Earth & Life History Notes: Solar System to Space Exploration
advertisement

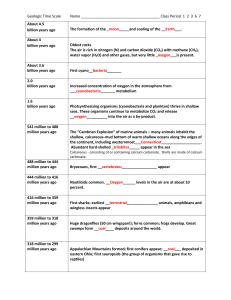
NOTES: THE WHOLE HISTORY OF EARTH AND LIFE Formation of Solar System (00:01 - 09:59) Milky Way collision with dwarf galaxy accelerated star formation Solar system material circulation led to zonal distribution of particles Formation of Planets Collisions among particles formed planetesimals o Planetesimals grew into planets through collisions Formation of Moon Earth collided with smaller mars-sized planet Debris from impact formed moon Early Earth's Environment Bombardment enriched earth with water Toxic ocean transformed into habitable environment through geological processes Emergence of Life Liquid core formed creating strong magnetic field Conditions in geyser cave facilitated synthesis of biomolecules o Wet and dry cycles crucial for building blocks of life Formation of Primitive Proto-Cellular Life (10:02 - 20:00) Ribozymes with self-replicating ability laid groundwork for life reproduction Molecules enclosed within lipid membranes formed primitive proto-cellular life Changes in Earth's Environment Plate tectonics subsumed primordial continent by 4 billion years ago o Life on margins of fragmented landmass Subducted primordial continent caused upper core to melt by 4.2 billion years ago o Liquid outer core strengthened Earth's magnetic field, protecting surface environment Energy Supply for Life Endless flow of electrons necessary for maintaining life Mutations allowed life to evolve and adapt to harsh environments Evolution of Proto-Life Proto-life evolved to utilize sunlight for energy o o Metabolism converted light energy into electrochemical energy Sugars used to store energy for sunless night hours Survival in Toxic Ocean Some proto-life-forms developed protective mechanisms against toxic ocean environment o Coalesced into larger and more complex forms Development of Prokaryotic Organisms Unstable RNA evolved into more durable DNA, allowing reliable information transfer across generations Beginning of prokaryotic organisms - ancestors of today's archaea and bacteria Adaptation to Oxygen First photosynthetic organisms were anaerobic microbes o Life adapted to use oxygen as an additional source of energy Appearance of cyanobacteria led to alteration of Earth's atmosphere o Oxygen production altered the Earth's atmosphere Formation of Banded Iron Oxygen produced by cyanobacteria led to the creation of banded iron formation Accumulation of ferric and ferrous iron on ocean floor created massive banded iron formation Iron Formation and Evolution of Life (20:03 - 30:01) Rapid decrease in iron content changed the color of the ocean to blue o Coevolution of the earth and its inhabitants Collision between Milky Way and a nearby dwarf galaxy produced countless glowing stars o Some stars ended in supernova explosions Cosmic rays from the supernova bombarded the earth o Helped generate cloud condensation nuclei, leading to a thick cloud cover o Resulted in global glaciation event known as the snowball earth o Caused another global mass extinction o Some life survived beneath the ice sheet Evolution of Complex Life Prokaryotes evolved into more complex life o Developed endosymbiotic systems, forming mitochondria and chloroplasts Eukaryotes appeared, growing larger and more complex Plate tectonics caused small continents to assemble into a supercontinent called Nuna o Provided cyanobacteria with expanding habitat to produce free oxygen o Large landmass helped increase atmospheric oxygen levels Geological and Environmental Changes Nuna supercontinent broke up into smaller continents o Plate tectonics reassembled a supercontinent called Rodinia Slabs of oceanic plates fell into the core, changing the Earth's magnetic field Milky Way galaxy collision and transition into starburst conditions led to supernova explosions and extreme environmental changes o Genetic mutations accelerated the appearance of new species Earth's core reverted to a stronger magnetic field, and ongoing photosynthesis returned oxygen levels to previous levels Inner Earth cooling down led to the release of water components, affecting sea levels known as the "leaking earth" phenomena Impact of Leaking Effect (30:06 - 40:05) 3% of seawater moved into deeper mantle Sea level dropped by 600 meters o Surface land areas and continental shelf areas grew o Rivers carried nutrients from inlands to continental shelves Evolution of Life-forms Explosive evolution due to processes setting stage o Extreme climate changes put life on new evolutionary stages o Prokaryotes and eukaryotes living together led to larger symbiotic organisms Appearance of multicellular life was a critical leap for evolution o Periods of glaciation led to mass extinction and gradual warming Ediacaran Period Appearance of soft-bodied creatures without shell or skeleton o Lived in warm shallow marine environments around Rodinia supercontinent Increase in ferrous iron, phosphorus, and calcium levels in oceans o Calcium helped protect and form hard scales for organisms Climate Changes and Evolution Earth's climactic instability led to extreme heat and cold periods Continental rifts exposed erupting magma and radioactive elements o Radiation played a significant role in the evolution of life Continental collisions created more diverse surface environments, aiding in diversification Cambrian Explosion Cambrian explosion created 35 new phyla o Foundation for the types of plants and animals seen today Evolution of life linked to mass extinctions, stem evolution, and crown evolution o Environmental changes and continents assembling and breaking apart played a crucial role Evolution onto Land Decrease in seawater salinity made the ocean more hospitable to diverse life-forms o Algae transitioned out of water onto land before animals Fish were the oldest vertebrate ancestors, followed by amphibians o Plants flourished, producing free oxygen through photosynthesis Evolution of Life on Earth (40:07 - 49:57) Breakthroughs for human civilization began with the Industrial Revolution o Vertebrates equipped with lungs appeared and made their way onto land o The tree of life evolved from fish to amphibians to reptiles, then dinosaurs and mammals, eventually leading to humans The earth experienced a collision with a Dark Nebula, leading to global cooling and mass extinctions o Plants were affected, reducing oxygen supply to the atmosphere o Lack of oxygen killed off species of amphibians, reptiles, and insects Evolution of Species Mammals and reptiles appeared on the supercontinent Pangea under a warm climate o Reptiles diversified into many varieties while mammals remained nocturnal rat-sized animals o Dinosaurs prevailed against many other animal species and won the struggle for survival Hybridization of life occurred as continents rejoined, leading to the emergence of new species o Dinosaurs flourished all over the world, while angiosperms and gymnosperms appeared in the plant world o Primate ancestors of humans appeared at the rift of the Gondwana supercontinent Universe-Scale Events The solar system collided with a Dark Nebula, causing global cooling and mass extinctions o Galactic cosmic rays directly affected DNA, promoting evolution A meteorite impact on the Yucatan Peninsula triggered the mass extinction of dinosaurs o Universe-scale events can cause global cooling and mass extinctions o Cosmic rays cause mutations that influence all aspects of life on earth Earth's History (50:09 - 00:07) Dinosaurs went extinct o Explosive volcanic activity continued along the African Rift Valley Old world monkeys, thought to be our remote ancestors, appeared Evolution of Human Beings Human accelerated regions (HARs) differentiate humans from other animals o Enlarged brains enabled language capabilities, consciousness, memory, and imagination Human brain volume increased in three stages, synchronized with large-scale volcanic eruptions Human Migration and Civilization Humans started moving out of the African continent 1.2 million years ago o Mitochondrial Eve left Africa 200,000 years ago Humans spread to North and Central America 15,000 years ago, and to the southern tip of South America 10,000 years ago Invention of agriculture and livestock production led to a stable food supply and rapid population growth o Various occupational specializations arose Small cities developed into city-states with economies, laws, and courts o Four great civilizations appeared along large rivers Religions spread to replace governance by royal families o Modern democratic nations appeared Industrial Revolution and Information Age Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain after the Principia by Isaac Newton was published o Invention of steam locomotive, cars, and airplanes revolutionized transportation Information revolution led to the exploration of the universe and the invention of the internet Future of Human Beings Fossil fuel consumption and population growth will lead to food shortages around 2020 o World's population is expected to decrease to 5 billion by 2100 after peaking at 10 billion in 2050 Increasing population will cause serious environmental contamination until 2050 Innovative technologies will be developed at an accelerated pace o Humans will build a space base on the moon and create artificially intelligent robots Future of Space Exploration (00:10 - 05:24) Self-replicating robots will evolve beyond human limits o Artificial life-forms will travel out into the galaxy New technology enabling travel into different dimensions will be developed Earth's Future Supercontinent Amasia formation o Increase in land area for carbon fixation o Decrease in atmospheric CO2 levels Impact on plant and animal life o Extinction of C4 plants and dependent animals Geological changes o Termination of plate tectonics o Disappearance of the geomagnetic field o Earth's atmosphere removed by solar wind End of Earth Extinction of surface-dwelling multicellular animals o Extinction of ocean-dwelling animals Earth becomes Venus-like planet o Collision with Andromeda galaxy Earth's disappearance from the universe o Life reaching other galaxies as self-replicating artificial life