Geologic Time Scale Name Class Period 1 2 3 6 7 About 4.5 billion
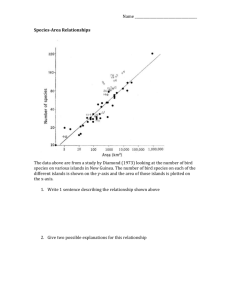
Geologic Time Scale Name ______________________________________ Class Period 1 2 3 6 7
About 4.5 billion years ago
The formation of the _ moon _____and cooling of the __ Earth ___.
About 4
billion years ago
About 3.6 billion years ago
2.0 billion years ago
1.6
billion years ago
542 million to 488
million years ago
488 million to 444
million years ago
444 million to 416
million years ago
416 million to 359
million years ago
359 million to 318
million years ago
318 million to 299
million years ago
Oldest rocks
The air is rich in nitrogen (N) and carbon dioxide (CO
2
) with methane (CH
4
), water vapor (H
2
O) and other gases, but very little _ oxygen ___is present.
First cyano__ bacteria _______
Increased concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere from
___ cyanobacteria _______ metabolism
Photsynthesizing organisms (cyanobacteria and plankton) thrive in shallow seas. These organisms continue to metabolize CO
2
and release
__ oxygen __________ into the air as a by-product.
The “Cambrian Explosion” of marine animals – many animals inhabit the shallow, calcareous-mud bottom of warm shallow oceans along the edges of the continent, including westernmost___ Connecticut ___________________.
Abundant hard-shelled _ trilobites _____ appear in the sea
Calcareous - consisting of or containing calcium carbonate. Shells are made of calcium carbonate.
Bryozoans, first __ vertebrates _________________ appear
Nautiloids common. __ Oxygen ______ levels in the air are at about 10
percent.
First sharks; earliest __ terrestrial _______________ animals, amphibians and wingless insects appear
Huge dragonflies (50 cm wingspan!); ferns common; frogs develop. Great swamps form __ coal ____ deposits around the world.
Appalachian Mountains formed; first conifers appear; __ coal ___ deposited in eastern Ohio; first sauropsids (the group of organisms that gave rise to reptiles)
Geologic Time Scale Name ______________________________________ Class Period 1 2 3 6 7
299 million to 251
million years ago
251 million to 201.6
million years ago
201.6 million to 145.5
million years ago
145.5 million to 65.5
million years ago
Warm-blooded reptiles, forerunners of mammals, appear. Very high levels of
___ oxygen _____ (30% compared to 21% today) allow huge insects to fly despite primitive respiratory systems. _ Pangea _ forms. Mass extinction, especially of marine life, at end of Permian.
Life takes tens of millions of years to recover from the Permian-Triassic extinction. More extinction marks the end of the Triassic, possibly due to
_ meteor ___ impacts or volcanic events. This eliminates the large land reptiles and clears the way for dinosaurs to expand. Dinosaurs appear; first
_ mammals ______ (small, rodent-like creatures)
_ Dinosaurs ____ dominate; flying reptiles appear; first known bird
65.5 million to 55.8
million years ago
55.8 million to 33.9
million years ago
33.9 million to 23
million years ago
23 million to 5.3
million years ago
5.3 million to 2.6
million years ago
2.6 million to 10
thousand years ago
Rocky Mountains began to form; first snakes; first _ grasses ____ and flowering plants appear; mass extinction of dinosaurs about 65 million years
ago
__ Himalayas ____ began to form; large radiation of mammals; earliest whales and dolphins; first bats; first large land mammals
Semi-tropical plants in _ Wyoming ______ at the beginning of the Eocene
First __ apes ___
First _ grassland _____ecosystems
__ Panama ______ land bridge forms
130
thousand years ago
10 thousand years
ago to present
Dramatic changes in climate; ice sheets cover and uncover_ Connecticut _____.
Ice ages, mammoths, and mastodons
__ Neanderthals ____existed
Most recent ice age ends about 10,000 years ago. The climate rapidly warms up to its present state, and _ plants _ and _ animals ___ familiar to us today inhabit our landscape.
Geologic Time Scale Name ______________________________________ Class Period 1 2 3 6 7