. I go to school in my dad's car whenever it rains. C. I drive my dad's car to school when it is raining. D. It's my only choice to go to school in my dad's car 37. you / really/be/able/dress/yourself/age A. You should really be able to dress yourself at your age! B. You must really be able of dressing yourself in your age. C. You have really been able of dressing yourself by your age. D. You are really able of dressing yourself this age! 38. hilltop/have/good/view/our village A. The hilltop can make our village views better. B. From the hilltop, our village can viewed very well. C. From the hilltop, we can have a better view of our village. D. From the hilltop, our village can have a better view. 39. museum/small/have/ a lot of/ unique artifacts A. This museum is small, but it has a lot of unique artifacts. B. This museum is small because it has a lot of unique artifacts. C. That museum is both small and has a lot of unique artifacts. D. Being small, this museum has a lot of unique artifacts. 40. disappointed /film/entertaining/expected A. We were disappointed as the film was more entertaining than we expected. B. We felt disappointed as the film was less entertaining than we had expected. C. We felt disappointed just because the film was entertaining as we expected. D. We were disappointed, so the film was more entertaining than we had PRACTICE TEST 2 Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word that differs from the other three in the position of primary stress in each of the following questions. 1. A. symbol B. stormy C. cancel D. device 2. A. character B. arrangement C. specialist by D. championship Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the word whose underlined part differs from the other three in pronunciation in each of the following questions. 3. A. route B. amount C. shout D. around 4. A. designed B. entertained C. responded D. changed Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the following questions. 5. The artist,……..painting you have bought, is a friend of my father's. A. whom B. whose C. from whose D. from whom 6.The lion _long a symbol of strength, power, and cruelty. A. is B. was C. has been D. will be 7. Will you __ me to water the flowers before we go out tomorrow? A. remember B. suggest C. remind D. advise 8. Most developing countries are in….of capital and technical assistance. A. lack B. need C. shortage D. excess 9. It was a complete…..; I never meant to hurt her! A. chance B. error C. happening D. accident 10. The more and positive you look, the better you will feel. A. confide B. confident C. confidently D. confidence 11. The weather is __this week than last week. A. more good B. very good C. too better D. much better 12. His school report last term was very A. satisfying B. satisfied C. satisfy D. satisfaction 13. My sister has gone to the baker's to buy a _ of bread. A. loaf B. piece C. bit D. packet 14. Although there is much pollution in this city, __ A. but it is an ideal place to live B. however it is an ideal place to live C. there it is an ideal place to live D. it is still an ideal place to live Mark the letter A, B, C or D to indicate the word(s) CLOSEST in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. 15. The mechanic tried hard to mend the washing machine, but without success. A. build B. repair C. design D. break 16. If you didn't contribute generously, we couldn't continue with our project. A. charitably B. generally in C. officially D. locally Mark the letter A, B, C or D to indicate the word(s) OPPOSITE in meaning to the underlined word(s) in each of the following questions. 17. Education is free, but some people pay to send their children to private schools. A. expensive B. popular grid C. public D. high 18. It is so good that the authorities have improved the public transport system here recently. A. changed basically B. stopped using C. made better D. made worse Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the option that best completes each of the following exchanges. 19.-"Would you like milk or sugar in your tea?" -"…………………………." A. No sugar, please. B. No, just black tea, please. C. Why not milk for me? D. Yes, a lot of milk. 20. - "What time did you phone Oggy last night?" | A. I didn't see him last night B. Oh, half of an hour C. From my home D. At a quarter past ten Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct answer to each of the questions from 21 to 25. Hurricane Who? Tropical cyclones are called typhoons in Asia and hurricanes in North and South America. These storms go around like a wheel turning to the left when they hit in the northern part of the world. They have wind speeds of 60kph or more. In the United States, the Tropical Prediction Center in Miami, Florida keeps! an eye out for hurricanes. When meteorologists detect a hurricane, they give it a name. They can use either a male or female name. Why should tropical cyclones have names? The name makes it easier for people to keep up with information about a hurricane and its possible dangers. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO), an international weather group, decides what names will be used. The WMO makes lists of names using the English alphabet. Each name on the list starts with a different letter. The first hurricane of the year gets the first name on that year's list. The second hurricane gets the next name. For example, if the first hurricane is named Abel, the second might be named Betty. The name lists do not include names beginning with the letters Q, U, X, Y, and Z. There aren't many names that begin with these letters. 91 Asian countries use a different list, which is made up by the WMO's Typhoon Committee. This list has a few personal names, but most of the names are of flowers, animals, trees, and other similar things 21. What is the main idea of this reading? A. Why tropical cyclones are named B. What tropical cyclones can do C. How tropical cyclones are named ad D. Who watches for tropical cyclones 22. What does the Tropical Prediction Center in Miami do? A. They monitor earthquakes. B. They monitor tropical cyclones. C. They monitor the population. D. They monitor people's food intake 23. Which name would a hurricane NOT have? A. Rita B. Veronica C. William D. Yanni 24. How are hurricanes named? A. Each name starts with a different letter. B. Each name starts with the same letter. C. The same names are used every year. D. Different names are used for different countries. 25. Why should tropical cyclones have names? A. It sounds interesting. B. The names help people. C. The names are a code for the. D. It is traditional. Read the following passage and mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the correct word that best fits each of the numbered blanks from 26 to 30. Do you like putting on an apron and cooking a delicious meal for your family? How about helping out at the stove, stirring and sniffing the sweet smells? Or (26)…… cookies by cutting out your favourite shapes? Although making food is fun, it's important to know how to be safe. This means knowing (27) ___ to get the help of an adult assistant, how to keep things clean, and how to use the kitchen safely. Let's get cooking! Before beginning any recipe, get an adult's (28)….. to work in the kitchen. If your recipe uses knives, the stove, or other kitchen appliances, you must have some adult help. Some things that adults use in the kitchen may seem (29)….. to operate, but once you use them yourself, you might be surprised by how difficult they actually are. By having your assistant around, you can avoid surprises, (30) ….. safe, and have fun while you cook. 26. A. making B. doing C. boiling D. burning 27. A. what B. which C. when D. while 28. A. opinion B. warning C. information D. permission 29. A. hard B. simple C. tough D. pleasant 30. A. continue B. stay C. keep D. maintain Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the underlined part that needs correction in each of the following questions. 31. I don't know why my father finds horse-riding very excited. A. Know B. my father C. horse-riding D. excited 32. It has been a long time since we last talked to each other, isn't it? A. a long B. since C. last talked D. isn't it 33. Mary enjoys to be able to meet a lot of interesting people during her vacation A. to be B. a lot C. interesting people D. her vacation 34. The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest alive structure in UNESCO's list of natural wonders . A. The Great Barrier Reef B. the C. alive D. UNESCO's list 35. Christopher Columbus firstly saw Native Americans when he discovered the M. Caribbean Islands on October 12, 1492. A. firstly saw B. when C. discovered D. on Mark the letter A, B, C, or D to indicate the sentence that is closest in meaning to 4 each of the following questions. 36. John is fat because he eats so many chips. A. If John doesn't eat so many chips, he will not be fat. B. If John didn't eat so many chips, he would not be fat. C. John is fat though he eats so many chips. D. Being fat, John likes to eat so many chips. 37. I have never had an easier exam. A. In fact I have never had any easy exam. B. This is the first time in my life that I have an easy exam. C. This is the easiest exam I have ever had. D. This exam is easy, but I have never passed it. 38. In spite of his poor health, he managed to finish his book before the deadline. A. Although he was unwell, he managed to finish his book before the deadline B. Even though he managed to finish his book before the deadline, he was sick C. He was in poor health when he managed to finish his book before the deadline D. He managed to finish his book before the deadline, but he was very ill. 39. We were all surprised when she suddenly came back. A. She suddenly came back, making us surprised. B. The fact that she came back suddenly was surprised. C. All of us are amazed to see her come back. D. All of us found it surprising that she suddenly came back. 40. My grandfather started collecting stamps when he was 65. A. My grandfather took up collecting stamps when he was 65 B. Collecting stamps was my grandfather's hobby when he was 65. C. At the age of 65 my grandfather was collecting stamps. D. My grandfather hasn't been collecting stamps until he was 65