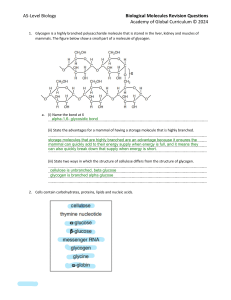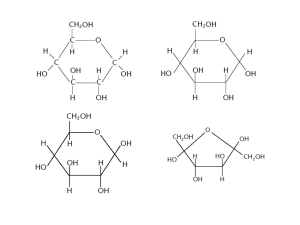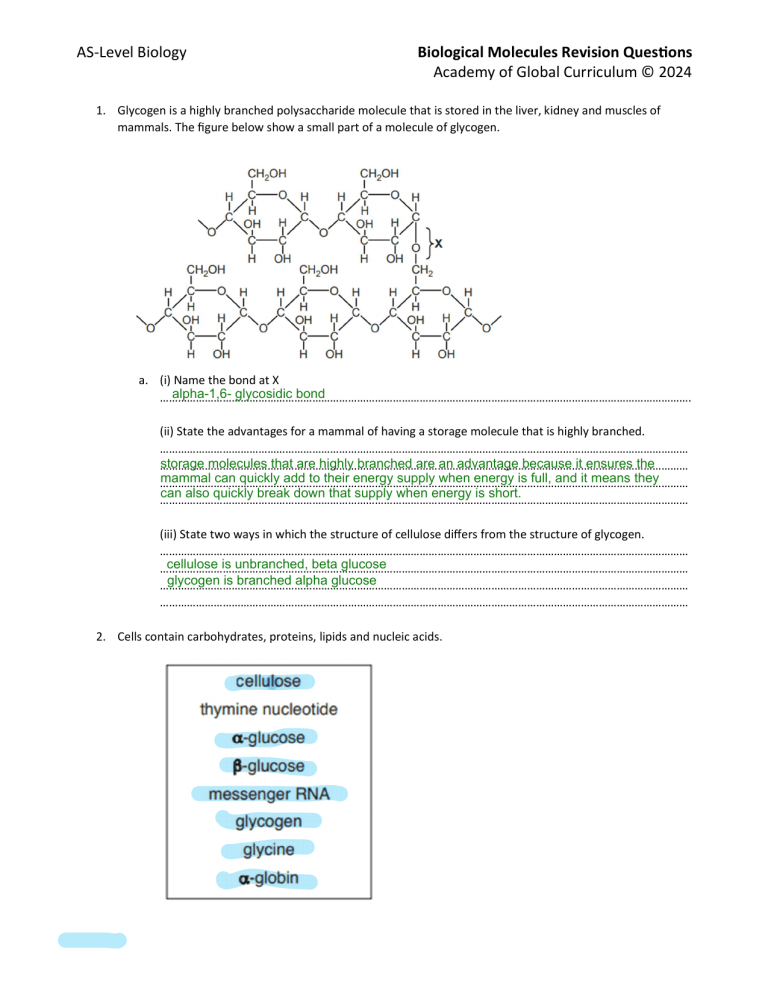
AS-Level Biology Biological Molecules Revision Ques ons Academy of Global Curriculum © 2024 1. Glycogen is a highly branched polysaccharide molecule that is stored in the liver, kidney and muscles of mammals. The figure below show a small part of a molecule of glycogen. a. (i) Name the bond at X alpha-1,6- glycosidic bond ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (ii) State the advantages for a mammal of having a storage molecule that is highly branched. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… storage molecules that are highly branched are an advantage because it ensures the …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… mammal can quickly add to their energy supply when energy is full, and it means they …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… can also quickly break down that supply when energy is short. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) State two ways in which the structure of cellulose differs from the structure of glycogen. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… cellulose is unbranched, beta glucose …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… glycogen is branched alpha glucose …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. Cells contain carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. AS-Level Biology Biological Molecules Revision Ques ons Academy of Global Curriculum © 2024 a. The figure below 1 is a list of biological molecules, some of which are components of larger molecules. Complete he figure by using only the molecules listed. Each example can be wri en under one or more correct headings. All the examples in the figure should appear at least once in the table. glucose a glucose b a-globin glycine cellulose glycogen messenger rna glucose a glucose b glycogen cellulose messenger rna b. Explain how the structure of phospholipids allows the forma on of the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… BeBecause their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane and …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… the polar head groups exposed on both sides, in contact with watercause their fatty acid tails are …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… poorly soluble in water AS-Level Biology Biological Molecules Revision Ques ons Academy of Global Curriculum © 2024 3. The figure below is a transmission electron micrograph showing two adjacent cells in a leaf. a. Cellulose is the main polysaccharide in cell walls of plants. Describe the structure of cellulose. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… linear, ribbon-shaped polymer of glucose molecules …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… b. State one feature visible in the figure, other than the cell wall, that iden fies the cells as plant cells nucleus …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Aphids are important vectors of plant viral diseases. a. (i) Describe the structure of a typical virus …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… a single molecule of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat, the capsid; the capsid and its …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… enclosed nucleic acid together constitute the nucleocapsid …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) Suggest how viruses are able to pass from one plant cell to the next without crossing membranes. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… viruses exploit the channels that plant cells use to communicate with each other. These channels are …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… called plasmodesmata. They are lined with proteins and can be tightly controlled by the plant …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… AS-Level Biology Biological Molecules Revision Ques ons Academy of Global Curriculum © 2024 5. Proteins are macromolecules composed of many amino acids. (i) Two amino acids are represented in the diagram in the Figure. Complete the diagram to show how the two amino acids react together to form a dipep de. 6. Amylose and cellulose are polysaccharides. The Figure shows the structure of part of a cellulose molecule. a. With reference to Fig. 2.2, state how the structure of a cellulose molecule differs from the structure of an amylose molecule. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… amylose's glucose units are linked with glycosidic bonds, whereas cellulose's monomeric units are …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… linked by glycosidic bonds …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………