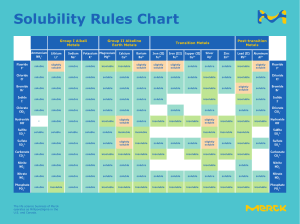
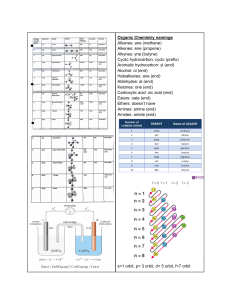
Effect of pressure on solubility: Liquids in Liquids: slightly affects solubility Gases in Liquids: increases solubility Increase in temp of gases dissolved in liquids- decrease solubility solids – increase solubility Size of atom dependent on: space occupied by electrons Water biggest density – liquid Most common solution -seawater Negativity of covalent: 0.5 to 1.9 Attract shared electrons – electronegativity Attract additional electrons – electron affinity Van der Waals – Diderick van der Waals Bose Einstein – Einstein Doined the term ‘Plasma – Irving Langmuir First identified plasma – William crookes Smog acid rain – nitrogen Representative element0 – rightmost digi of group number Transition elements- group number Dry Air: CO2 – 0.03% N – 78.1% O- 20.9% ‘Solubility of gas in liquids is directly proportional to partial pressure – henry’s law “rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass – Thomas graham Uncertainty principle – Heisenberg MOST ABUNDANT ELEMENT: Atmosphere: Nitrogen Oxygen Human Body: Oxygen Carbon Chalcogens – Oxygen family, group 6a Ernest Rutherford – proton John Joseph Thompson – electron - revised atomic theory of Dalton to plum-pudding model John Dalton – Atomic Theory Henri Becquerel – radioactivity Prometheum – Pacemakers for heart Phosphoric Acid – Tart test Not a metalloid- magnesium Table salt- Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide Equal forward and backward reax – chemical equilibrium Point where added base or acid is enough to neutralize – equivalence point Uses redox to generate electricity – voltaic cell Reduced substance – oxidizing agent Oxidized substance – reducing agent Bronsted-Lowry theory – acid donates proton, base accepts proton Arrhenius acid – increase concentration of H Arrhenius base - increase concentration of OH (Lewis acid) – electron pair acceptor Bronsted Lowry base – proton acceptor Product of lewis acid base- adduct Lewis – donates(base and accepts(acid) pair of electrons Arrhenius – gives H+ (acid) and OH-(base) ions in dissociation in water Bronsted-Lowry – donates proton (acid) and accepts proton (base) Gilbert Lewis, acid base reaction will form – Coordinate covalent bond Soren sorenses – ph scale 1909 Remove CO2 from air- lithium hydroxide Antacid with no restriction – magnesium hydroxide; milk of magnesia Fertilizers- Phosphoric acid Vinegar- Acetic Acid Batteries of cars and automobiles- sulfuric acid Glass itching -hydroflouric acid Reduce pain – acetylsalicylic acid Explosives – nitric acid, HNO3 6.5 ph – saliva and milk Tertiary acid: 2 nonmetals is oxygen - oxyacids Bases – metal and hydroxide ion Colloidal dispersion of liquid in liquid or solid - emulsions Suspension of liquid or solid particles in a gas – aerosols Cosmetics and ointments- emulsions Colloidal dispersion of gas bubbles- foams Rate at w/c chemical reactions occur- chemical kinetics “oldos” – glue appearance Extent of chemical reaction – equilibrium position Ratio of equilibrium concentration of products and reactants- equilibrium constant How far from equilibrium the reaction is – reaction quotient Alkanes – parrafins Alkenes – olefins Charge to mass ratio of electrons – J.J Thomson Lightest metal -lithium Human Body: Carbon – 18%