Aldehydes: Chemistry Notes, Properties & Nomenclature
advertisement

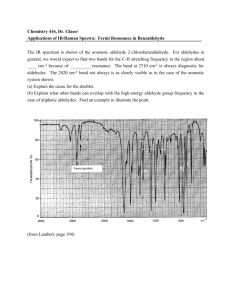
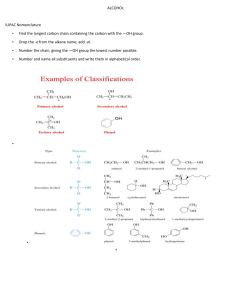
Notes in Chemistry : ALDEHYDES Aldehydes are considered the most important functional group. They are often called the formyl or methanoyl group. Aldehydes derive their name from the dehydration of alcohols. Aldehydes contain the carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. The double bond between carbon and oxygen is characteristic of all aldehydes. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Aldehydes 1. They are non-polar chemicals. 2. Aldehyde boiling points are greater than those of the other non-polar compounds. 3. A double bond exists between carbon and oxygen in the carbonyl group of aldehydes. 4. Hydrogen bonding makes it possible for the lower members of the aldehydes to be soluble in water, and this is especially true for those with up to four carbons in their structure. As the carbon chain increases in length, solubility in water decreases. 5. Many aldehydes are volatile, flammable liquids which at normal room temperature form vapor in explosive concentrations. 6. Most of the common aldehydes are liquid at ordinary temperature. 7. The lower molecular mass aldehydes have a sharp rather unpleasant smell but higher molecular mass aldehydes are pleasant smelling. 8. Aldehydes have low melting point. Naming Aldehydes According to the IUPAC system of nomenclature -al is attached as a suffix to parent alkane for the naming of aldehydes. Here are simple rules for naming Aldehydes Ex. To indicate the position of a substituent on an aldehyde, the carbonyl carbon atom is always considered to be C1; it is unnecessary to designate this group by number. 4. For dialdehydes the location numbers for both carbonyls are omitted because the aldehyde functional groups are expected to occupy the ends of the parent chain. The ending –dial is added to the end of the parent chain name. example Common Names to Memorize: Swk. Classify if the compound is an aldehyde or not. Put a check if an aldehyde and X if not. 1-3. 4-5. B. Give the IUPAC name for each compound: 1. 3. Prepared by: Maám Mariecel F. Tenmatay 4. 5.