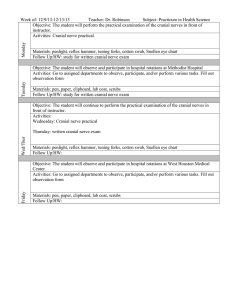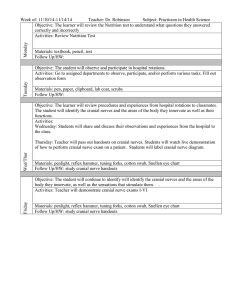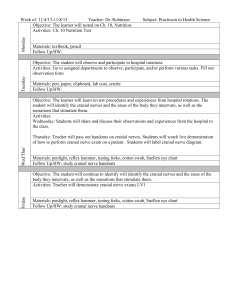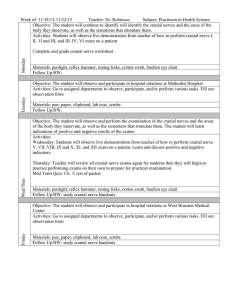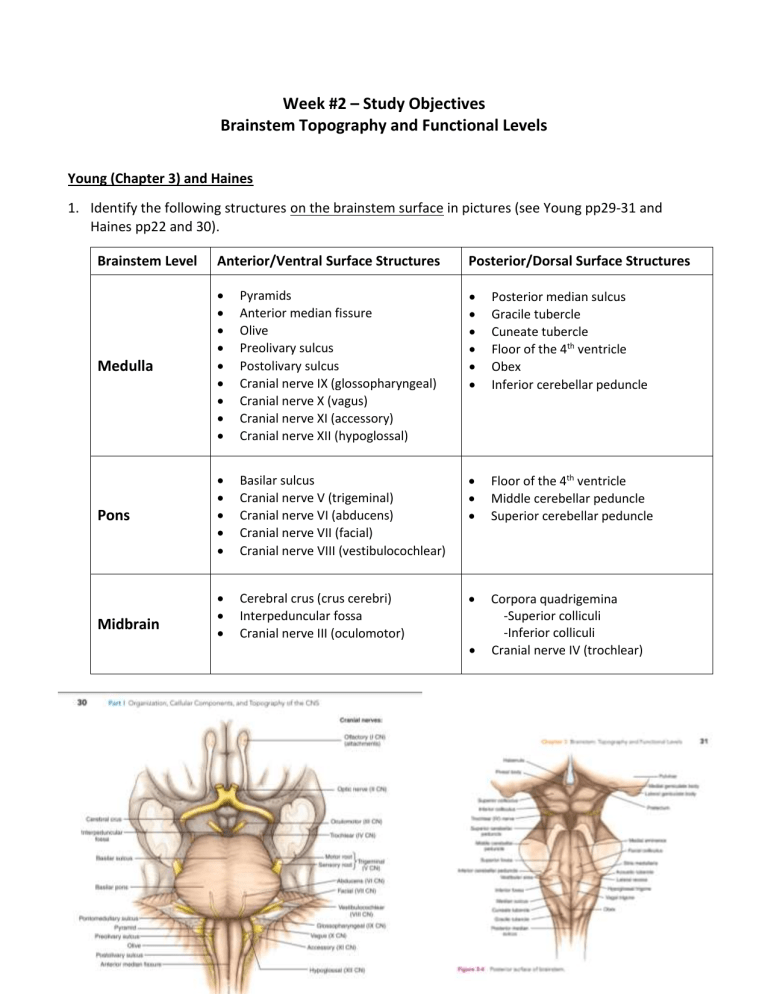
Week #2 – Study Objectives Brainstem Topography and Functional Levels Young (Chapter 3) and Haines 1. Identify the following structures on the brainstem surface in pictures (see Young pp29-31 and Haines pp22 and 30). Brainstem Level Anterior/Ventral Surface Structures Posterior/Dorsal Surface Structures Medulla Pyramids Anterior median fissure Olive Preolivary sulcus Postolivary sulcus Cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal) Cranial nerve X (vagus) Cranial nerve XI (accessory) Cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal) Posterior median sulcus Gracile tubercle Cuneate tubercle Floor of the 4th ventricle Obex Inferior cerebellar peduncle Pons Basilar sulcus Cranial nerve V (trigeminal) Cranial nerve VI (abducens) Cranial nerve VII (facial) Cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear) Floor of the 4th ventricle Middle cerebellar peduncle Superior cerebellar peduncle Cerebral crus (crus cerebri) Interpeduncular fossa Cranial nerve III (oculomotor) Corpora quadrigemina -Superior colliculi -Inferior colliculi Cranial nerve IV (trochlear) Midbrain Neuro 360 – Week 2 Page 1 of 2 2. Identify the following structures in brainstem sections (continued on next page). Section Level Structures to Know Anterior median fissure Pyramids Posterior median sulcus Gracile tubercle and nucleus Anterior median fissure Pyramids Principal olivary nucleus (inferior olivary nucleus) 4th ventricle Basilar sulcus Descending (corticospinal) fibers Transverse (pontocerebellar) fibers Middle cerebellar peduncle Superior cerebellar peduncle Cuneate tubercle and nucleus Reticular formation Principal olivary nucleus (inferior olivary nucleus) Inferior cerebellar peduncle (also called the restiform body and juxtarestiform body) Reticular formation Reticular formation 4th ventricle Cranial nerve VI (abducens) Cranial nerve VII (facial) Caudal medulla (also called the closed medulla, see Young figure 3-6 and Haines pp112-117) Rostral medulla (also called the open medulla, see Young figures 3-7 and 3-8, and Haines pp118-121) Caudal pons (see Young figure 3-9 and Haines pp130-133) Neuro 360 – Week 2 Page 2 of 2 Section Level Structures to Know Basilar sulcus Descending (corticospinal) fibers Transverse (pontocerebellar) fibers Middle cerebellar peduncle Superior cerebellar peduncle Reticular formation 4th ventricle Cranial nerve V (trigeminal) Basilar sulcus Descending (corticospinal) fibers Transverse (pontocerebellar) fibers Superior cerebellar peduncle Reticular formation Cerebral aqueduct Cranial nerve IV (trochlear) Middle pons (see Young figure 3-10 and Haines pp134-135) Rostral pons (see Young figure 3-11 and Haines pp136-137) Neuro 360 – Week 2 Page 3 of 2 Section Level Structures to Know Tectum Tegmentum Cerebral peduncle Inferior colliculus Periaqueductal gray Cerebral aqueduct Reticular formation Substantia nigra Cerebral crus (crus cerebri) Tectum Tegmentum Cerebral peduncle Superior colliculus Periaqueductal gray Cerebral aqueduct Reticular formation Substantia nigra Cerebral crus (crus cerebri) Caudal midbrain (see Young figure 3-12 and Haines pp140-143) Rostral midbrain (see Young figure 3-13 and Haines pp144-149) 3. Given a brainstem section, you should be able to identify what level of the brainstem it is (caudal medulla, rostral pons, etc). Neuro 360 – Week 2 Page 4 of 2 4. Given the name of any of the structures in objectives 1 or 2, you should be able to explain where on/in the brainstem it is located. (For example…Where is the cuneate tubercle? On the dorsal aspect of the caudal medulla) Neuro 360 – Week 2 Page 5 of 2