L04 - Biochemistry I
advertisement

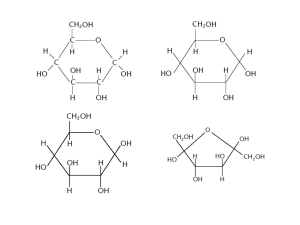
disaccharides • Sucrose: glucose+fructose (from suger cane or sugar beet), hydrolyzed by sucrase • Lactose: galactose+glucose (from milk) hydrolyzed by lactase • Maltose: glucose+glucose (from starch) hydrolyzed by maltase QuickTime™ and a TIFF (U ncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this pi cture. In animals, sucrase, lactase and maltase are located on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells lining the small intestine. Brach point in glycogen. Glycogen Glycogen is stored in liver and in skeletal muscle Starch and Cellulose cellulose • Cellulose is one o the most abundant organic compounds in the biosphere. • It is an unbranched polymer of glucose residues joined by -1,4-linkages. • Mammals lack cellulases and therefore cannot digest wood and vegetable fibers. • Soluble fibers, pectin, slows the movement of food through the gastrointestinal track. Increases better digestion and absorption of nutrients. • Insoluble fibers, cellulose increase the rate at which digestion products pass through the large intestine. Minimizes exposure to toxins in our diet. Structures or five repeating units of important glpycosaminoglycans Proteoglycans • Proteoglycans are proteins attached to a particular type of polysaccharides. • (about 95% sugar, 5% protein) • Cartilage (made of aggrecan and collagen) • Shock-absorber • Osteoarthritis result from the proteolytic degredation of aggrecan and collagen in the cartilage. Electron micrograph of proteoglycan from cartilage A, B and O antigens in blood groups Each person inherits the gene for one of the glycosyltransferases from each parent. Type A transferase adds N-acetylgalactosamine, whereas the type B transferase adds galactose. • Evolutionary perspective: Why different blood types present in the human population? Erythropoietin: a glycoprotein • EPO is secreted by the kidneys and stimulates the production of red blood cells. Availability of recombinant human EPO has greatly aided the treatment of anemias • The mature EPO is 40% carbohydrate by weight. Unglycosylated protein has only 10% bioactivity. Fat synthesis Two most common fatty acids in humans Phospholipid bilayer membrane • Fovured structure for most phospholipids in aquous media is a bimolecular sheet. • Lipid bilayers form spontaneously by a self-assembly process. • Hydrophobic interactions are the major driving force. Membrane fluidity • Membrane fluidity is controlled by fatty acid composition and cholesterol content. Melting temperature depends on the leghth of the fatty acid chains and on their degree of unsaturation. Cell membranes Rhodopsin: a 7-transmembrane helix protein porin